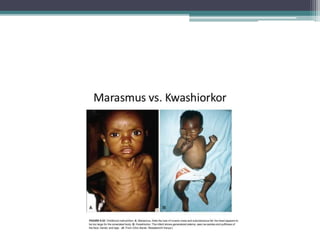
The document discusses several main health problems faced by children, including low birth weight, malnutrition, infections and parasites, accidents and poisoning, and behavioral issues. Low birth weight babies are those under 2.5 kg and can be either premature or small-for-date due to stunted growth. They are at higher risk of mortality, infections, and malnutrition. Malnutrition in children can be protein-energy based or micronutrient based and leaves them more susceptible to infection and slower growth. Common infections faced by children include diarrhea, respiratory illnesses, measles, polio, and tuberculosis. Accidents such as burns, trauma, traffic incidents, falls and drowning are also a health issue. Behavioral problems can be difficult to identify