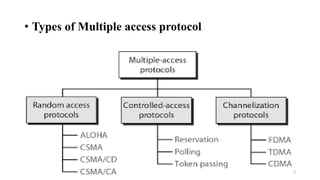
Multiple access protocols allow multiple nodes to access a shared network channel. They operate in the MAC sublayer of the OSI model. Random access protocols assign equal priority to all nodes, allowing any idle node to transmit. The four main random access protocols are ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CD, and CSMA/CA. ALOHA is a simple protocol where each node transmits whenever it has a frame, potentially causing collisions. It was later improved with slotted ALOHA which divides time into slots. CSMA protocols first check if the channel is idle before transmitting to avoid collisions.