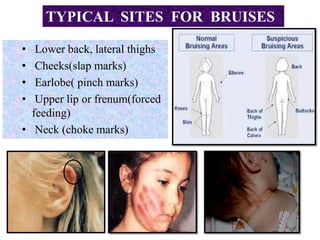
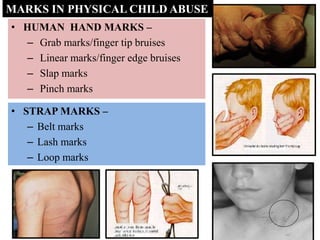
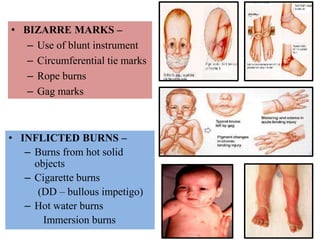
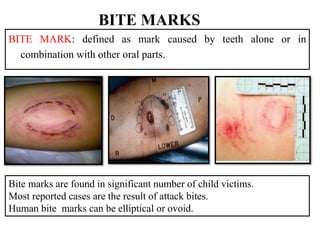
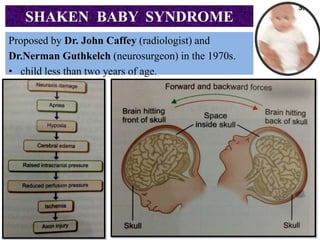
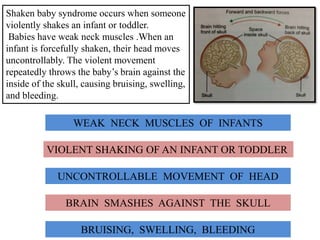
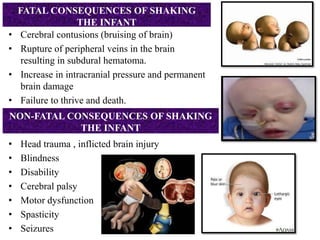
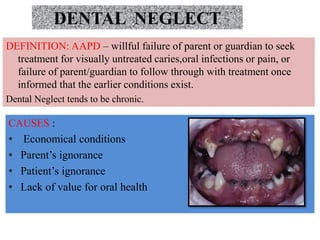
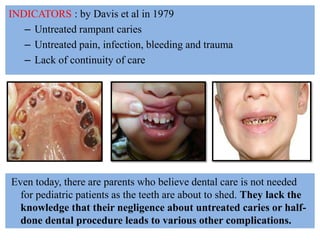
This document discusses various types of child abuse and neglect, including physical abuse, emotional abuse, sexual abuse, neglect, dental neglect, shaken baby syndrome, and Munchausen syndrome by proxy. It provides details on the typical signs and symptoms of each type of abuse. For physical abuse, it describes common injury sites for bruises and other marks, like grab marks, slap marks, and burns. It also discusses how to diagnose physical abuse based on the history provided, witness accounts, implausible stories, and delays in medical care.