The tractor chassis is the base frame that supports all other components of a tractor. It is built to be very strong to bear heavy loads and shocks from farm work. The chassis frame distributes the load of the engine, transmission, and other components. It also carries the load of any implements and manages forces experienced while working on uneven fields. The location of the center of gravity, hitch point design, and traction surface all impact the mechanics of the chassis. Weight transfer refers to how weight shifts from the front axle to the rear axle, affecting soil reaction and traction. Non-parallel pulling implements introduce additional complexities to the tractor's mechanics and stability.











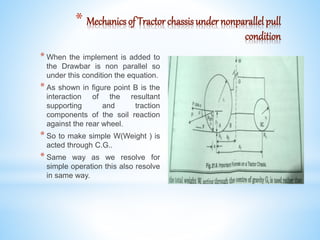
![The algebraic sum of all horizontal forces is zero.
F – P cos α = 0………….. 1.
*Now algebraic of all vertical forces is equal to Zero.
R1 + R2 – W – P sin α = 0…………… 2.
*Taking Moment about Point B,
Wx2 – R1x1 – y1 P cos α – e P sin α = 0……….. 3.
*Solving equation 3. for R1
R1 =
𝑊𝑥2
𝑋1
−
𝑦1 𝑃 cos α + 𝑒𝑃 sin α
𝑥1
;
Also
R1 + R2 = W => R2 = W – R1
R2x1 = [W-
𝑊𝑥2
𝑋1
+
𝑦1 𝑃 cos α + 𝑒𝑃 sin α
𝑥1
]
R2x1 = W
(𝑥2 −𝑥1)
𝑋1
+ P
𝑦1 cos α + 𝑒 sin α
𝑥1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tsc-170117160419/85/Tractor-Systems-and-Controls-13-320.jpg)


