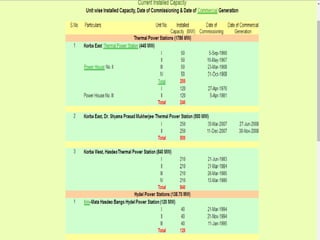
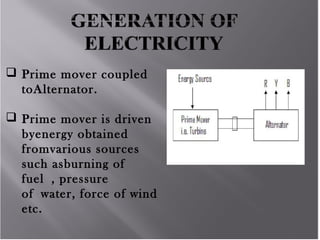
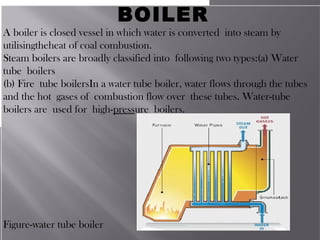
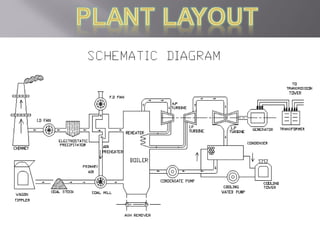
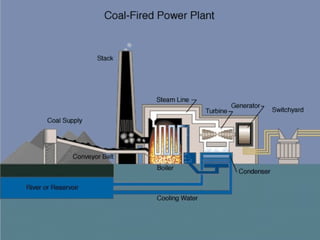
The Chhattisgarh State was formed in November 2000 according to the Madhya Pradesh Reorganization Act 2000. The Chhattisgarh State Electricity Board was then formed and started functioning on December 1, 2000. In 2008, the Chhattisgarh State Electricity Board was reorganized into 5 companies according to the Electricity Act 2003: the Chhattisgarh State Power Holding Company Limited, the Chhattisgarh State Power Generation Company Limited, the Chhattisgarh State Power Transmission Company Limited, the Chhattisgarh State Power Distribution Company Limited, and the Chhattisgarh State Power Trading Company Limited.