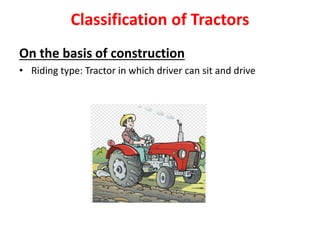
The document classifies tractors based on construction, number of wheels, and purpose of use. It discusses the development of tractors in India from 1960-2000 as manufacturers like Eicher, Hindustan Tractors, Escorts, and others began production. Technical terms related to tractors are also defined, including track, ground clearance, wheel base, and height of frame.