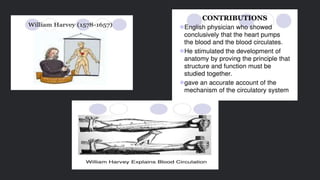
This document provides an overview of biology and the key features of life. It discusses biology as the study of living organisms, including their history, organization at the cellular level, metabolism, homeostasis, growth, reproduction, evolution, and response to stimuli. The key features that define life are highly organized structures, intricate chemical reactions that drive metabolism, maintenance of internal conditions, regulated growth, ability to reproduce, potential for evolution over time in response to environmental pressures, and irritability or response to changes in the environment.