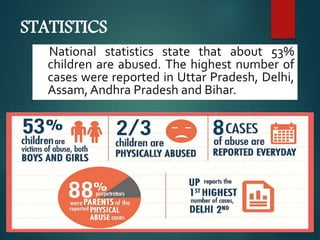
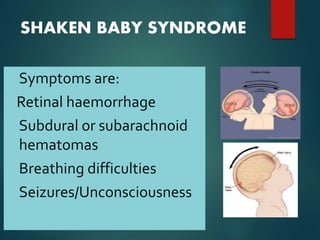
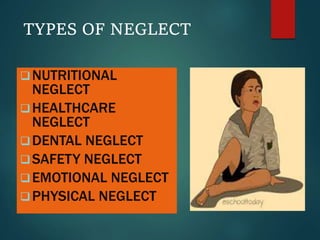
This document discusses child abuse and neglect. It defines the different types according to WHO and US law, including physical abuse, sexual abuse, emotional abuse, and neglect. It describes common signs of abuse seen in dental examinations such as fractures, injuries to the mouth. It outlines the various forms of neglect including nutritional, healthcare, dental, safety, emotional and physical neglect. The document emphasizes the importance of dental professionals screening children for signs of abuse and neglect.