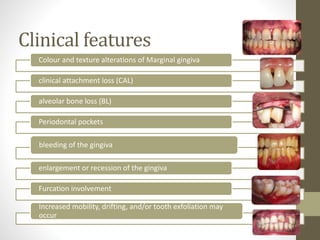
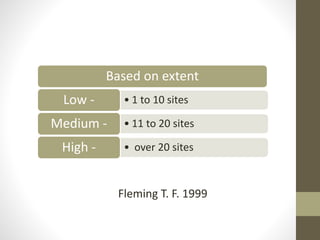
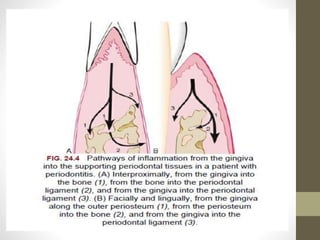
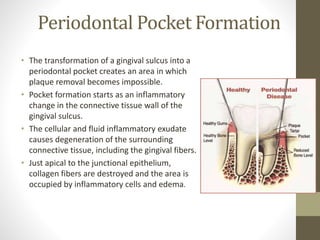
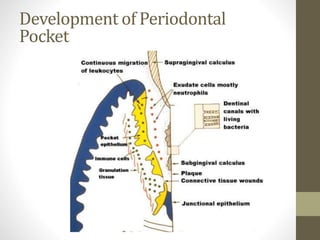
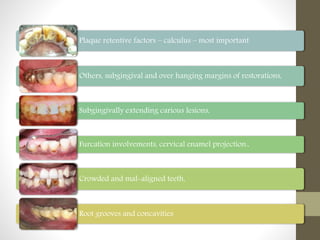
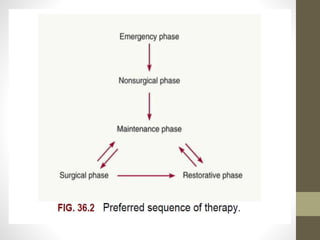
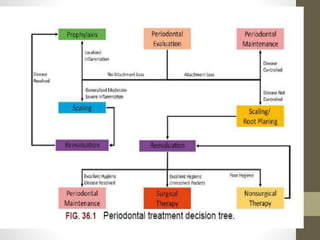
Chronic periodontitis is a slowly progressing infectious disease resulting in inflammation of the supporting tissues of the teeth and progressive bone and attachment loss. It is caused by bacterial plaque accumulation at the gumline. Key characteristics include site-specific or generalized bone and attachment loss, commensurate with plaque levels and modified by systemic and environmental risk factors like smoking and diabetes. The disease progresses in an episodic, intermittent manner with periods of rapid tissue destruction. Risk factors include prior history of periodontitis, specific pathogenic bacteria like P. gingivalis, local factors like calculus, and environmental factors like smoking which impair the host response.