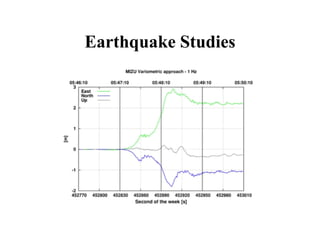
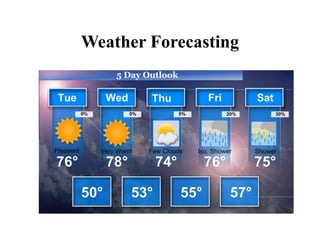
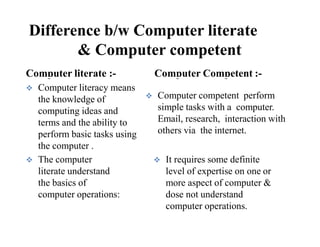
The document provides an overview of computer education, categorizing computers into supercomputers, mainframe computers, mini computers, and microcomputers. It discusses the differences between professional and user computers, as well as between computer literate and computer competent individuals. Applications of various computer types in fields like research, weather forecasting, and data management are highlighted, along with definitions of key terms related to computer proficiency.