This document provides an introduction to crop production and management. It discusses that plants can produce their own food through photosynthesis, while animals and humans obtain food from plants or other animals. It also defines crops as plants of the same kind cultivated on a large scale. The two main types of crops are kharif crops, which are grown during the rainy season, and rabi crops, which are grown during the winter. The document outlines several important agricultural practices for crop production, including soil preparation, sowing, adding manure and fertilizers, irrigation, weed control, harvesting, and storage. It provides examples and illustrations of tools used at different stages of crop production.





















![HOMEWORK
1] What is crop? Give examples.
2] Name the agricultural practices in the cultivation of crops
3] What is ploughing?
4] Draw a neat labelled diagram of plough and explain it
5] Draw a neat labelled diagram of hoe and explain it
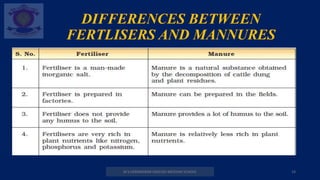
6] What are manures and fertilisers?
7] What are the advantages of manures?
8] Explain the modern methods of irrigation
9] Define the following terms i)harvesting ii)threshing iii)winnowing
10] What is animal husbandry?
M.V.HERWADKAR ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class8cropproductionandmanagement-220623051100-dcb1e899/85/CLASS-8-CROP-PRODUCTION-AND-MANAGEMENT-pptx-23-320.jpg)