Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


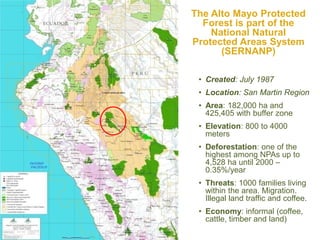



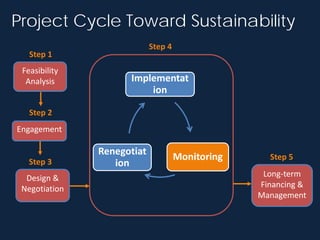

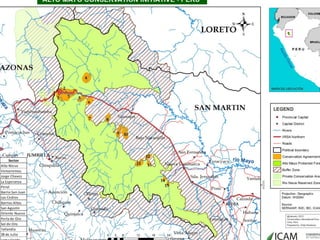
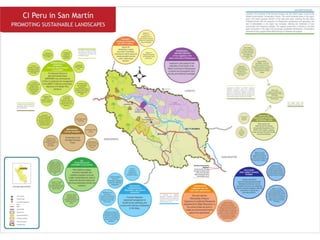


The Alto Mayo Protected Forest in Peru, established in 1987, spans 182,000 hectares and faces significant deforestation threats due to illegal land use and economic activities. Conservation strategies have been developed to strengthen management and promote sustainable practices through financial mechanisms such as REDD+. A conservation agreement model outlines steps for implementing and monitoring actions to prevent biodiversity loss while ensuring community benefits.










