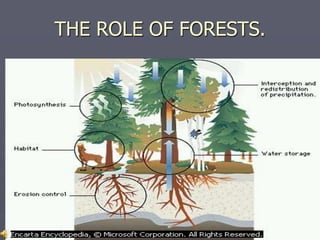
This document provides an overview of resources and conservation. It defines resources as any substance that can satisfy a need. Resources are classified as natural, human, and human-made. Natural resources come directly from nature, human resources refer to people's education and skills, and human-made resources are natural substances modified by human technology. Conservation is the protection and wise use of resources so they last into the future. It involves reducing consumption, recycling, and sustainable development according to principles like careful resource use and meeting needs of present and future generations.