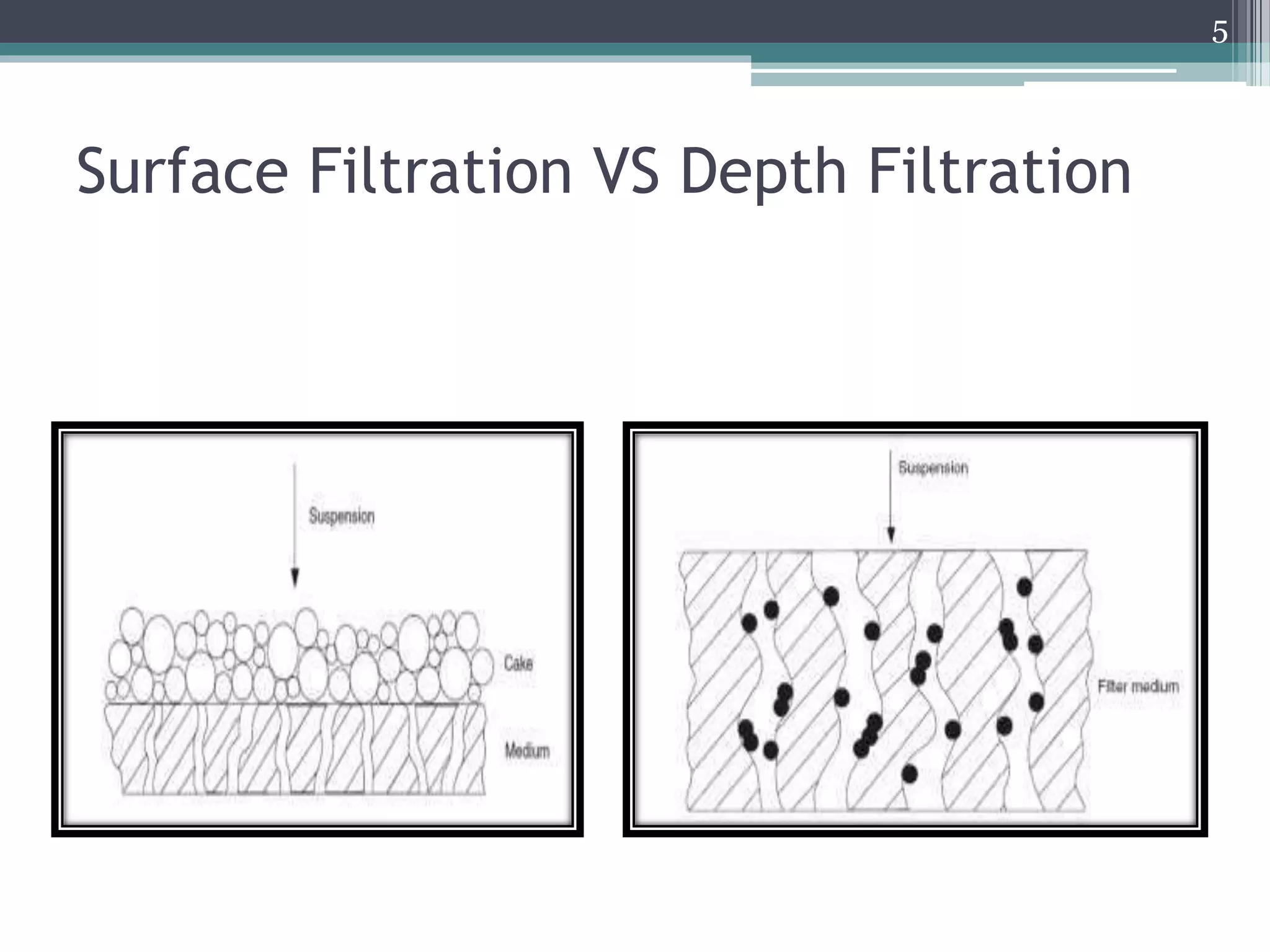
This document discusses filtration, which is defined as the separation of solids from liquids by passing the mixture through a porous medium. It describes different types of filtration including surface and depth filtration. Key factors that affect the filtration rate are also outlined. Various filter media are discussed, along with theories of filtration like Poiseuille's equation and Darcy's equation. Finally, common industrial filters used in pharmaceutical industries like filter presses and rotary filters are briefly introduced.