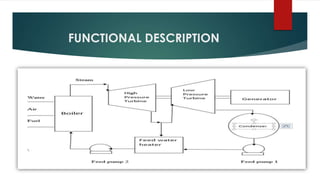
Thermal power plants generate electricity by burning coal to produce steam that drives turbines connected to generators. The document describes the key components and processes in a thermal power plant, including:
1) Coal is pulverized and blown into boilers to produce high-pressure steam.
2) The steam powers turbines which spin generators to produce electricity.
3) After passing through the turbines, the steam is condensed in condensers and recycled to the boilers using feed pumps.
4) The plant uses various components like economizers, superheaters, condensers, and cooling towers to improve efficiency of the steam cycle.