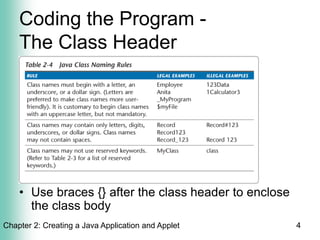
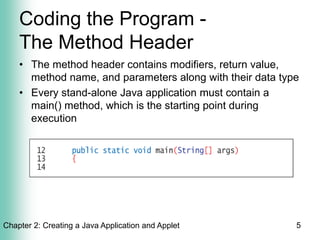
The document discusses creating Java applications and applets using TextPad as an IDE. It covers using TextPad features like the coding window and color coding. It also discusses important aspects of coding Java programs like using comments for documentation, specifying the public class header that matches the file name, and defining the main method header which is required for standalone applications. The class body is enclosed in curly braces and method headers specify modifiers, return types, names, and parameters.