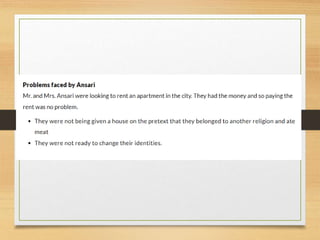
1) In reality, equality does not fully exist in India as there are differences between the rich and poor and the caste system remains rigid, denying Dalits and minorities dignity and equality.
2) Article 15 of the Indian Constitution prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth but in practice social and economic inequalities remain.
3) Government schemes like the mid-day meal program have helped increase school enrollment and attendance of poor children but have not fully ensured social and economic equality.