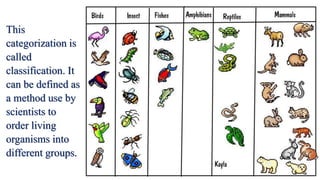
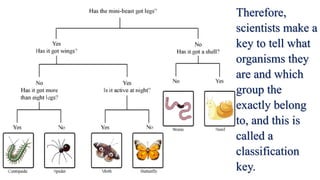
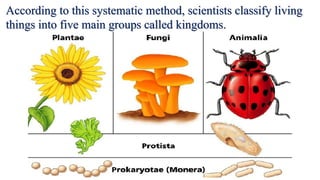
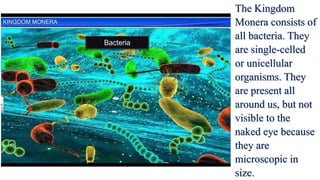
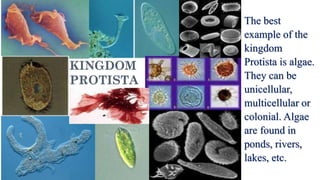
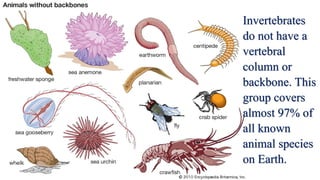
This document discusses the classification of living things into five kingdoms: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Animalia, and Plantae. It describes some key characteristics of each kingdom, such as bacteria being unicellular microorganisms in Monera, algae having characteristics of both plants and animals in Protista, fungi lacking chlorophyll and obtaining nutrients from dead matter, animals being multicellular and further divided into vertebrates and invertebrates, and plants being multicellular autotrophs divided into flowering and non-flowering groups. The classification system helps scientists identify and categorize different types of organisms.