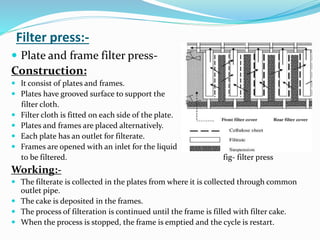
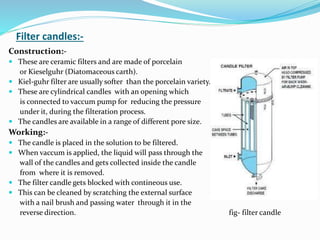
Rahul Kumar's document discusses filtration in the pharmaceutical industry. It defines key terms like filtration, clarification, filter medium, filter cake and filtrate. It also describes various filter media types including filter paper, cotton wool, glass wool and membrane filters. Different filtration equipment are discussed such as filter presses, meta filters, filter candles and sintered filters. Factors that affect the filtration rate like pressure, viscosity and particle size are also summarized.