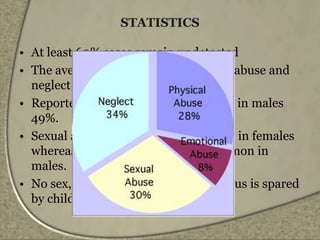
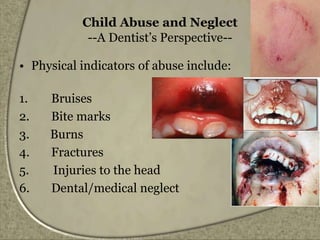
The document presents an overview of child abuse and neglect, covering definitions, types, statistics, and factors contributing to it, with a focus on the situation in India. It highlights various forms of abuse including physical, sexual, emotional, and neglect, and discusses the roles of healthcare professionals in identifying and managing these cases. Additionally, it addresses the lack of comprehensive legal protection for children in India and presents recent cases that underline the urgent need for action against child abuse.