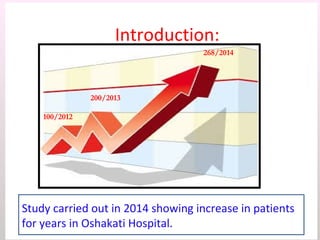
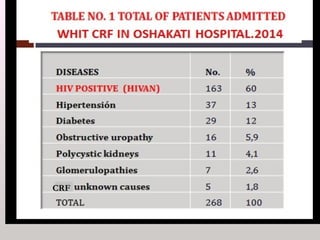
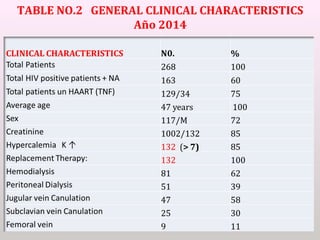
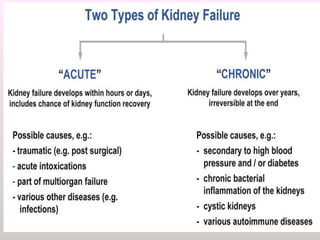
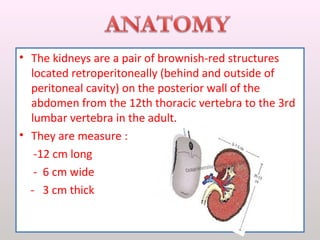
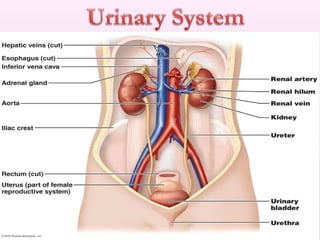
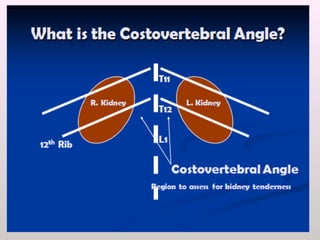
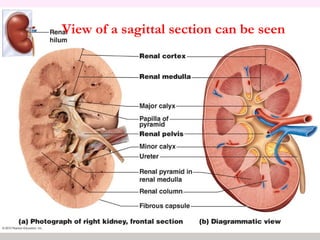
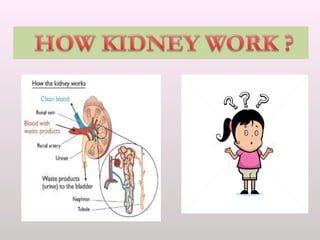
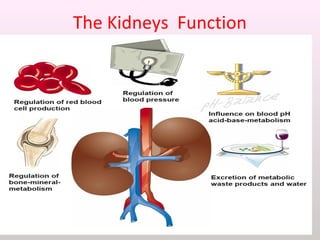
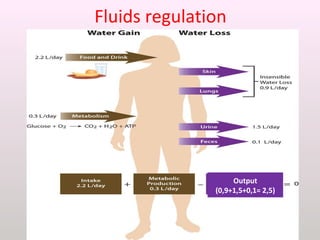
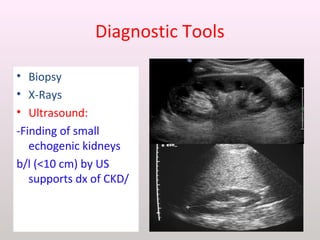
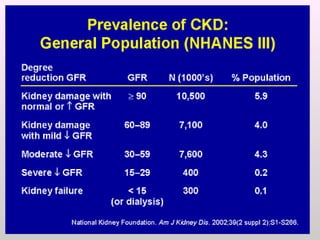
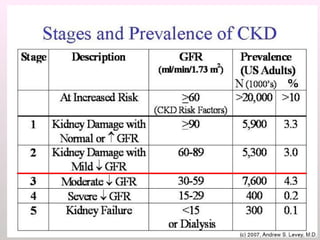
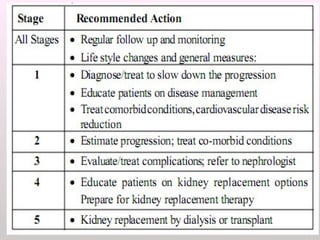
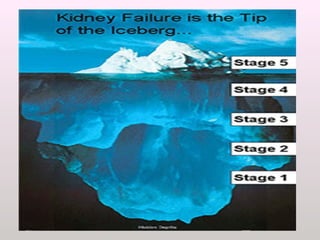
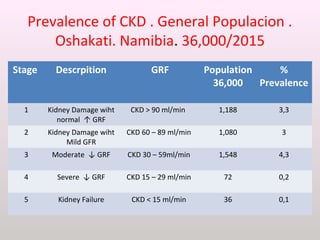
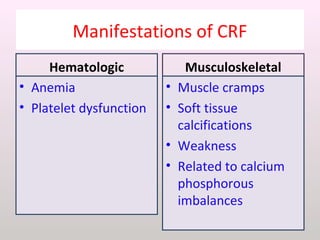
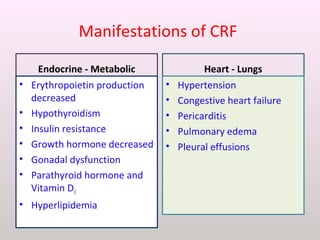
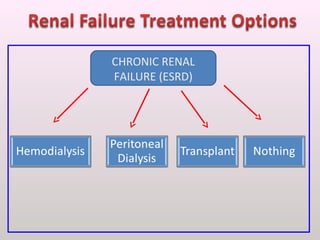
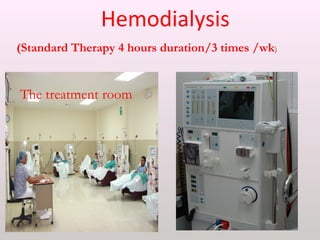
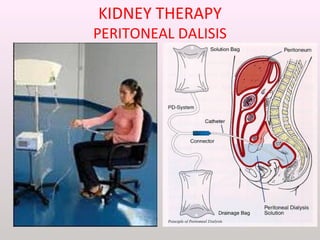
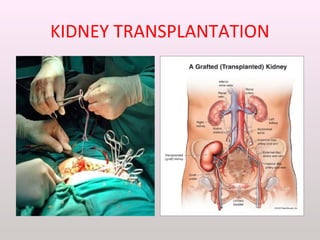
The document discusses a study conducted in 2014 on chronic renal failure (CRF) at Oshakati Hospital, emphasizing the rising patient numbers and associated high mortality due to late referrals. It details the kidney's functions, diagnostic tools, causes of chronic kidney disease (CKD), and potential treatment options, including conservative management and dialysis. The conclusion advocates for a national CKD prevention program to manage and treat the disease effectively.