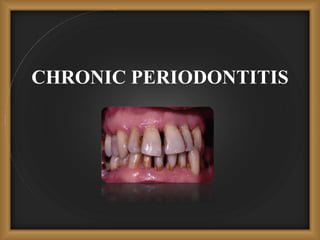
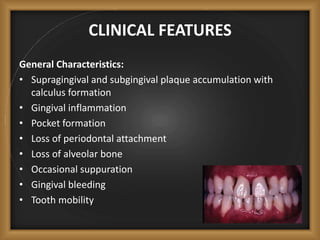
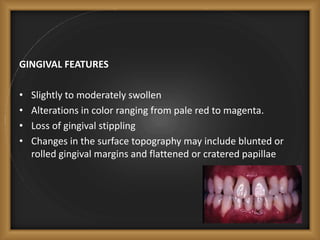
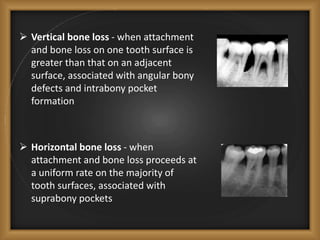
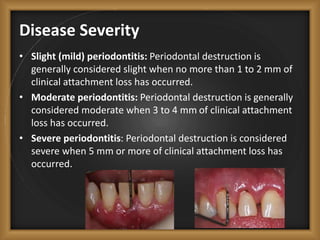
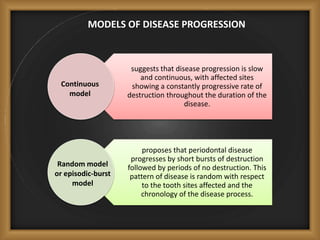
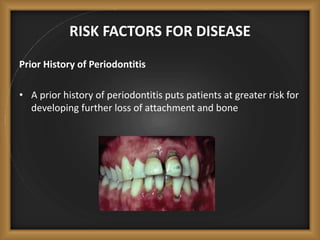
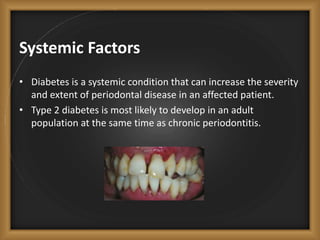
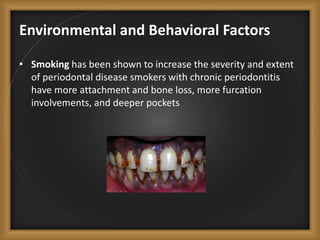
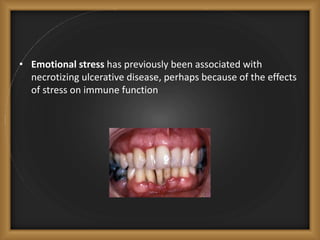
Chronic periodontitis is the most common form of periodontitis, characterized by a slowly progressive inflammation and destruction of the tissues surrounding the teeth. It is caused by an excessive host response to bacterial plaque accumulated at and below the gumline. Symptoms include bleeding gums, deepening pockets between teeth, and loose or mobile teeth. The disease progresses gradually over time as plaque accumulates. Risk factors include a prior history of periodontitis, poor plaque control, diabetes, smoking, stress, and certain genetic factors.