This document provides an overview of political, social, and economic developments in post-Classical Western Europe from 1000-1450 CE. Key points include:
1. Politics were decentralized, with the Holy Roman Empire in decline and independent states like France and England emerging. England was unified under the Norman conquest in 1066.
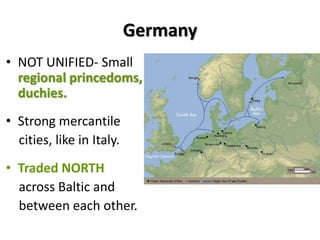
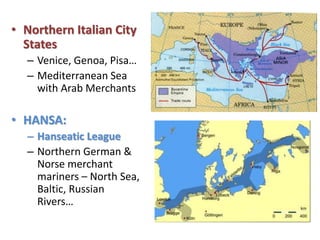
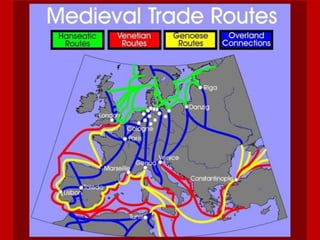
2. A new merchant class, or bourgeoisie, developed in growing cities and towns, challenging the traditional feudal hierarchy. Guilds and increased trade connected regions across Europe.
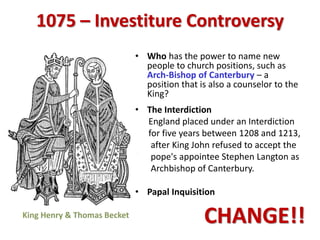
3. The Catholic Church remained powerful but faced challenges to its authority from secular rulers over issues like appointments and taxation. Events like the Magna Carta curbed royal power in England.