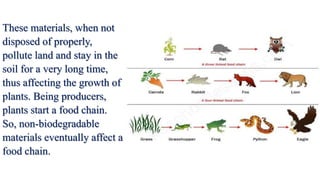
This document discusses biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste. It explains that biodegradable materials like fruit and vegetable peels can break down with the aid of microorganisms, water, and heat. Non-biodegradable materials like plastics and metals do not break down and can pollute the environment for long periods. The document also outlines several methods to reduce the impact of non-biodegradable waste, including the 4Rs approach of reduce, reuse, recycle, and rot.