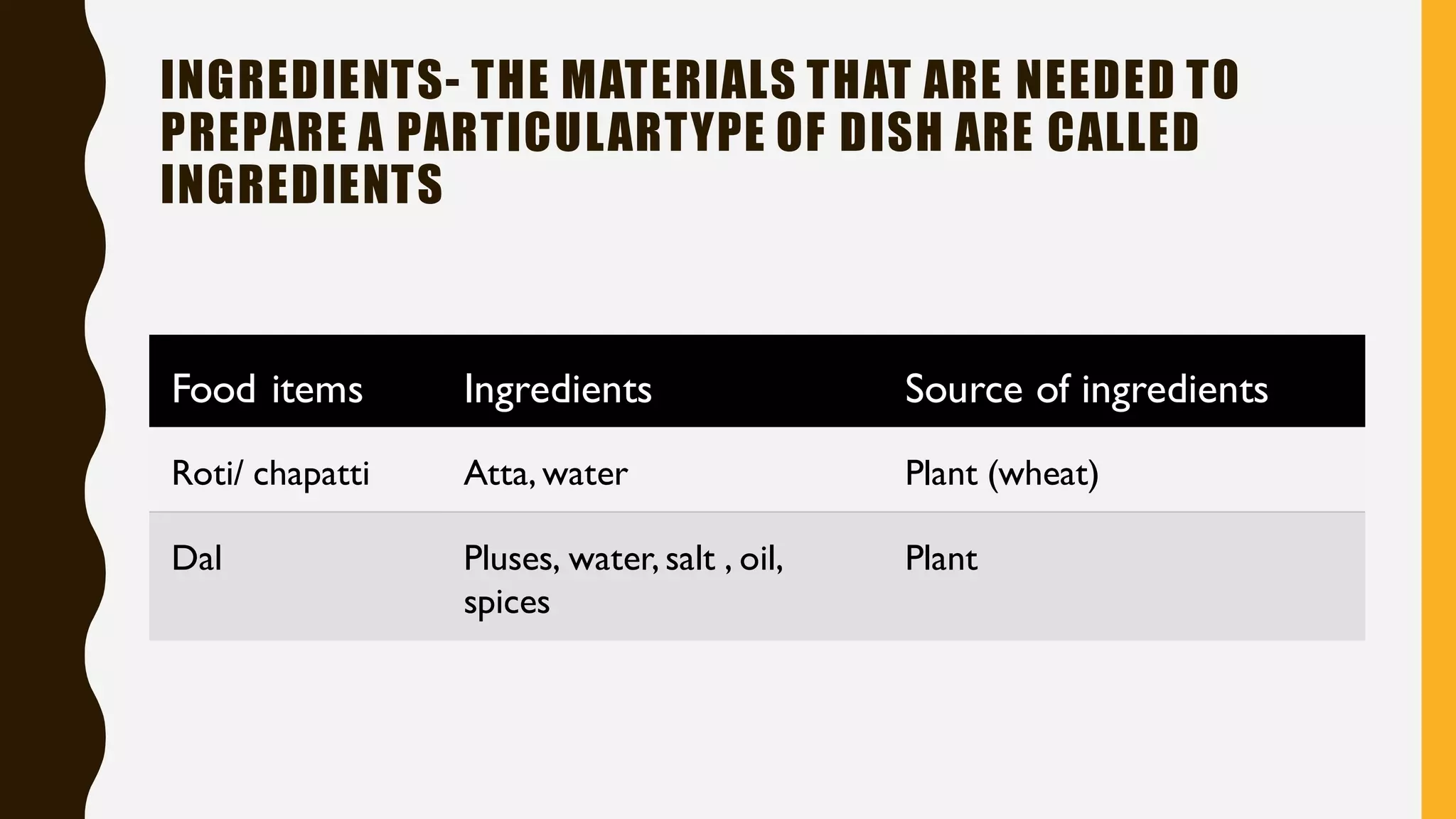
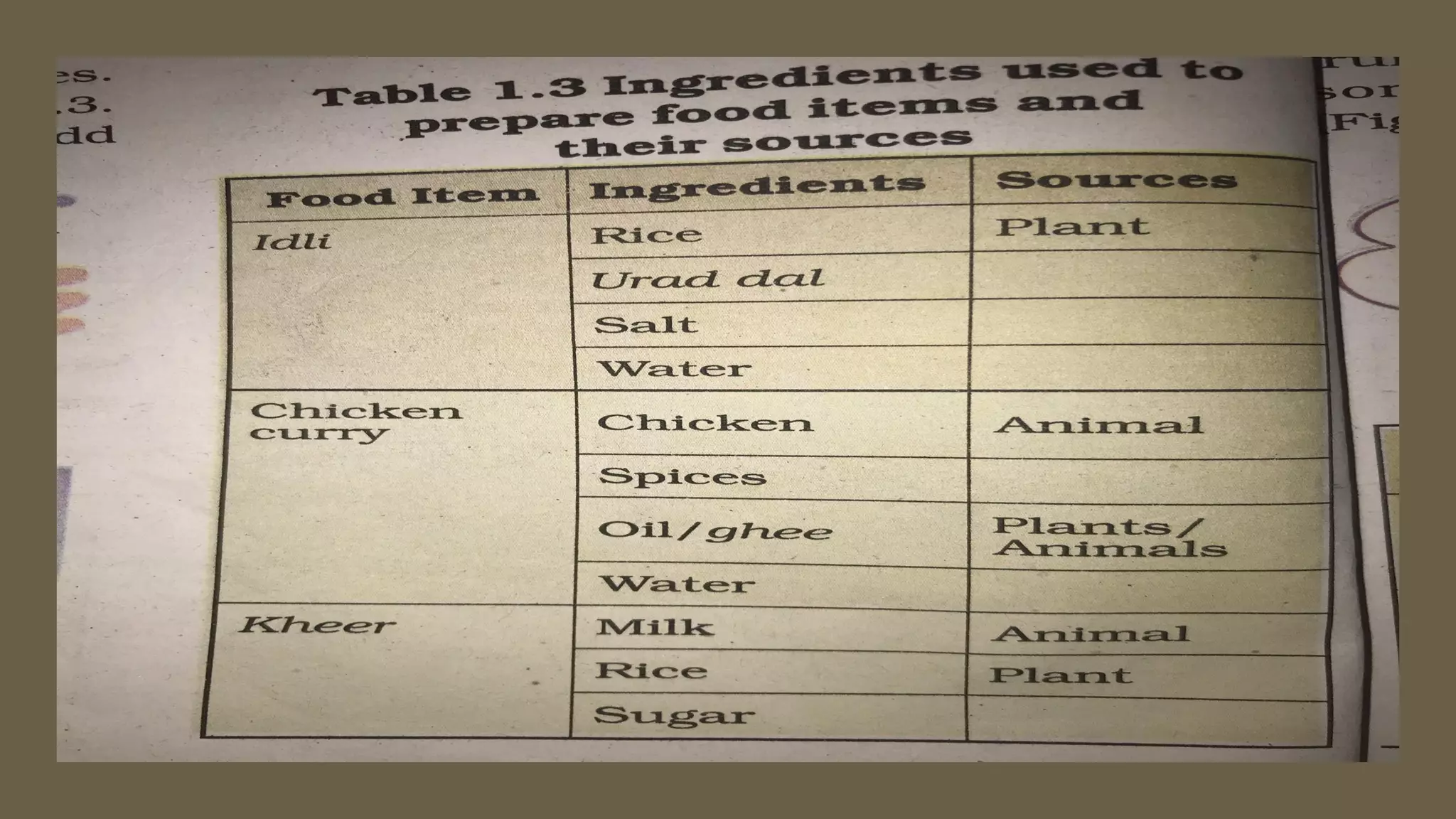
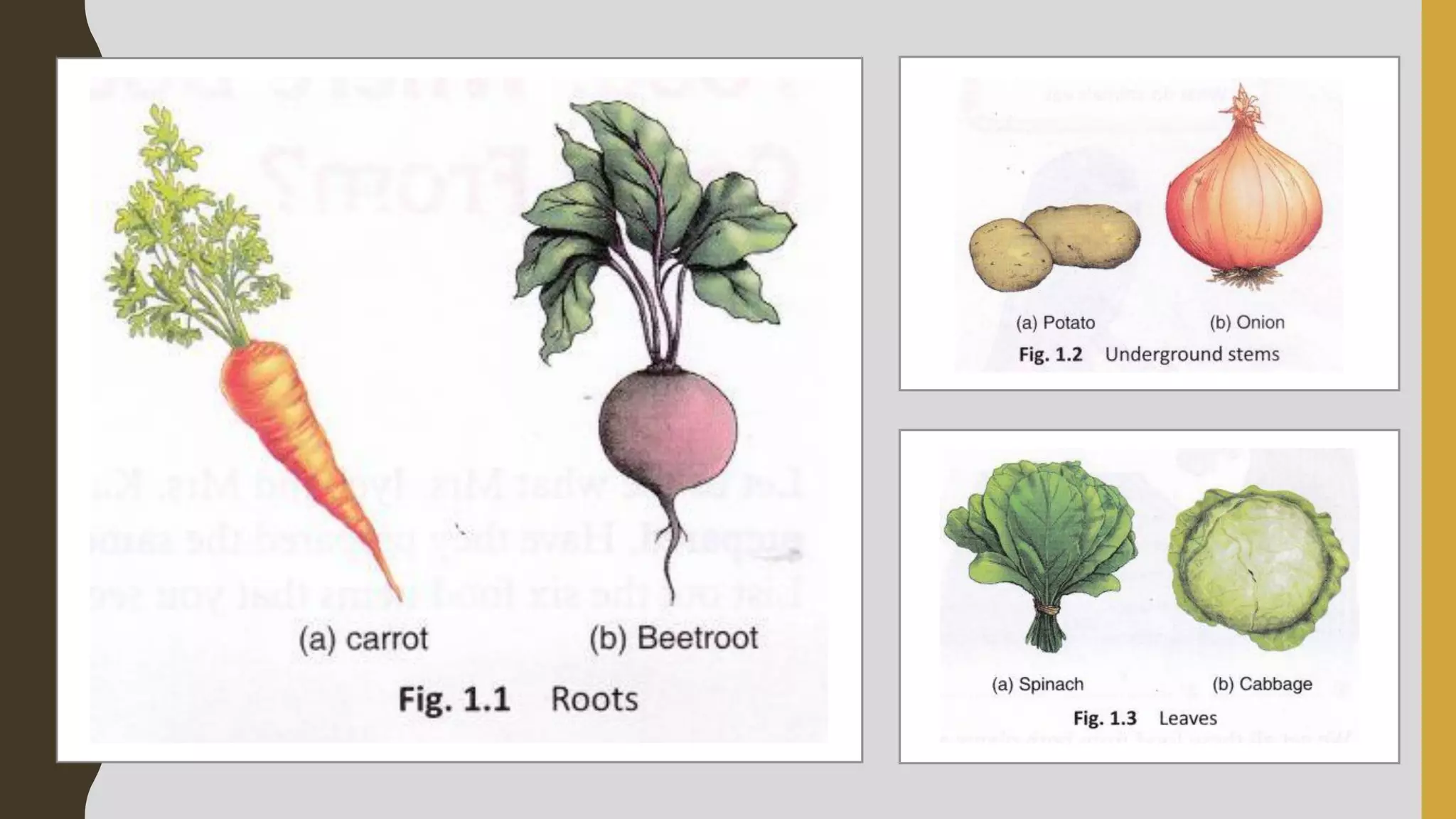
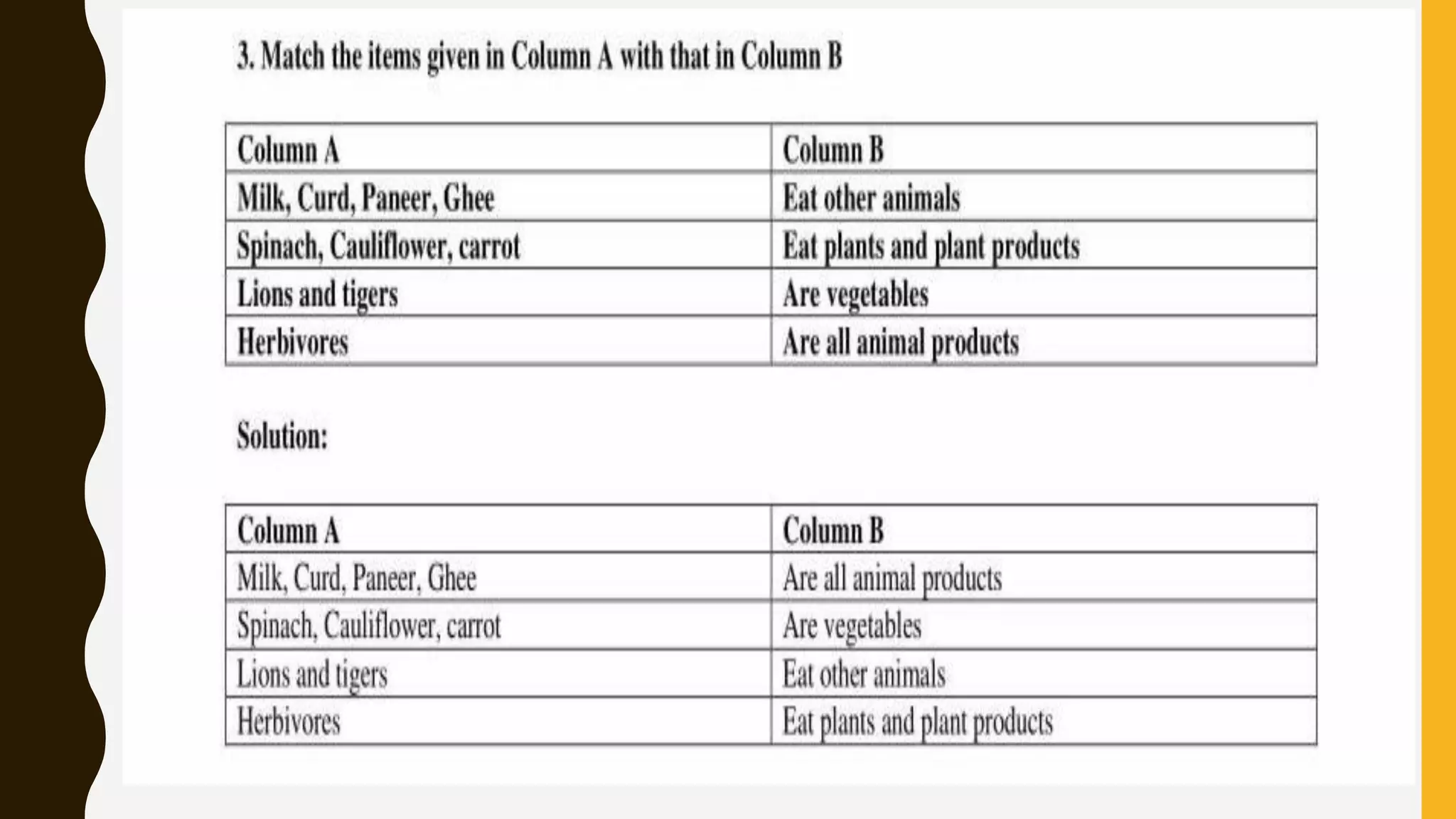
Here are drawings of the requested figures:
Fig1.4 (different edible parts of plant):
- Root
- Stem
- Leaf
- Flower
- Fruit
5 plant sources of food:
1. Carrot
2. Potato
3. Apple
4. Wheat
5. Spinach
5 animal sources of food:
1. Chicken
2. Fish
3. Milk
4. Egg
5. Honey