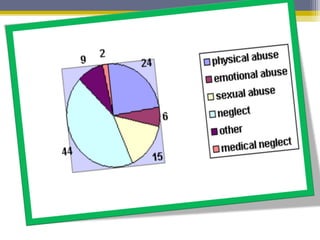
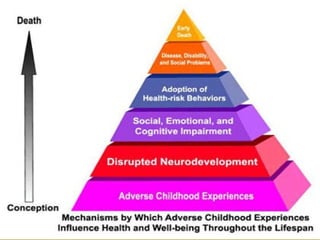
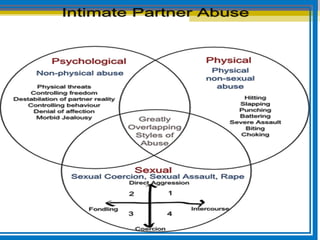
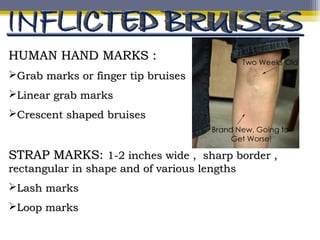
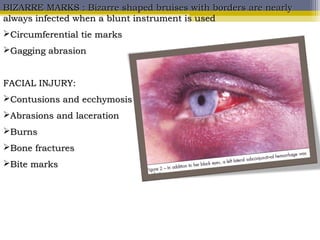
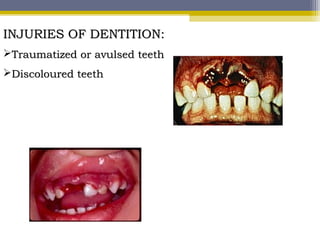
The document provides an overview of child abuse, defining it as non-accidental physical injury inflicted by caretakers and detailing various types including emotional and physical neglect. It highlights the prevalence of child abuse across different demographics, particularly in single-parent households and remote areas, and discusses the long-term effects on victims, including psychiatric problems and health issues. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of proper documentation, examination, and reporting by healthcare professionals, along with relevant laws in India and the role of various organizations in addressing these issues.