This document discusses packages and interfaces in Java. It covers:
- Packages organize related classes and provide encapsulation. Interfaces define methods without implementation.
- Packages and interfaces give greater control over program organization.
- Classes in a package are accessed through the package name and can control access. Namespaces avoid collisions.
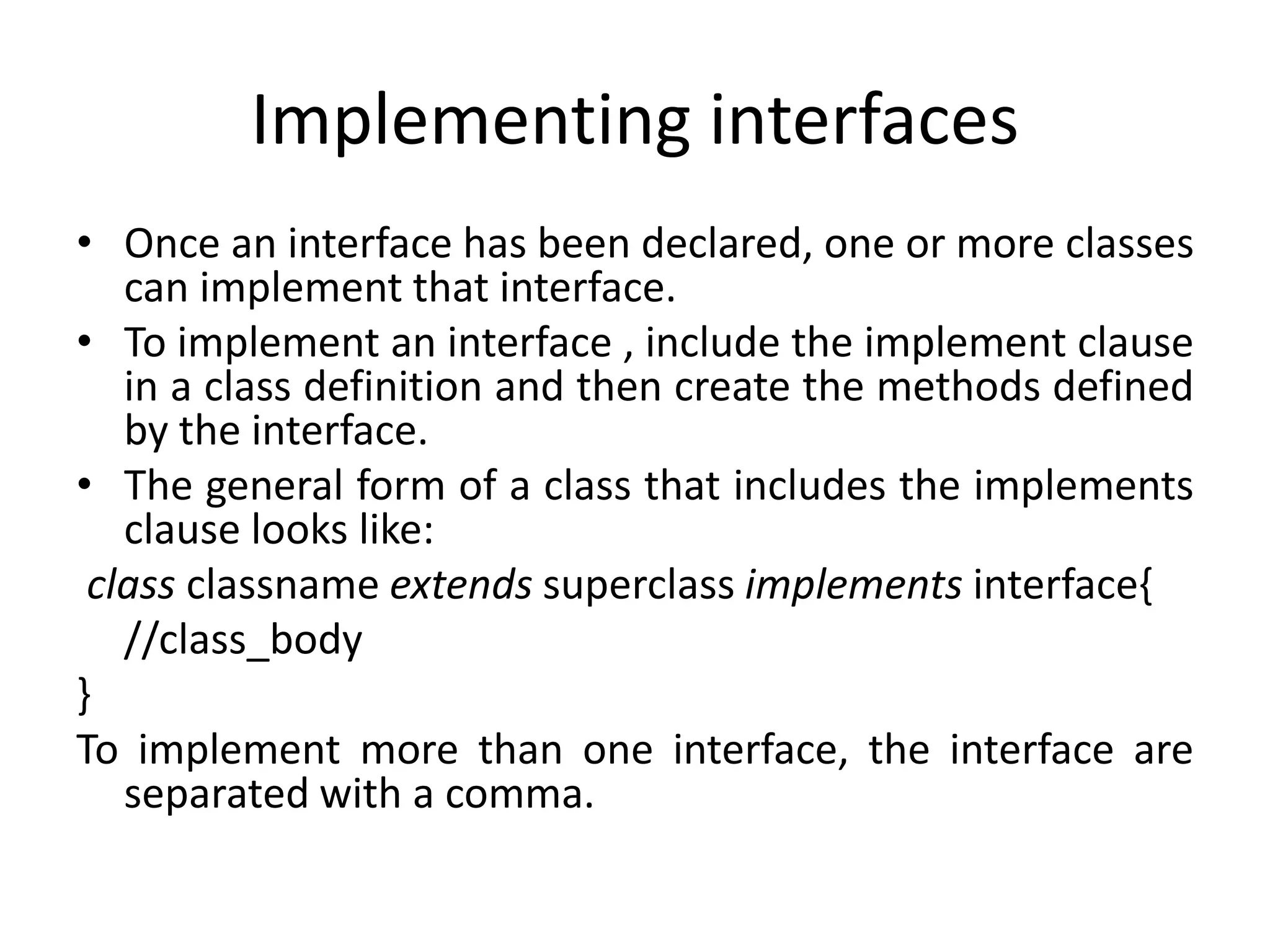
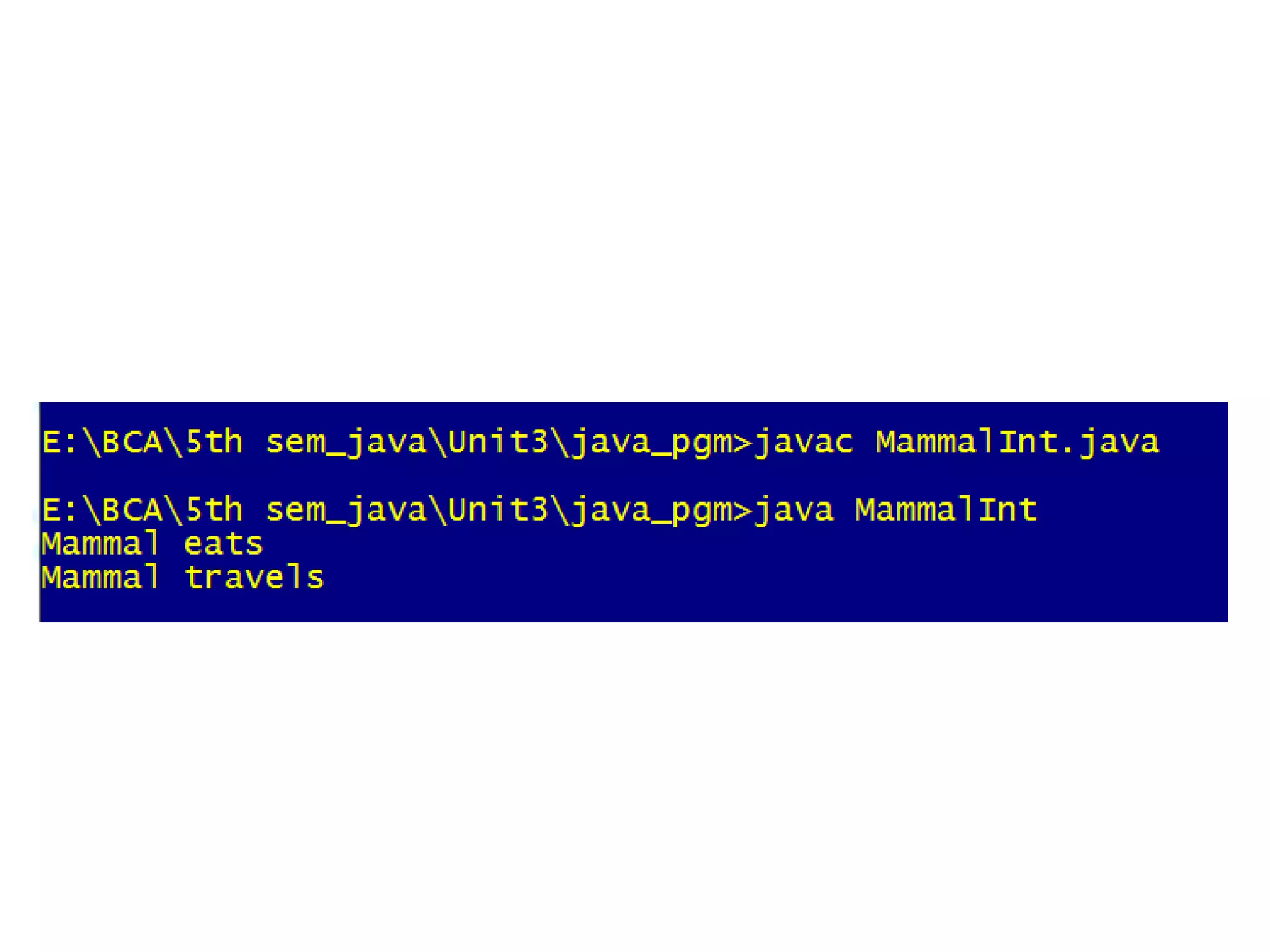
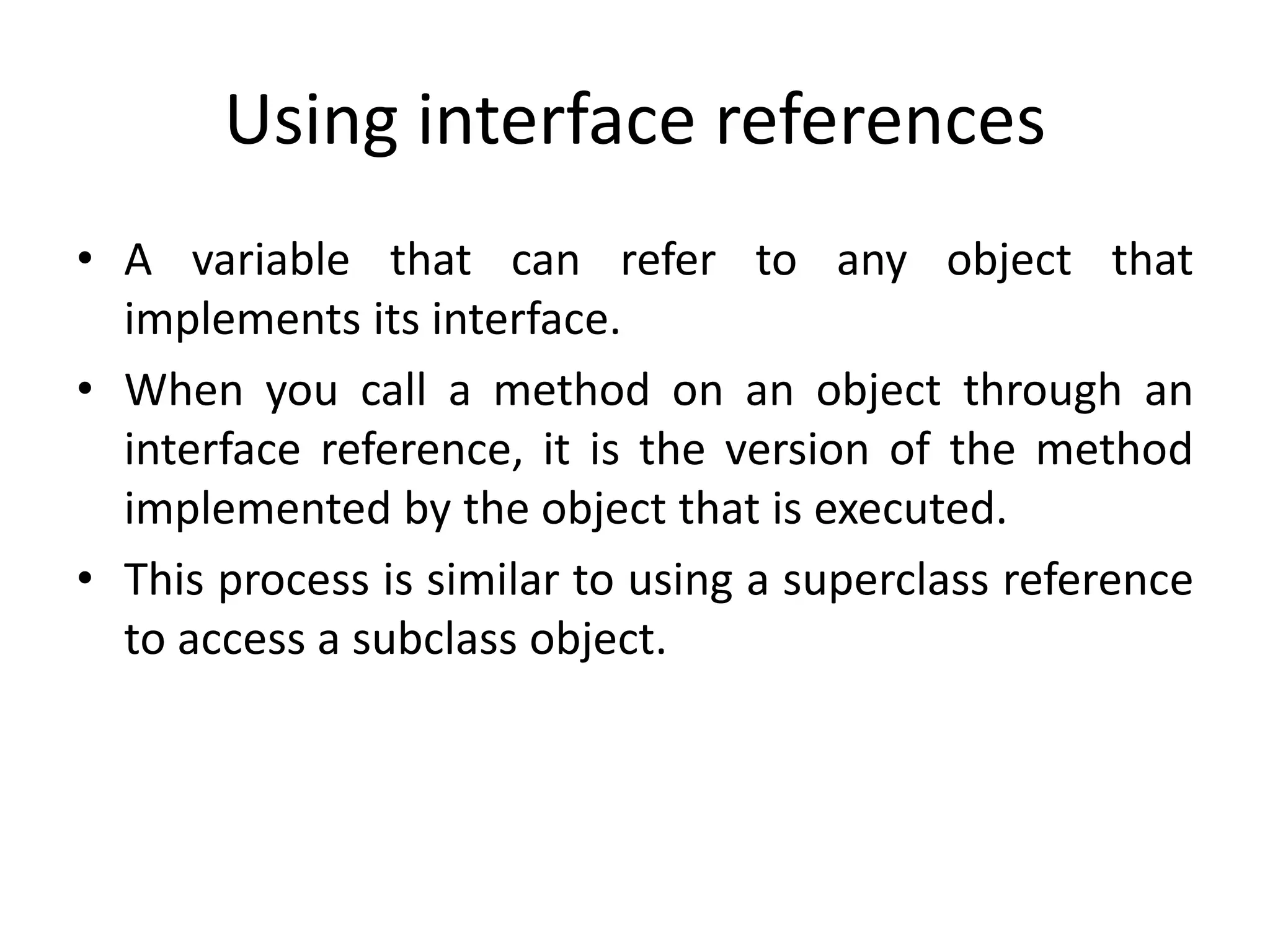
- Interfaces define methods without bodies. Classes implement interfaces by providing method bodies. Interface references allow polymorphism.
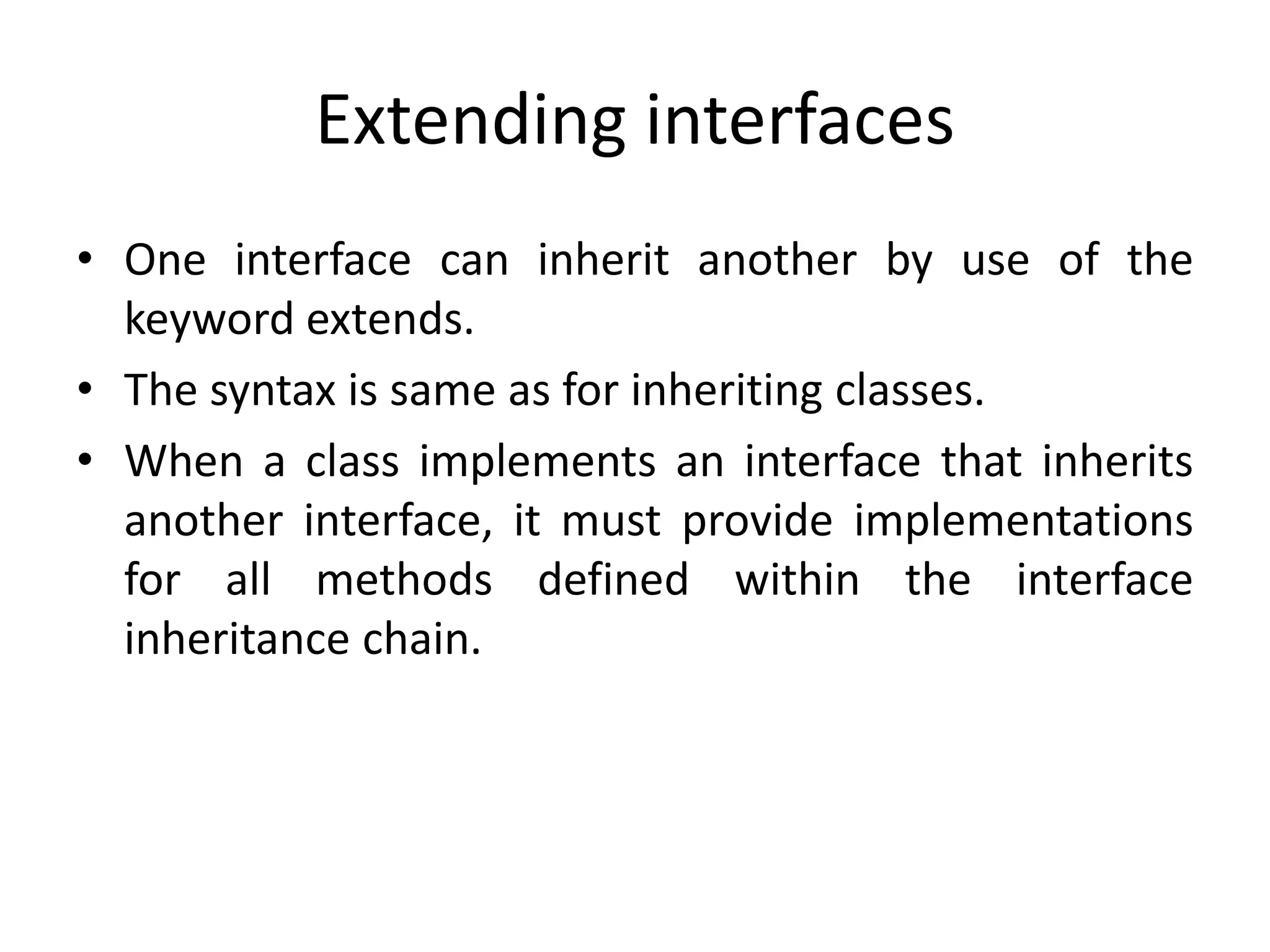
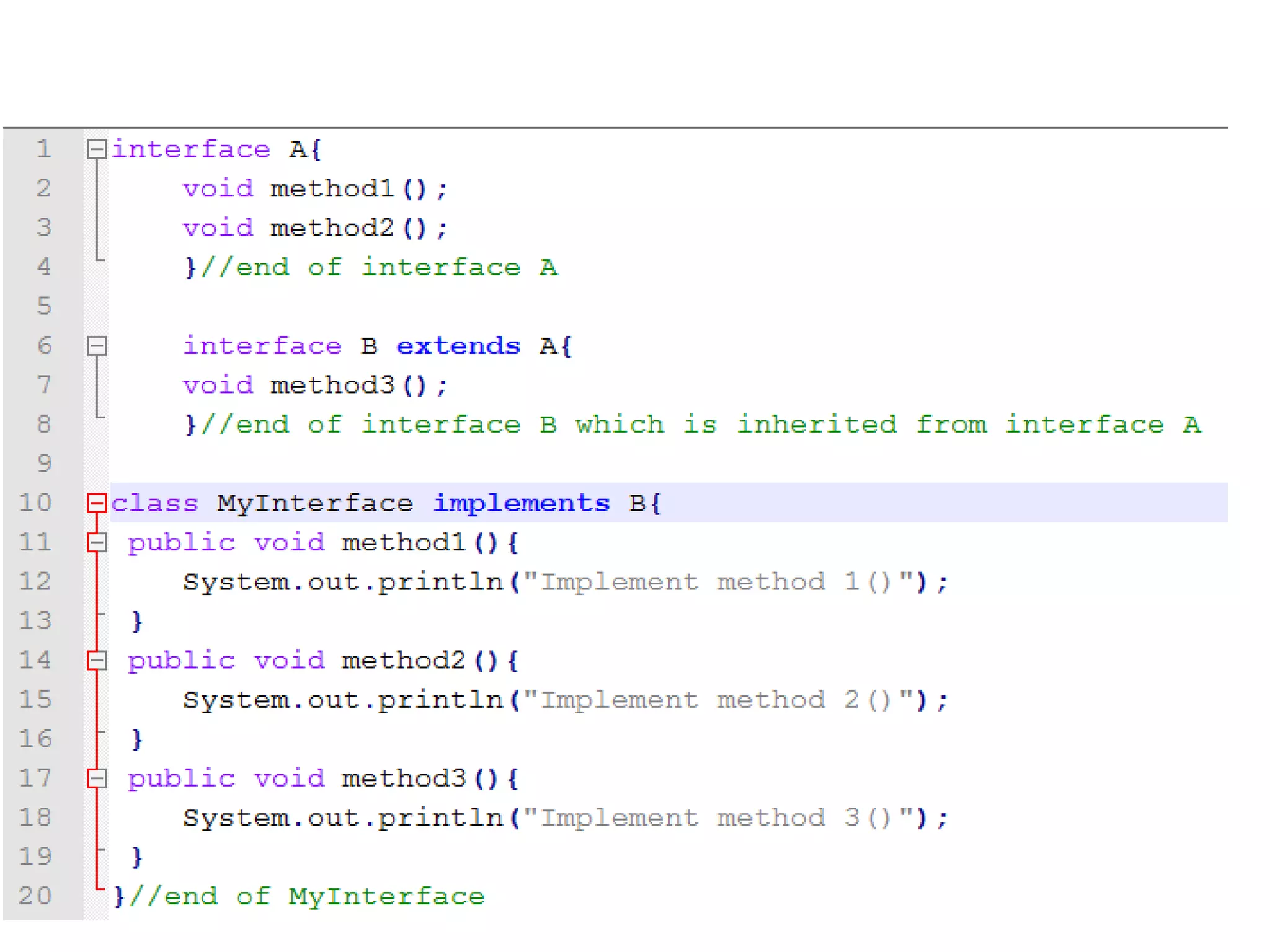
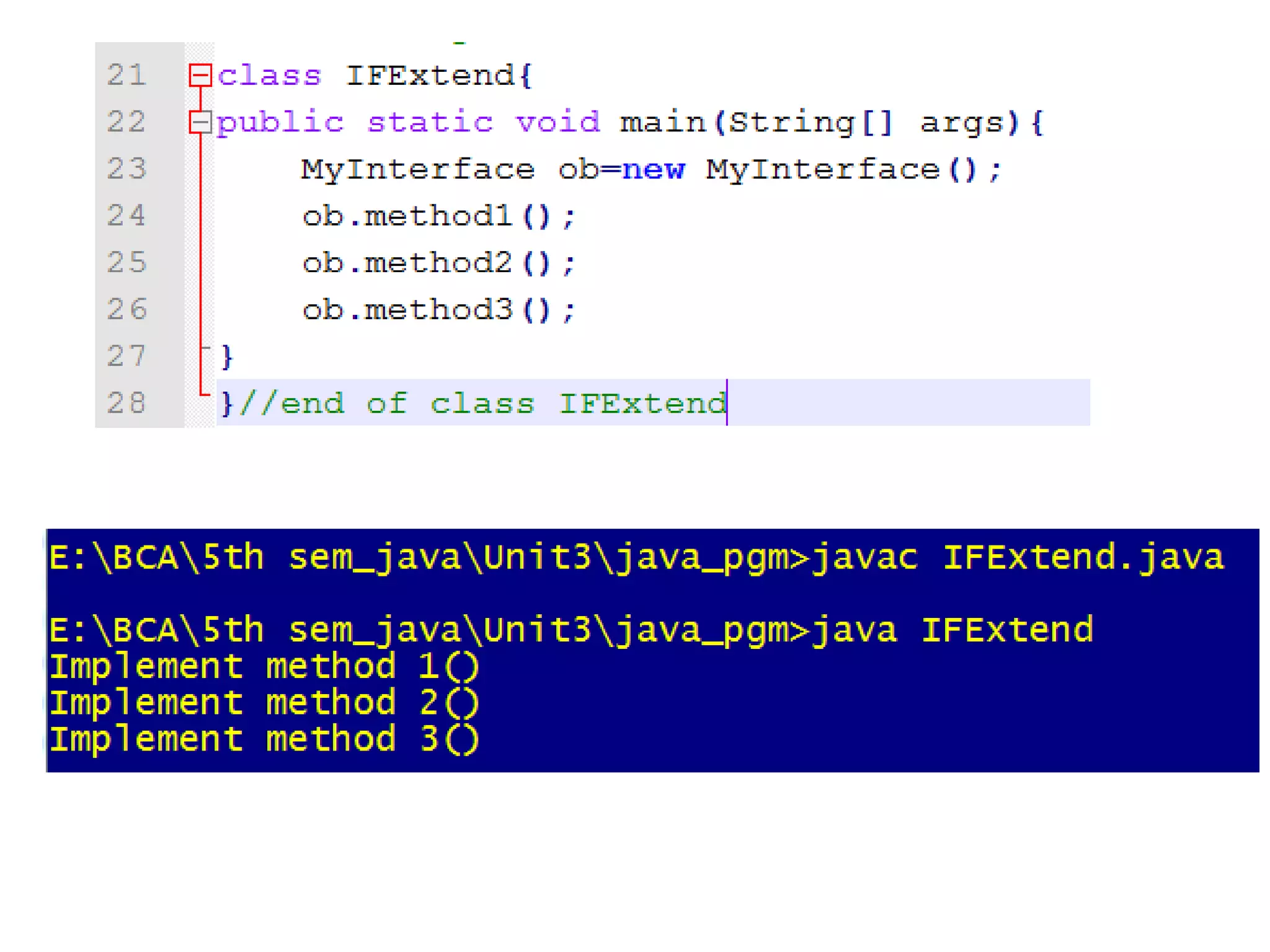
- Variables in interfaces are public, static, and final constants available to implementing classes. Interfaces can extend other interfaces.



































![Variables in interfaces-example
interface Iconst{
int MIN=0;
int MAX=100;
String ERROR_MSG= “Boundary error”;
}
class IConstD implements Iconst{
public static void main(String args[]){
int nums[]=new int [MAX];
for(int i=MIN;i<11;i++){
if(i>=MAX) System.out.println(ERROR_MSG);
else
System.out.println(nums[i]+ “ “);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1packages-150818071122-lva1-app6892/75/Chap1-packages-41-2048.jpg)