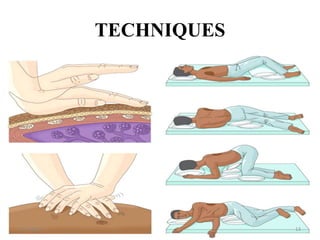
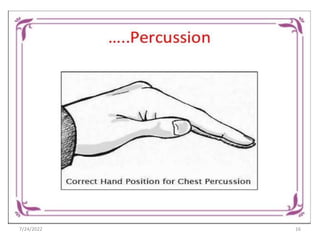
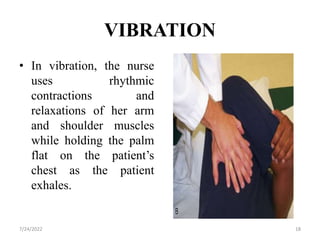
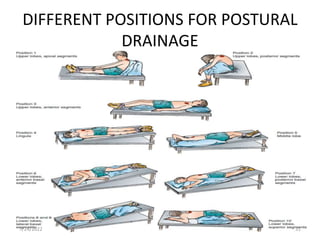
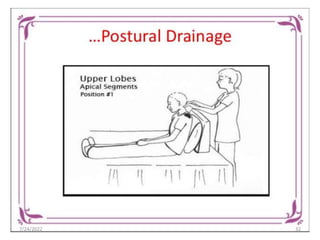
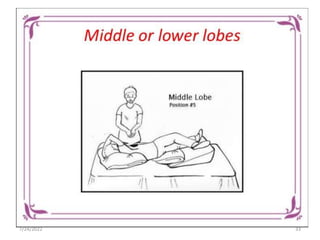
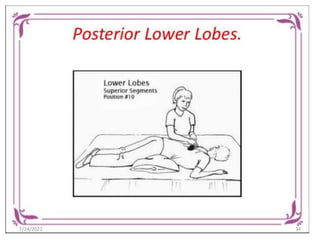
Chest physiotherapy (CPT) is a technique used to mobilize secretions in the lungs through methods like percussion, vibration, and postural drainage, particularly for patients with ineffective coughs or thick secretions. Indications for CPT include conditions like cystic fibrosis and pneumonia, while contraindications include increased intracranial pressure and unstable injuries. Nursing considerations emphasize patient assessment, the effectiveness of techniques, and the evaluation of patient tolerance and responses during therapy.