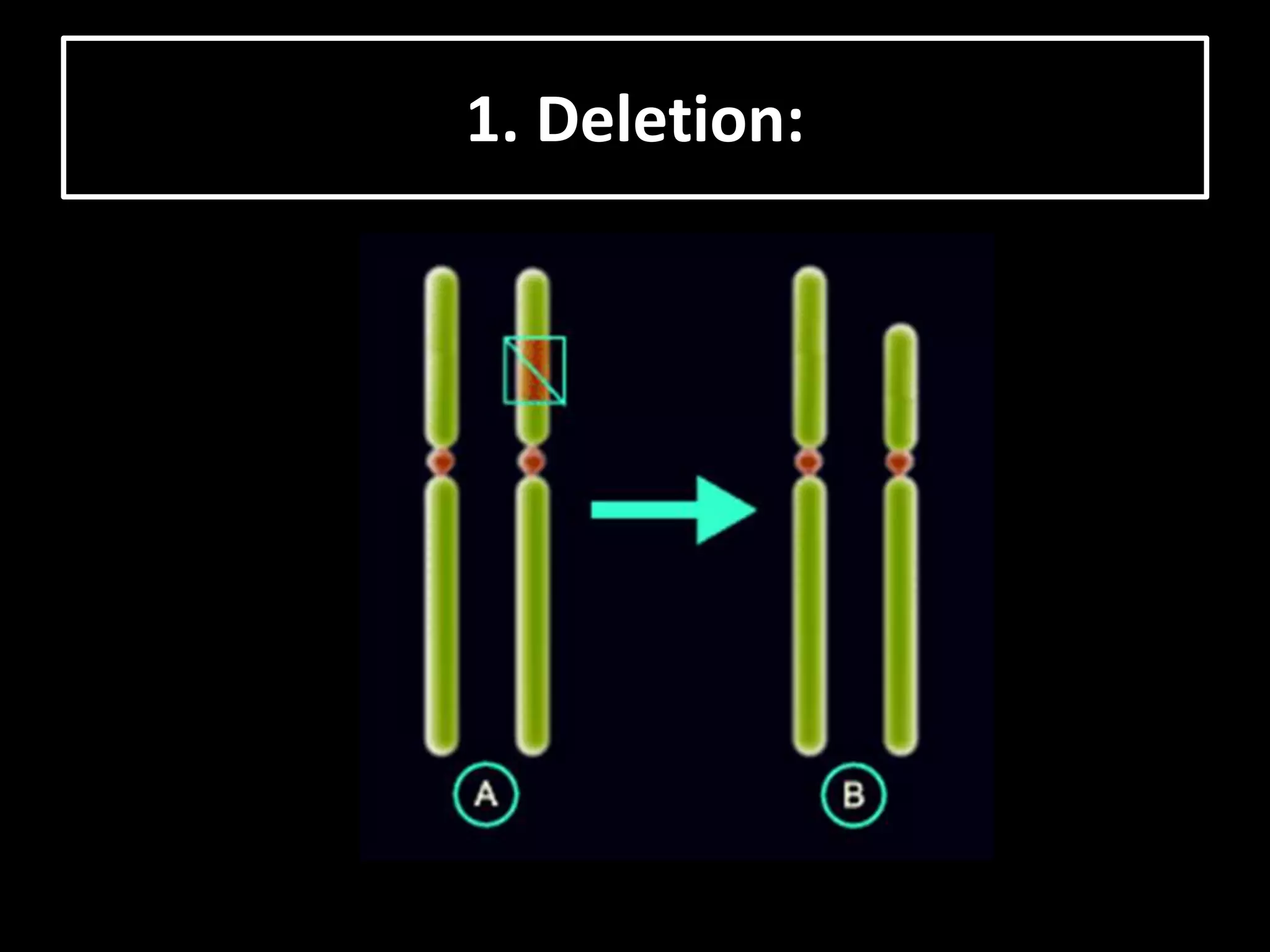
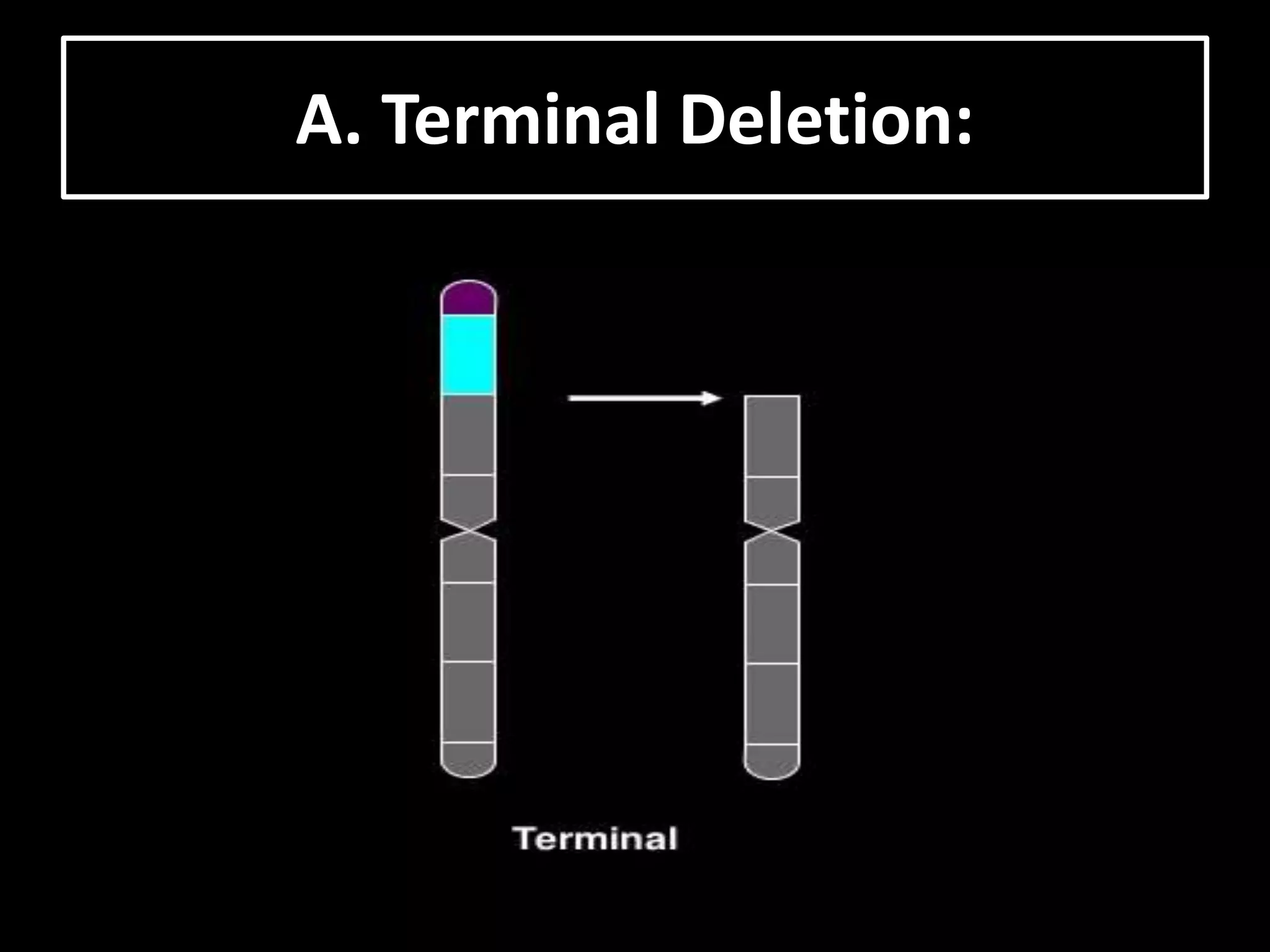
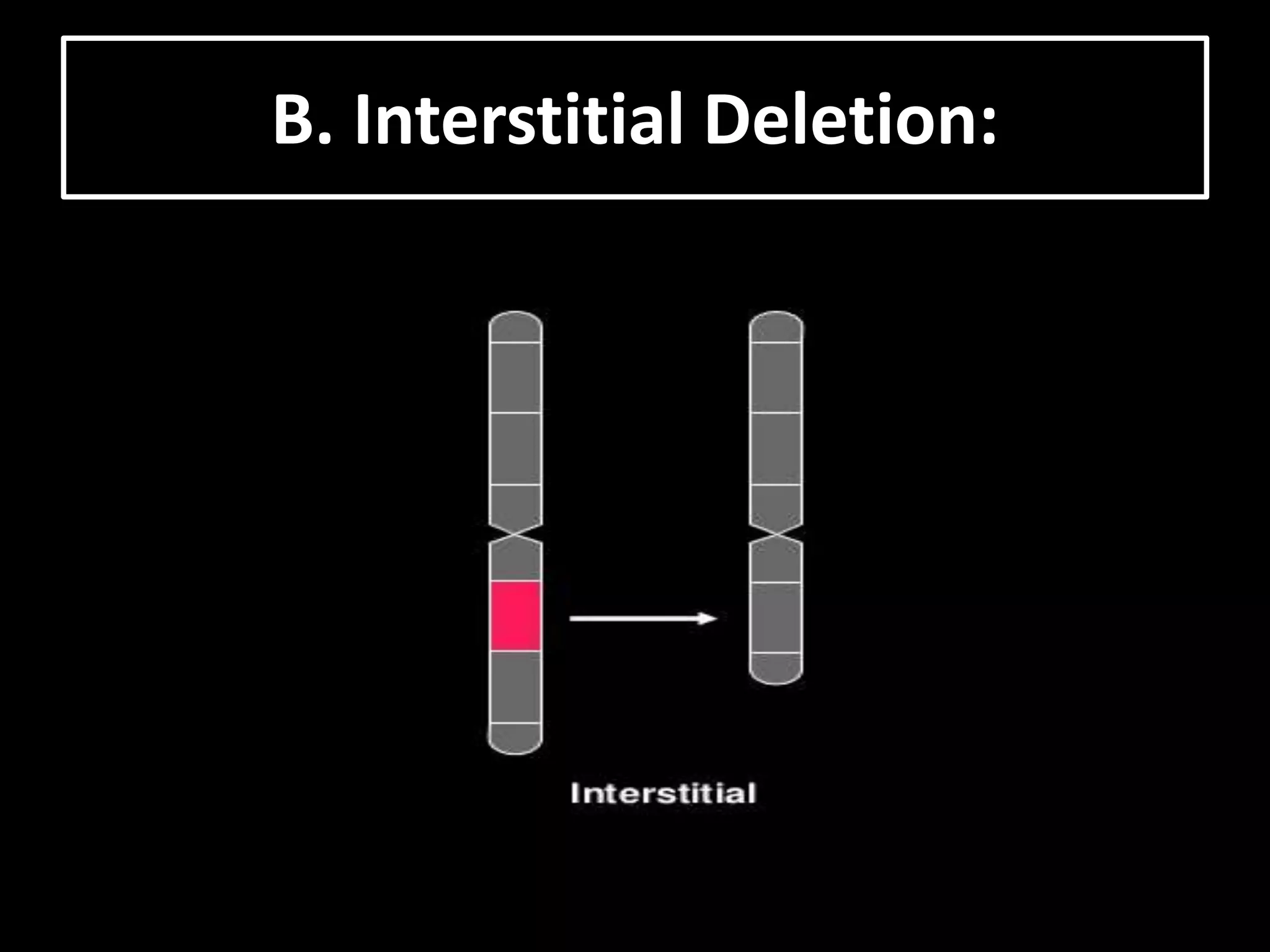
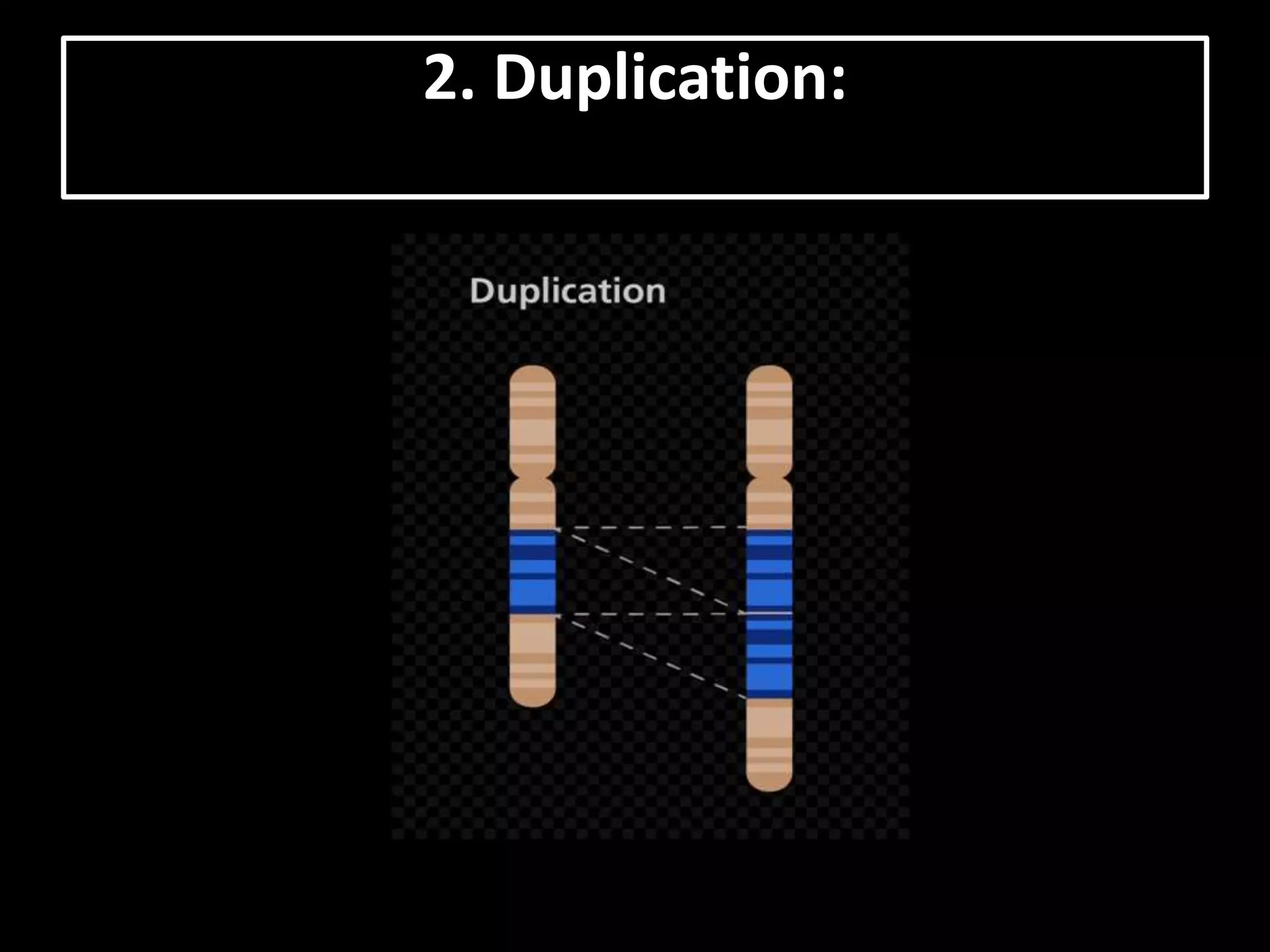
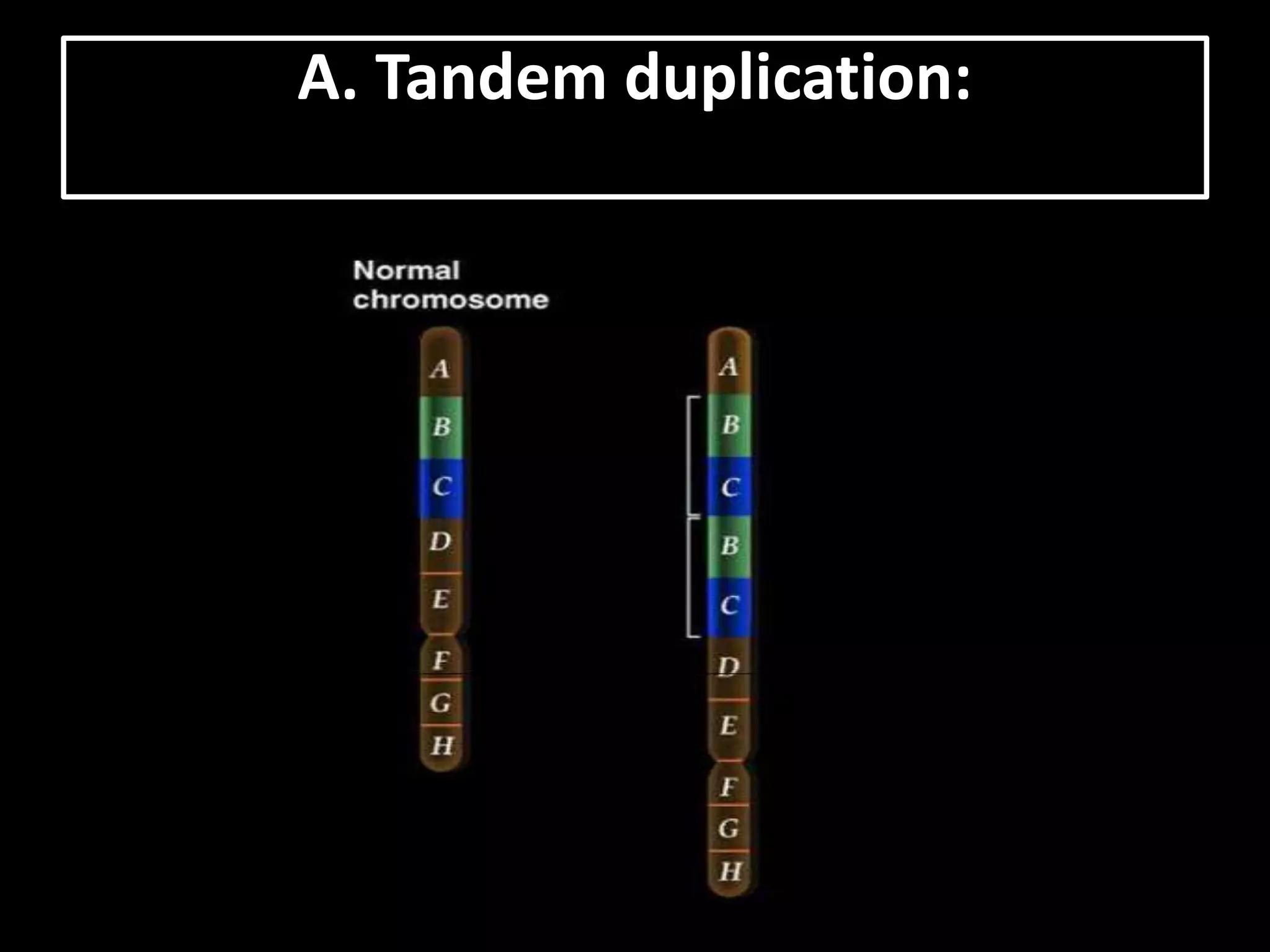
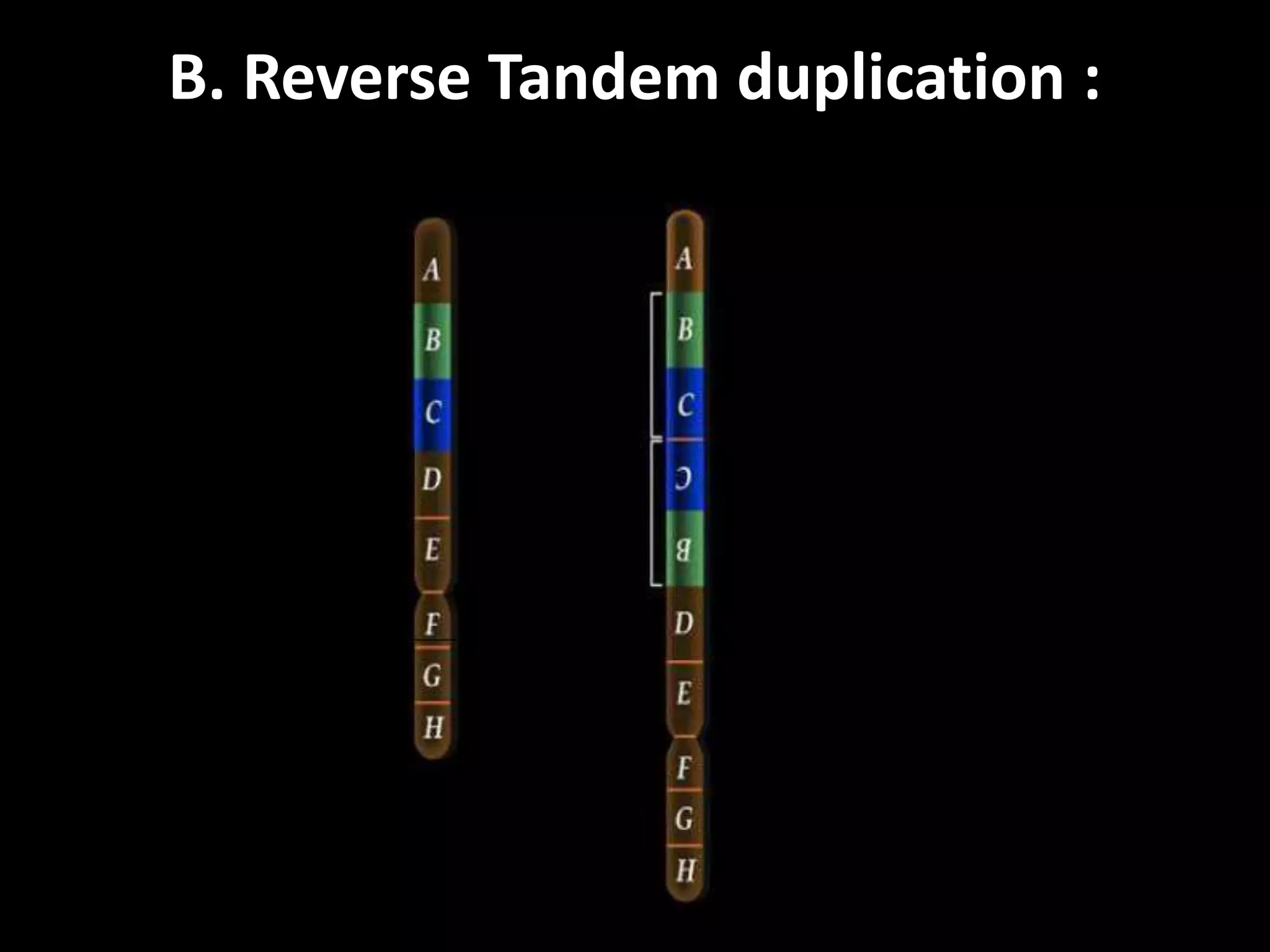
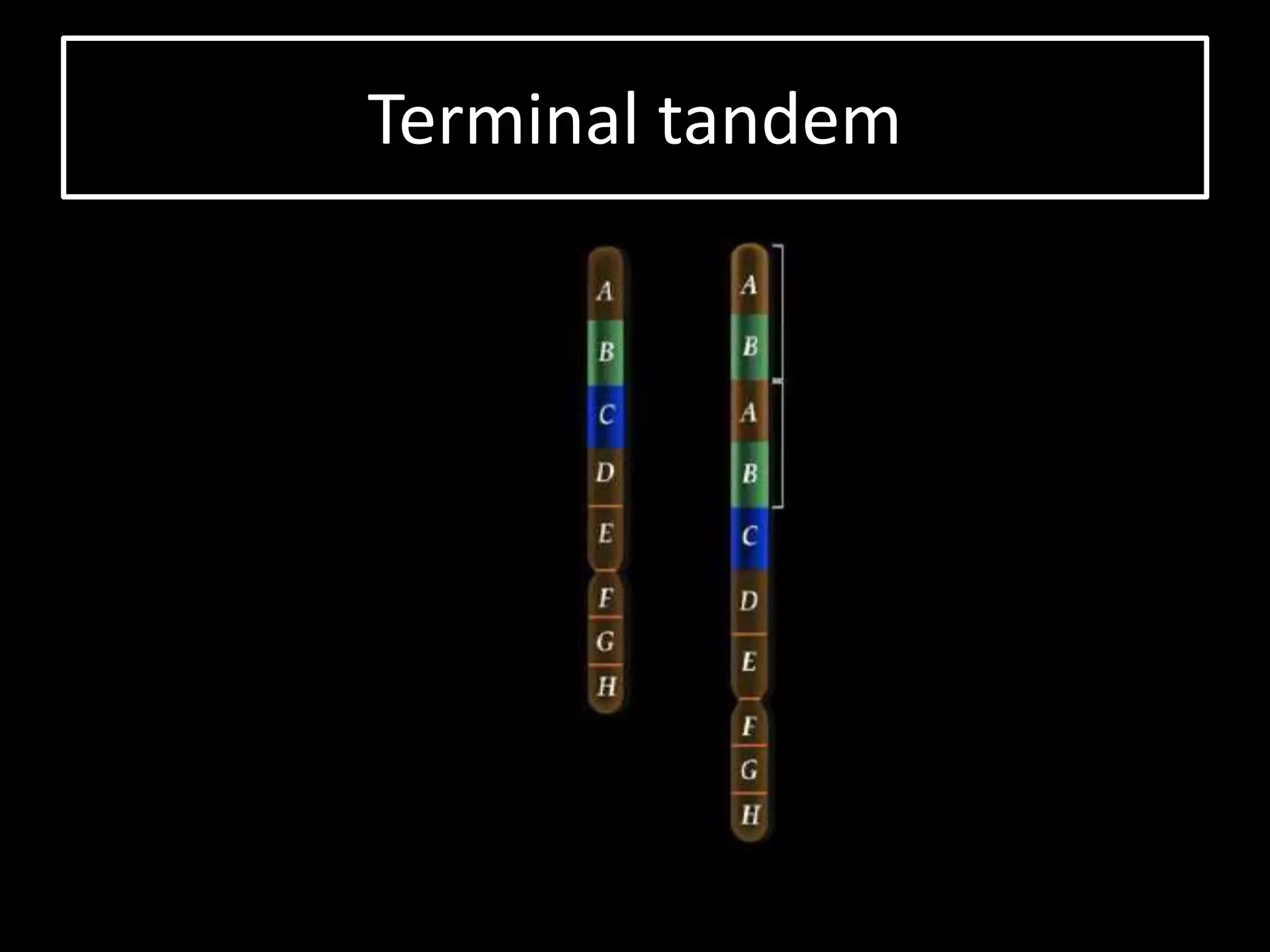
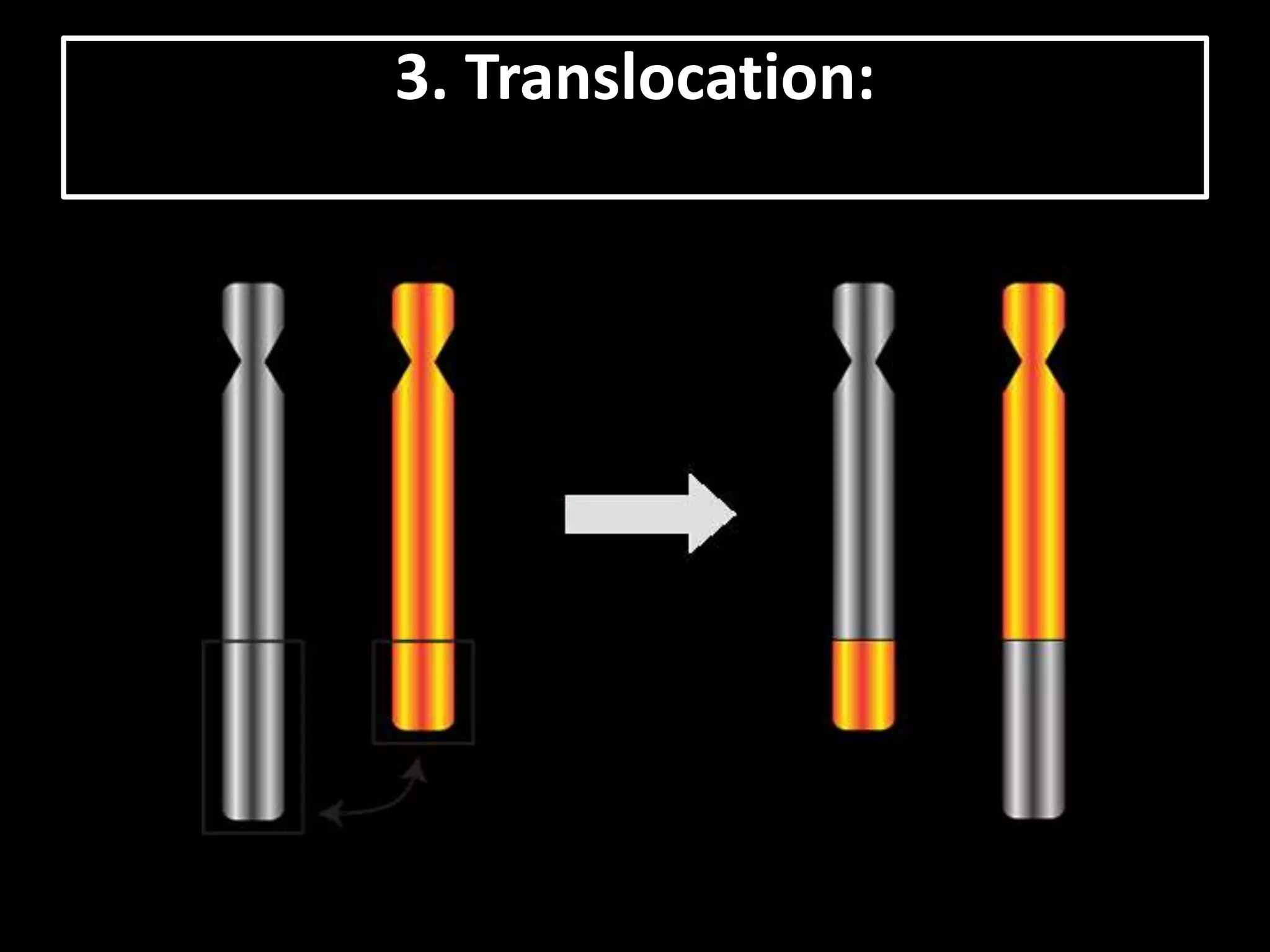
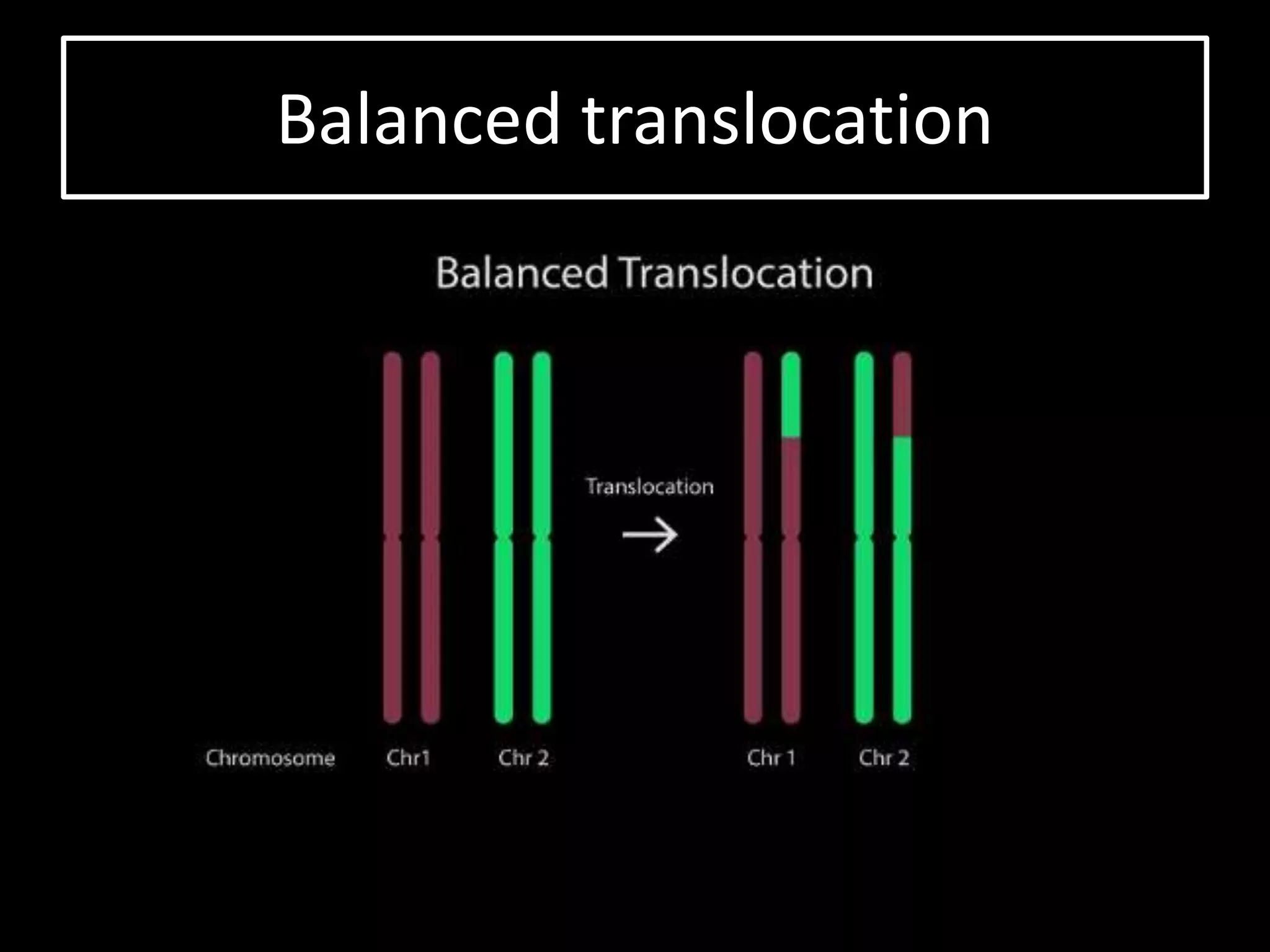
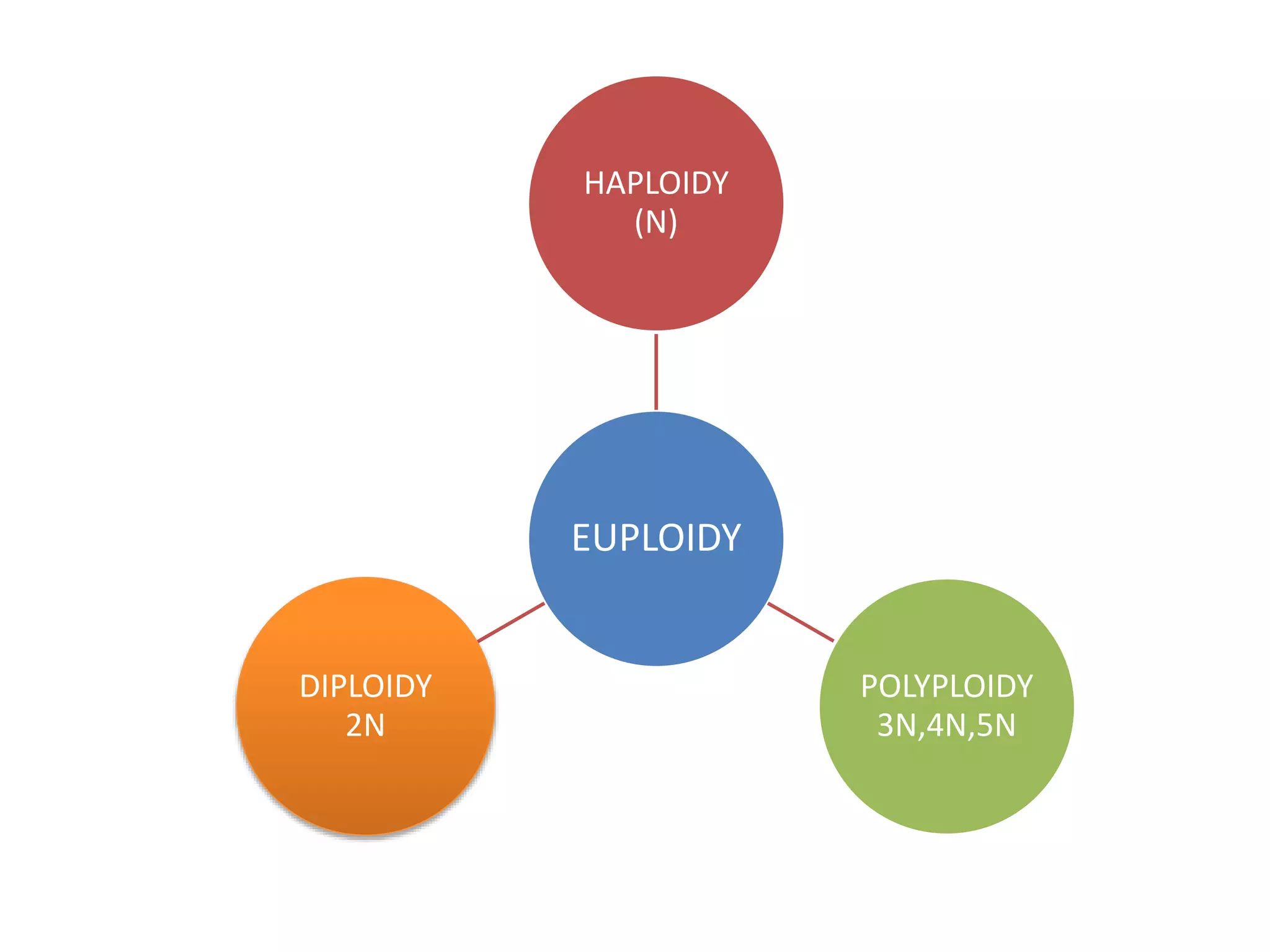
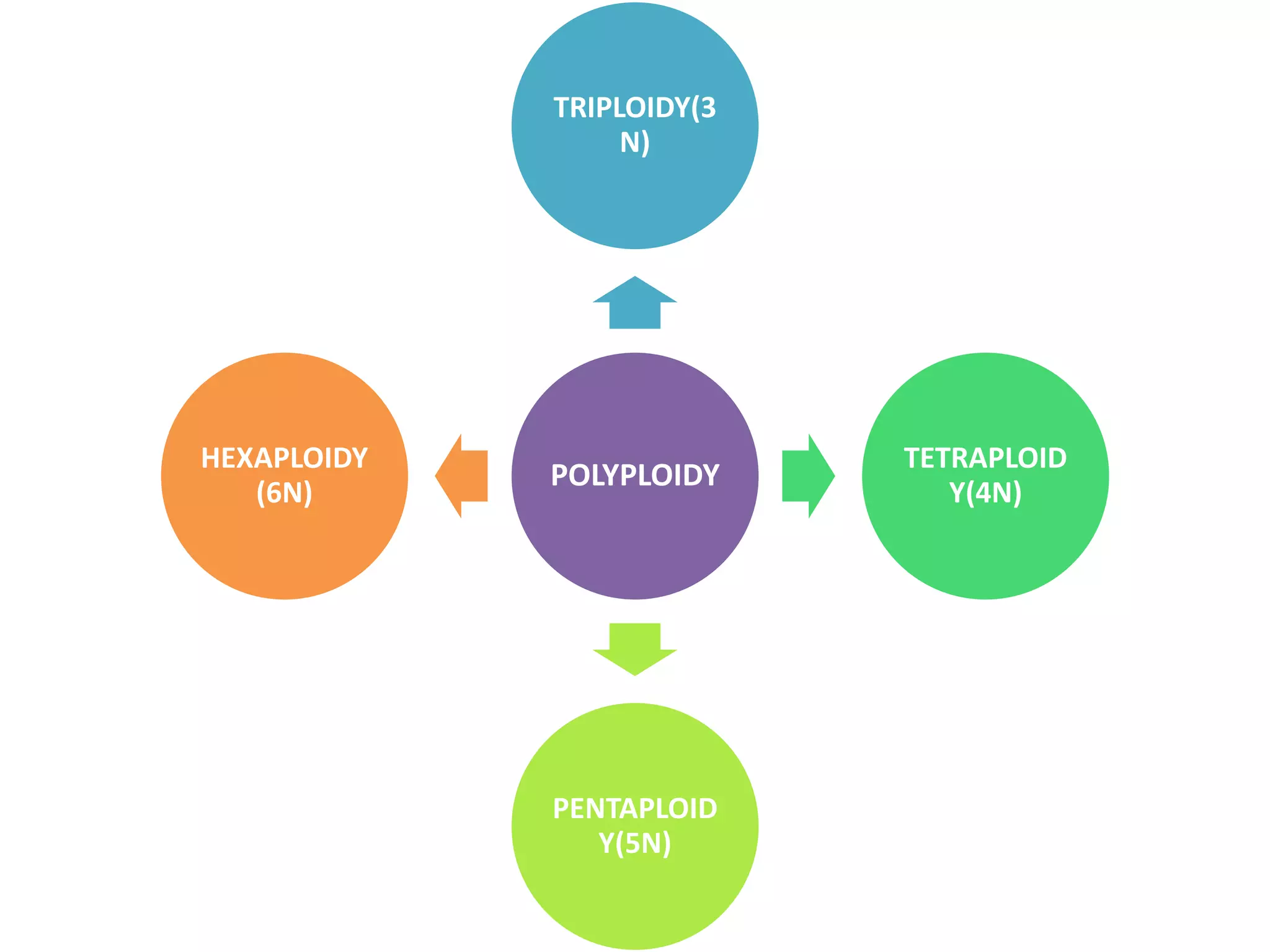
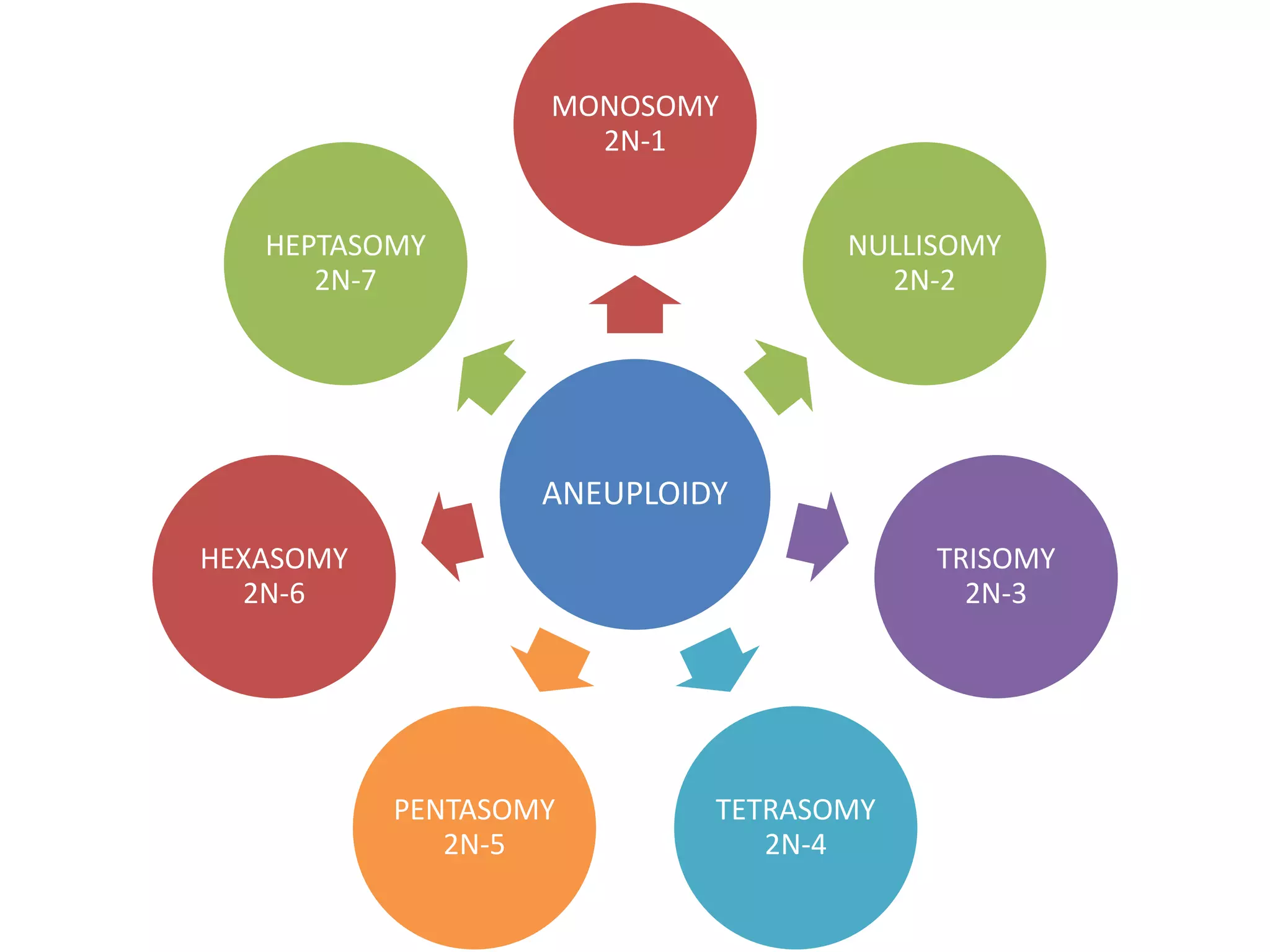
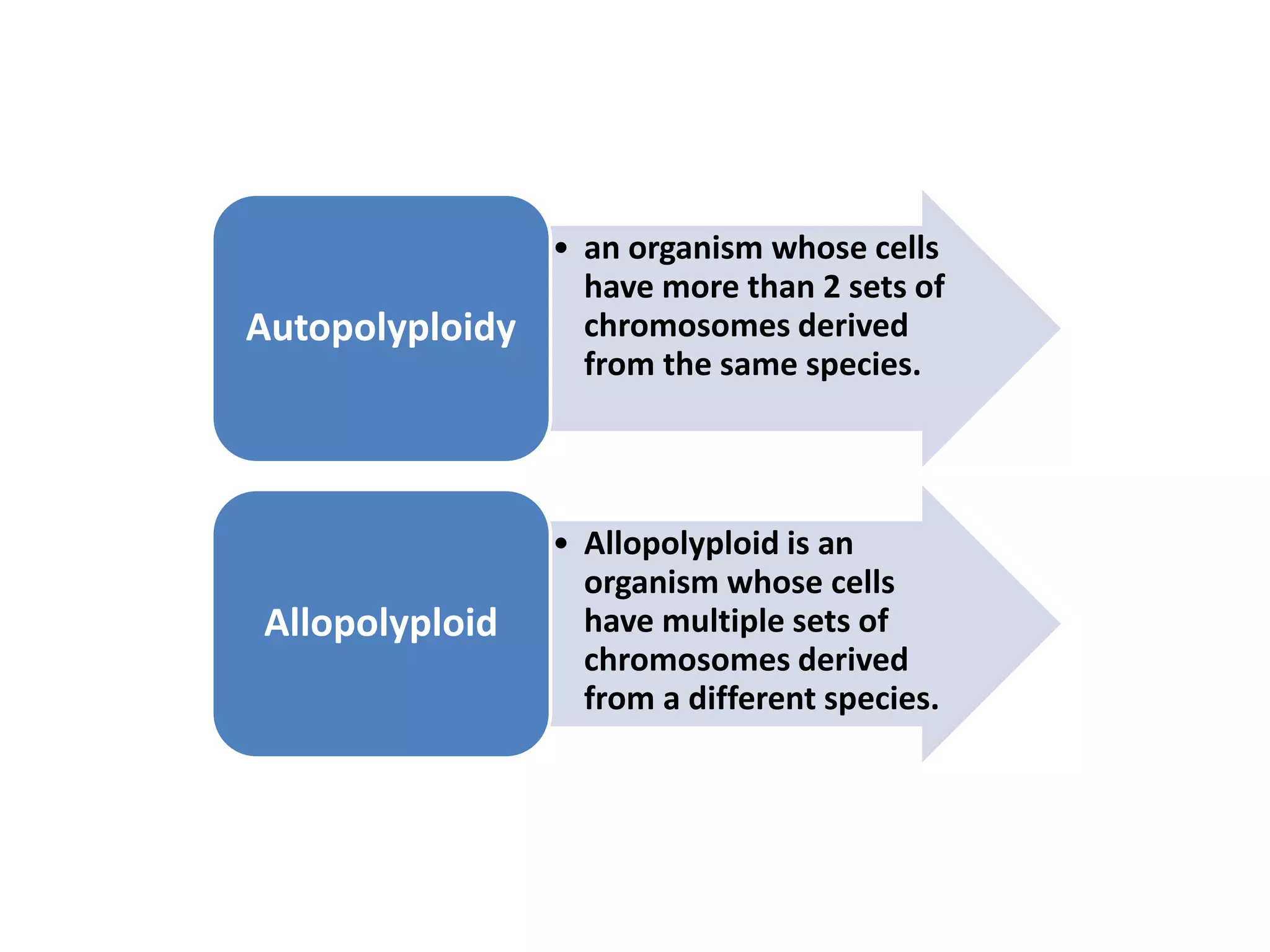
The document discusses various types of chromosomal aberrations including structural changes like deletions, duplications, translocations, and inversions. It also discusses numerical changes in chromosomes such as euploidy, aneuploidy, polyploidy, and aneuploidy. Specifically, it defines deletion as the removal of a segment of a chromosome, duplication as the addition of a segment to a chromosome in tandem or displaced positions. It also defines translocation as the transfer of a chromosome segment to another non-homologous chromosome, and inversion as the reversal of the orientation of a segment within the chromosome.