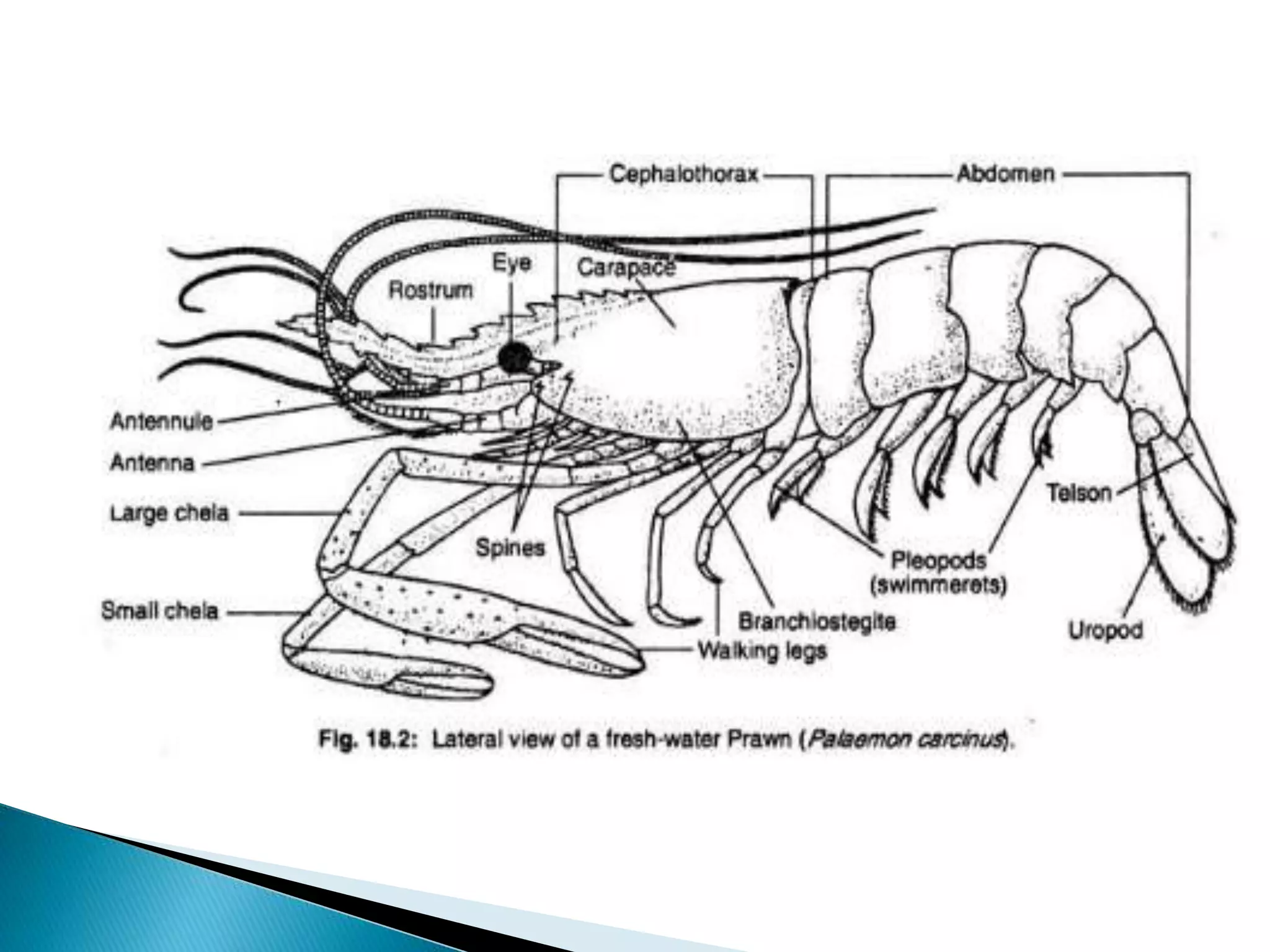
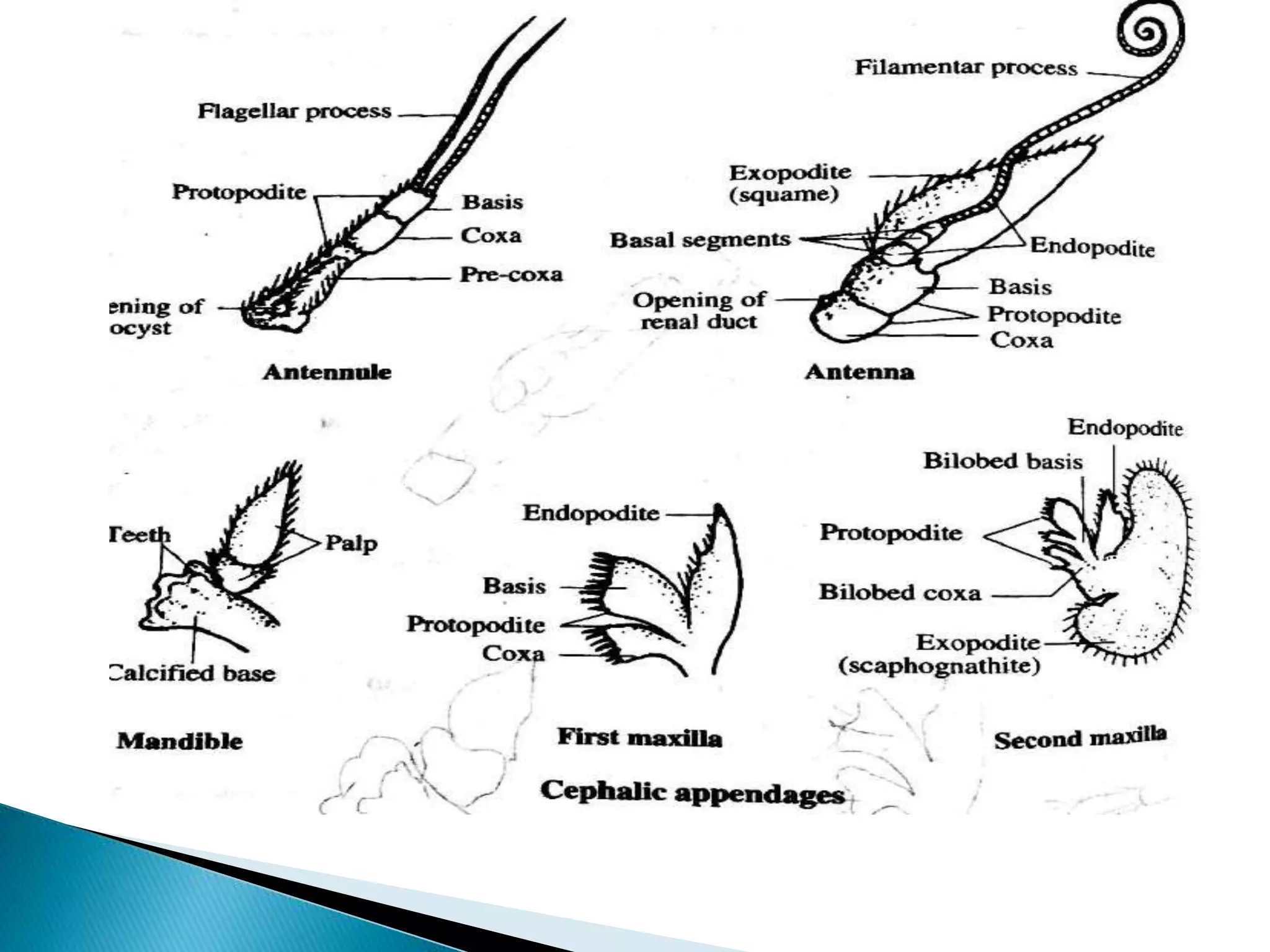
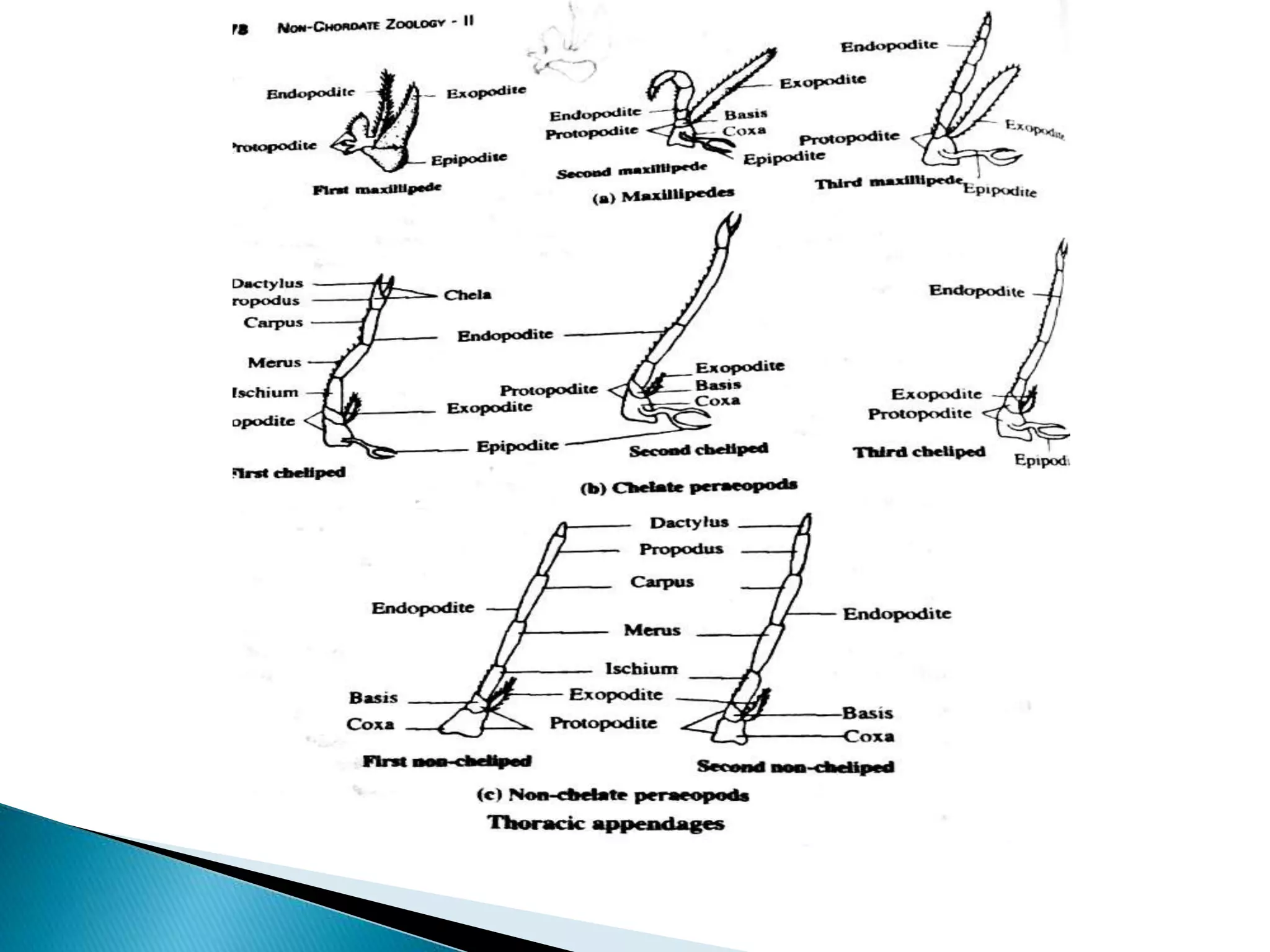
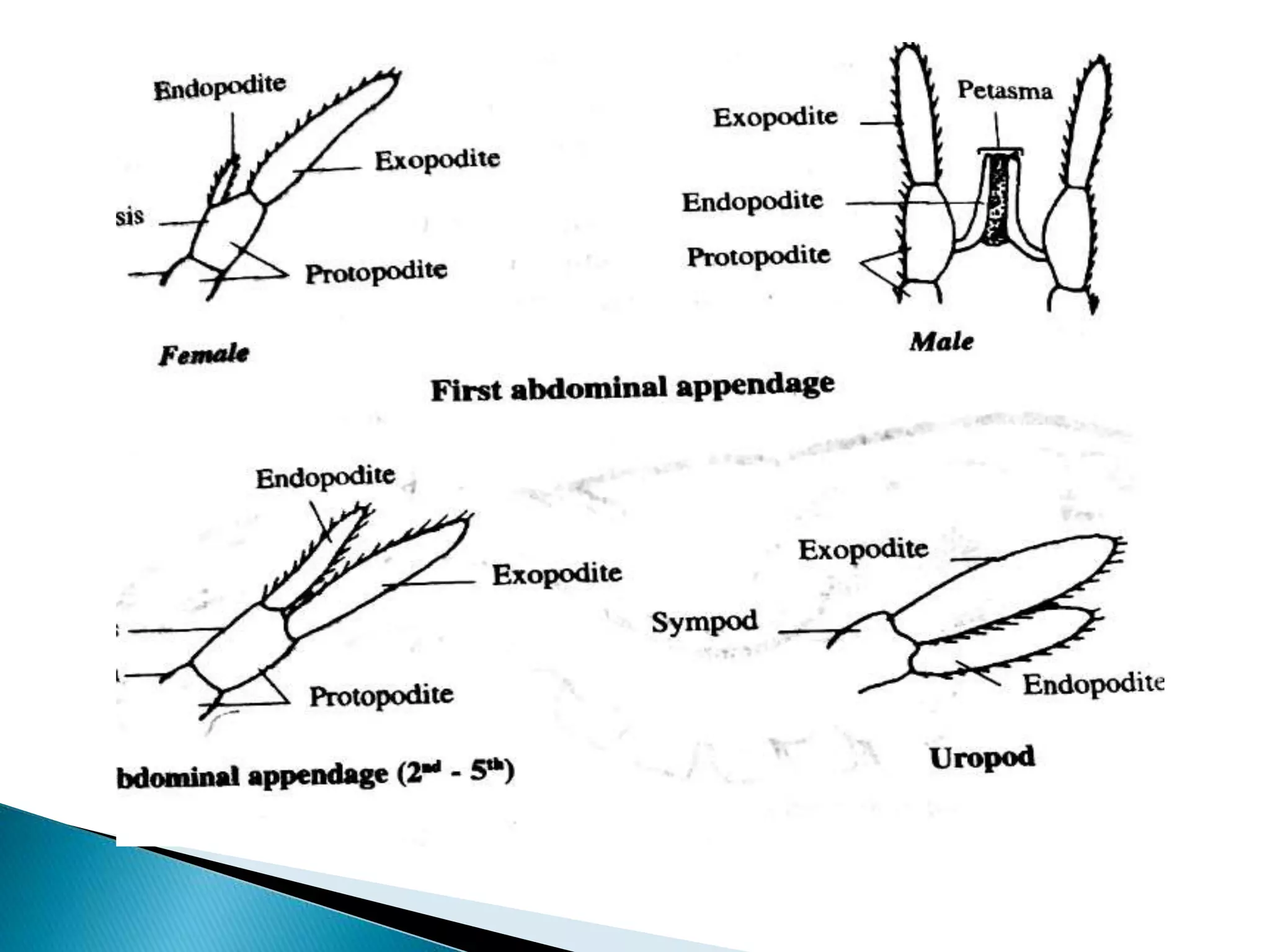
Penaeus indicus is a marine prawn found in tropical and temperate seas. Its segmented body consists of two main regions - the cephalothorax, formed from the fusion of thirteen segments including five cephalic and eight thoracic, and the abdomen. The prawn's elongated body tapers slightly at the rear and is covered by a segmented exoskeleton made of chitin and protein. This exoskeleton protects the internal organs, provides attachment points for muscles, and includes infoldings called apodemes that further strengthen and support the body. The prawn has nineteen pairs of appendages including five pairs of cephalic, eight pairs of thoracic, and six