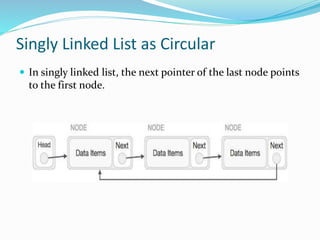
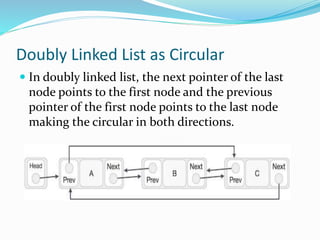
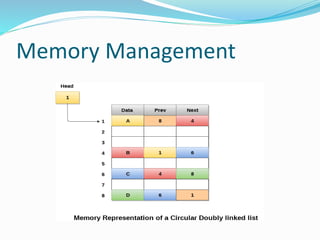
This document provides an introduction to circular linked lists. It explains that a circular linked list is a variation of a linked list where the first element points to the last element, forming a loop. Both singly and doubly linked lists can be made circular by having the next pointer of the last node point to the first node, and in doubly linked lists the previous pointer of the first node points to the last node. Basic operations like insert, delete, and display are supported. Memory management involves the head pointer storing the address of the first node, and each node storing the address of the next node and last node.