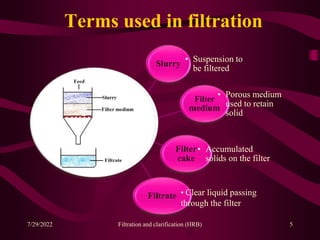
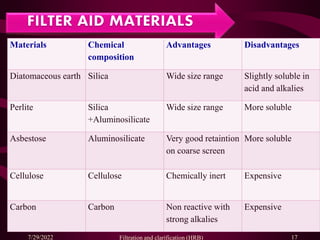
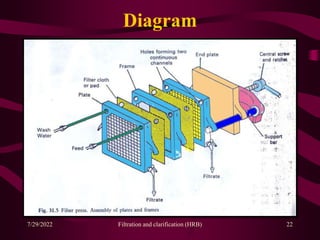
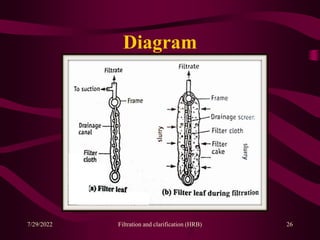
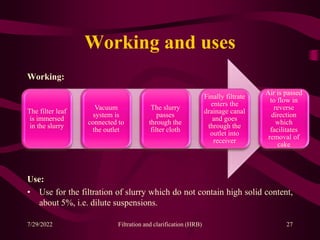
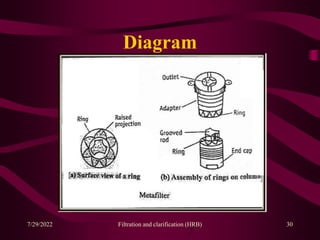
This document provides an overview of filtration and clarification processes. It defines filtration and clarification, and discusses various factors that affect filtration rates such as surface area, particle size, pore size, and viscosity. It also covers different types of filter media such as filter paper, cotton wool, asbestos, and membranes. Filter aids that are used to improve filtration rates such as diatomaceous earth, perlite, and cellulose are also described. Finally, it discusses various filtration equipment like plate and frame filters, leaf filters, and metafilters.