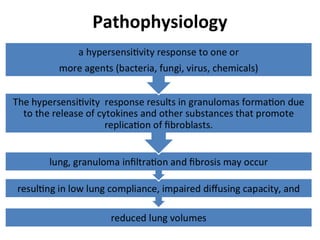
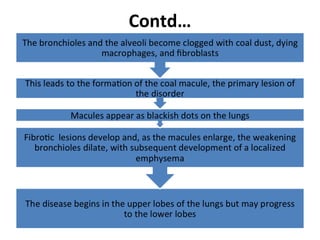
This document discusses occupational lung diseases, including sarcoidosis and pneumoconiosis. Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease that causes granulomas (lumps) in the lungs and lymph nodes, and is more common in African Americans, women, and those aged 20-40. Pneumoconiosis refers to fibrotic lung disease caused by inhaling mineral dusts, such as silica (silicosis), asbestos (asbestosis), or coal dust (coal worker's pneumoconiosis). Symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, and reduced lung function. Diagnosis involves exposure history, imaging, and lung biopsies. Treatment focuses on removing exposure, managing symptoms, and treating