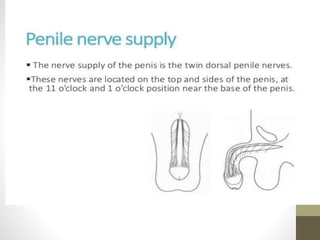
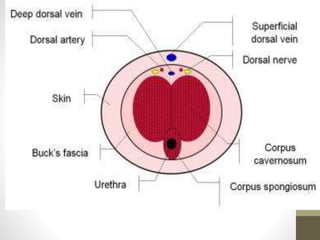
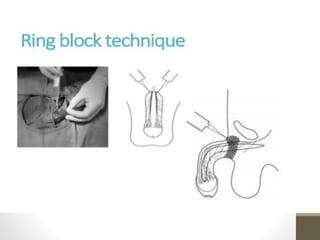
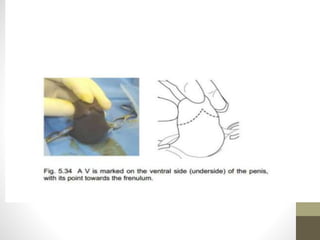
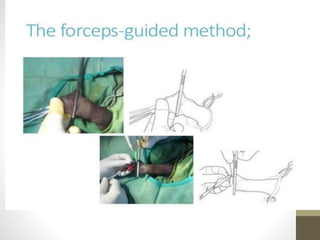
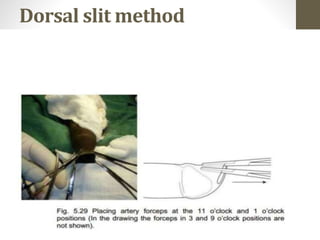
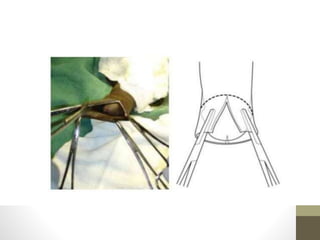
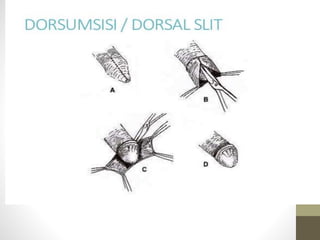
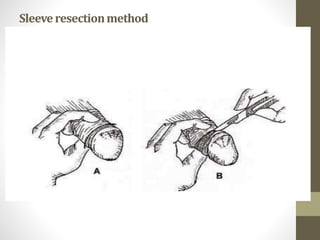
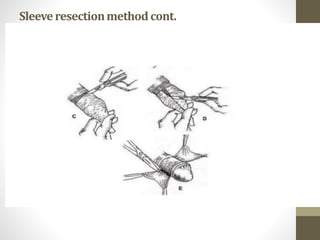
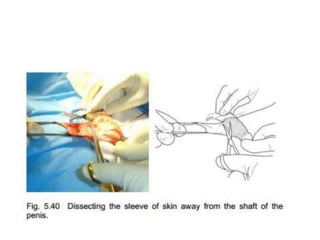
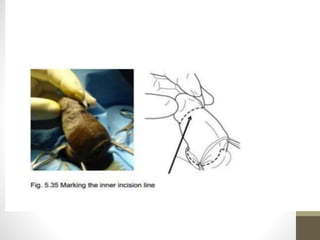
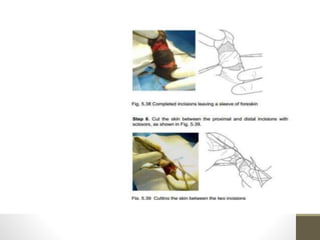
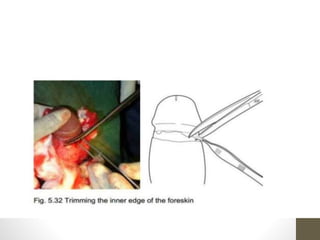
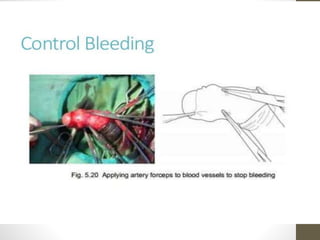
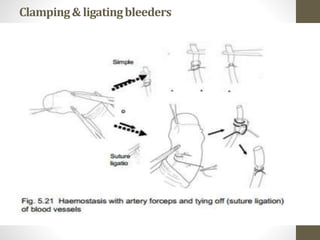
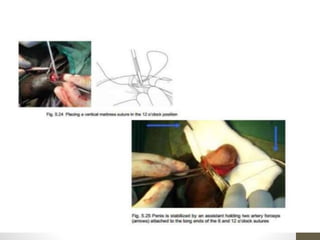
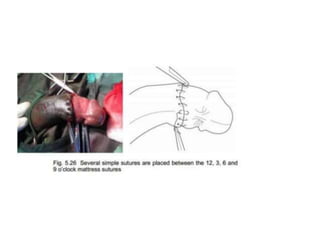
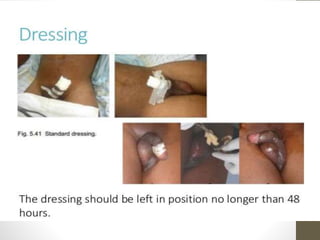
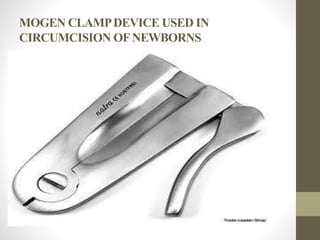
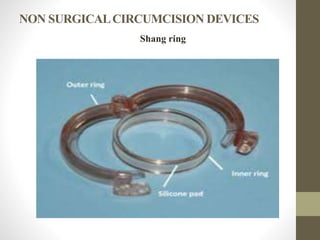
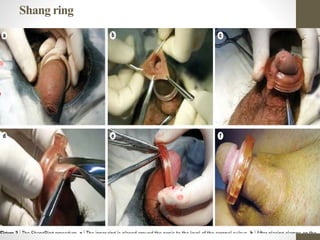
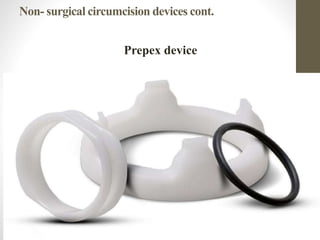
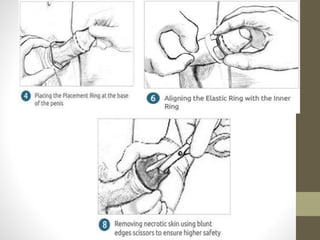
This document provides information on voluntary medical male circumcision (VMMC). It defines circumcision as the surgical removal of the foreskin and discusses its medical and cultural indications. Contraindications and pre-operative preparation are outlined. The dorsal slit method of circumcision is described along with post-operative care and potential complications. Non-surgical devices for circumcision like the Shang ring and Prepex are also mentioned.