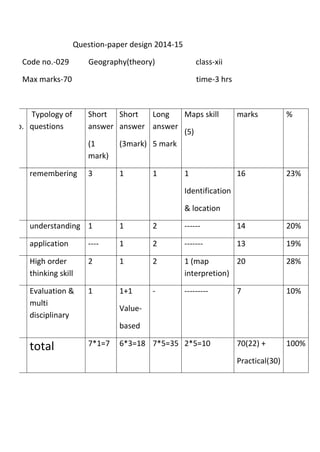
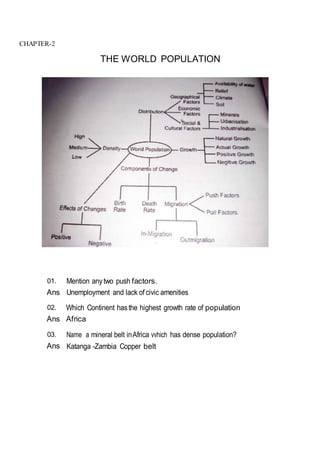
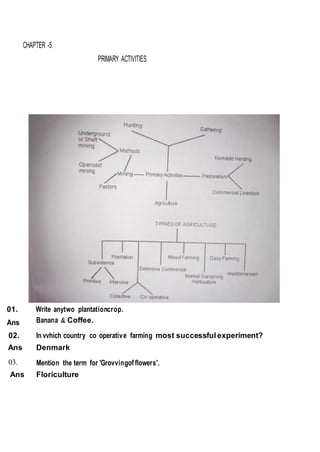
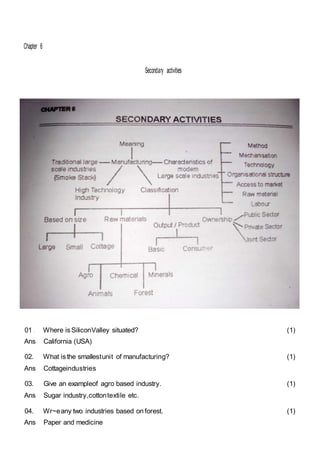
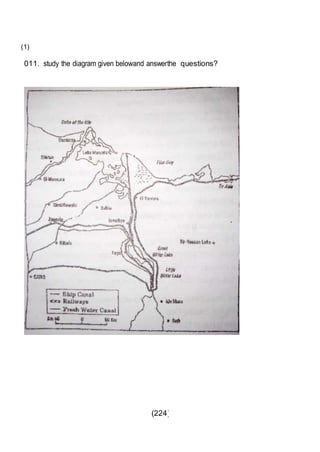
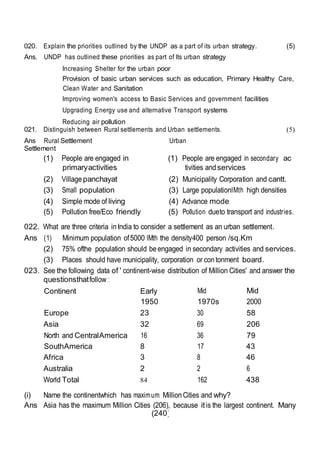
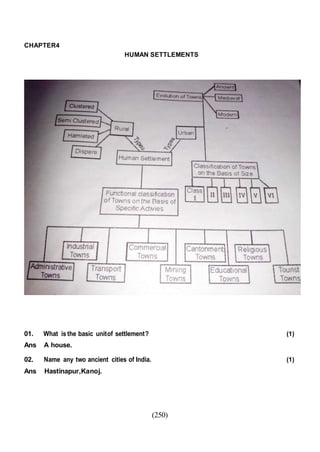
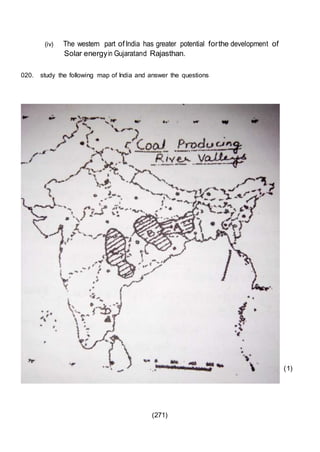
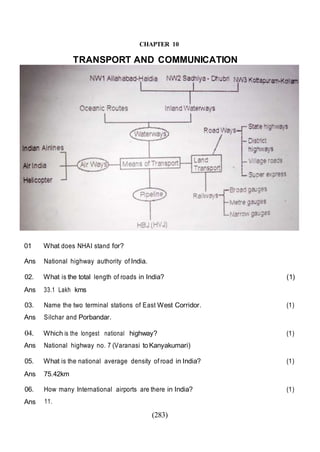
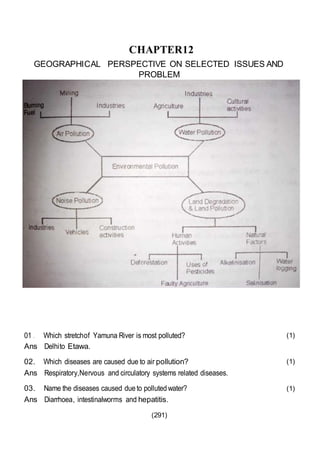
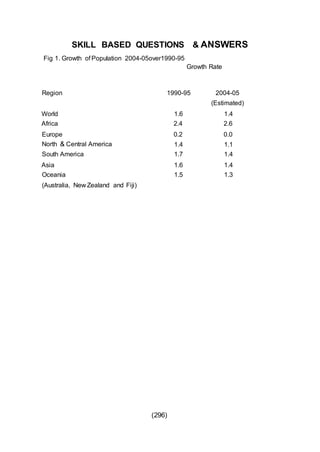
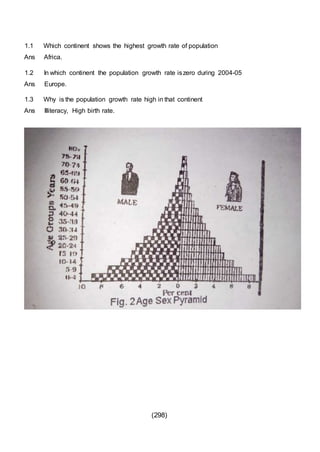
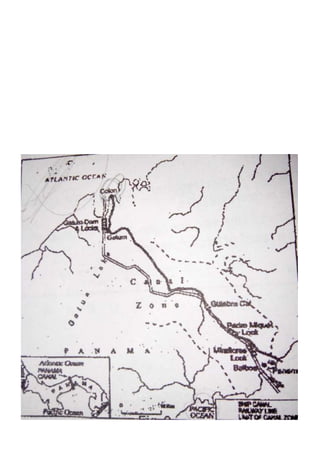
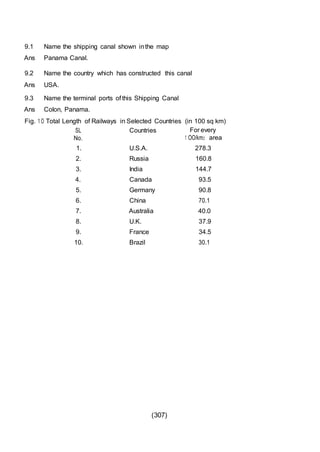
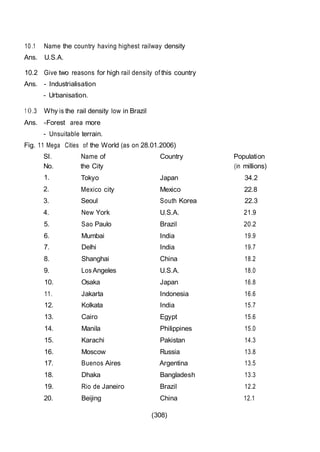
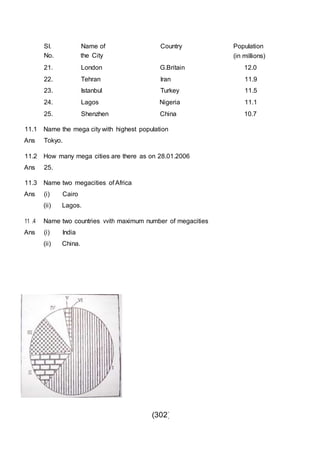
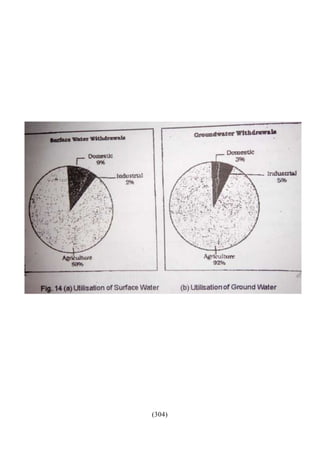
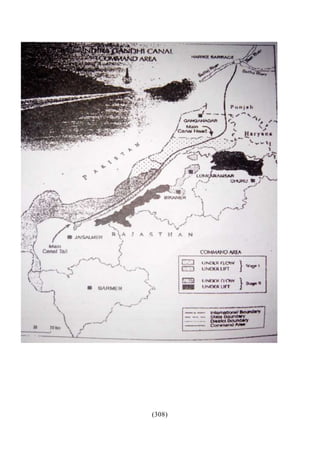
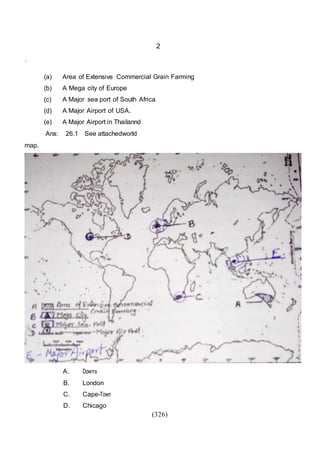
This document outlines the study material for Class XII Geography at Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Silchar region, detailing question paper design, key topics such as human geography and India's people and economy, as well as model and latest question papers. It includes specific map practices and skill-based questions, with an emphasis on understanding population dynamics, geographical concepts, and critical geographic locations. The content is organized into chapters covering various geographical and demographic themes essential for geography students.