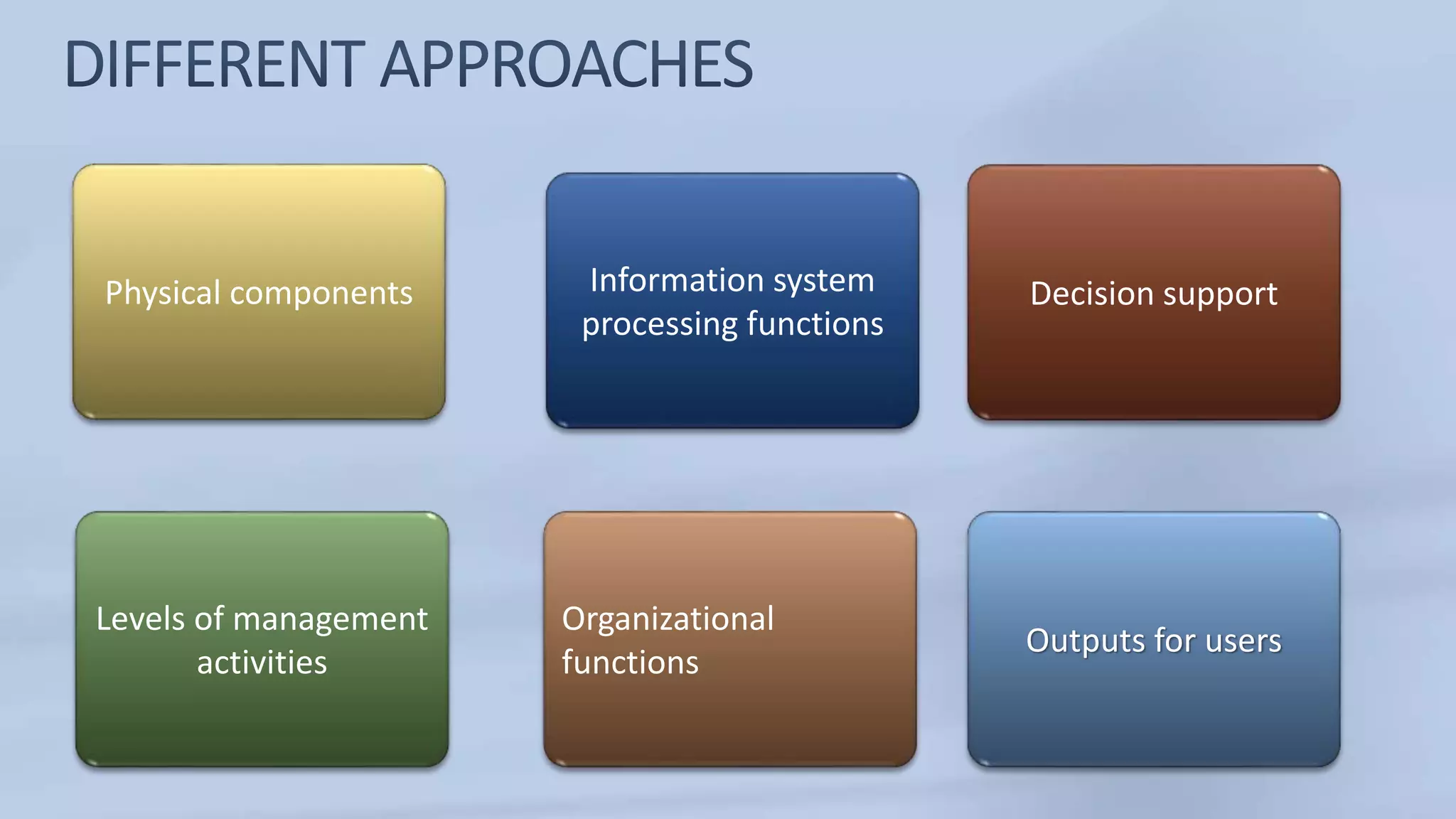
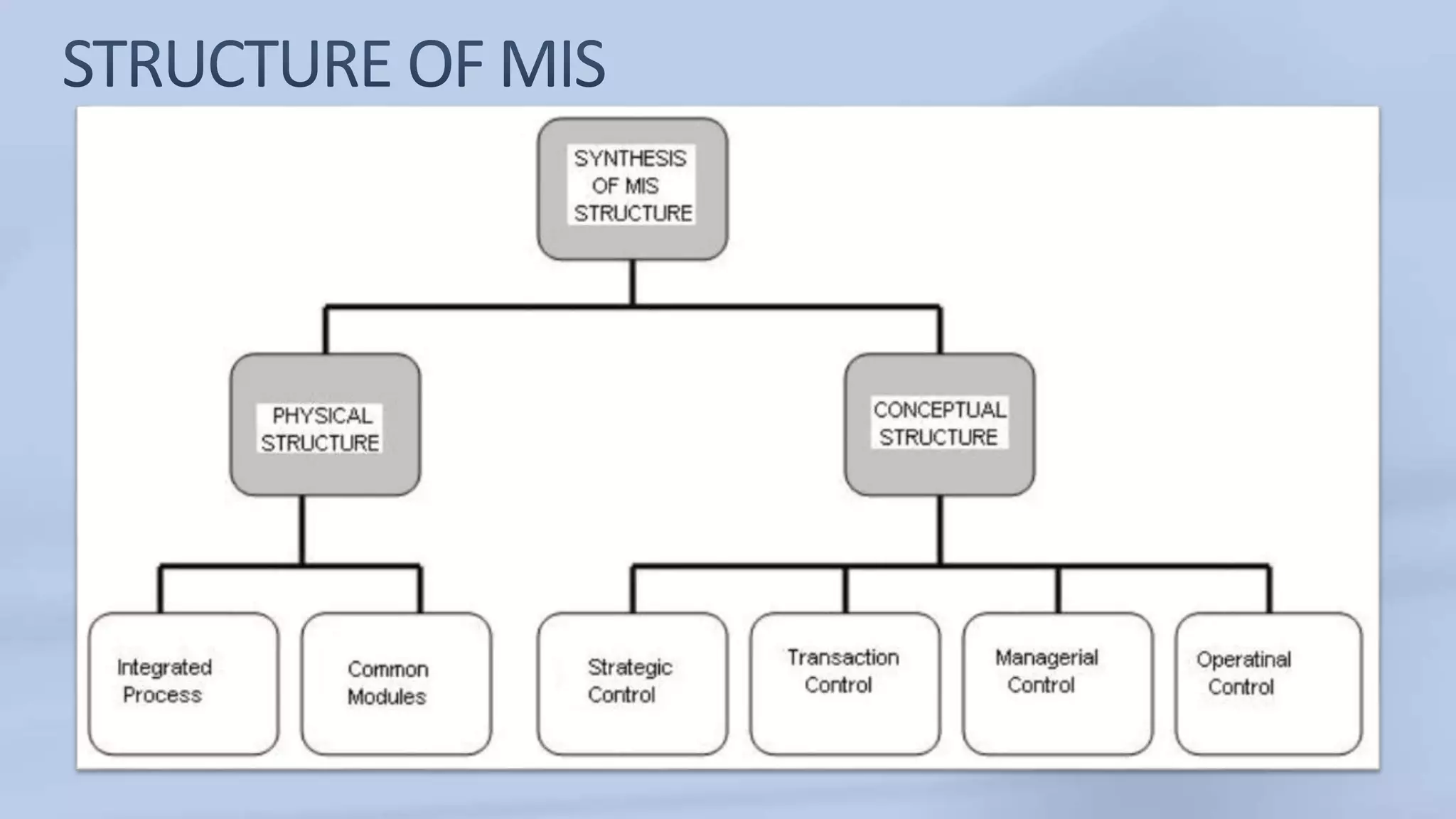
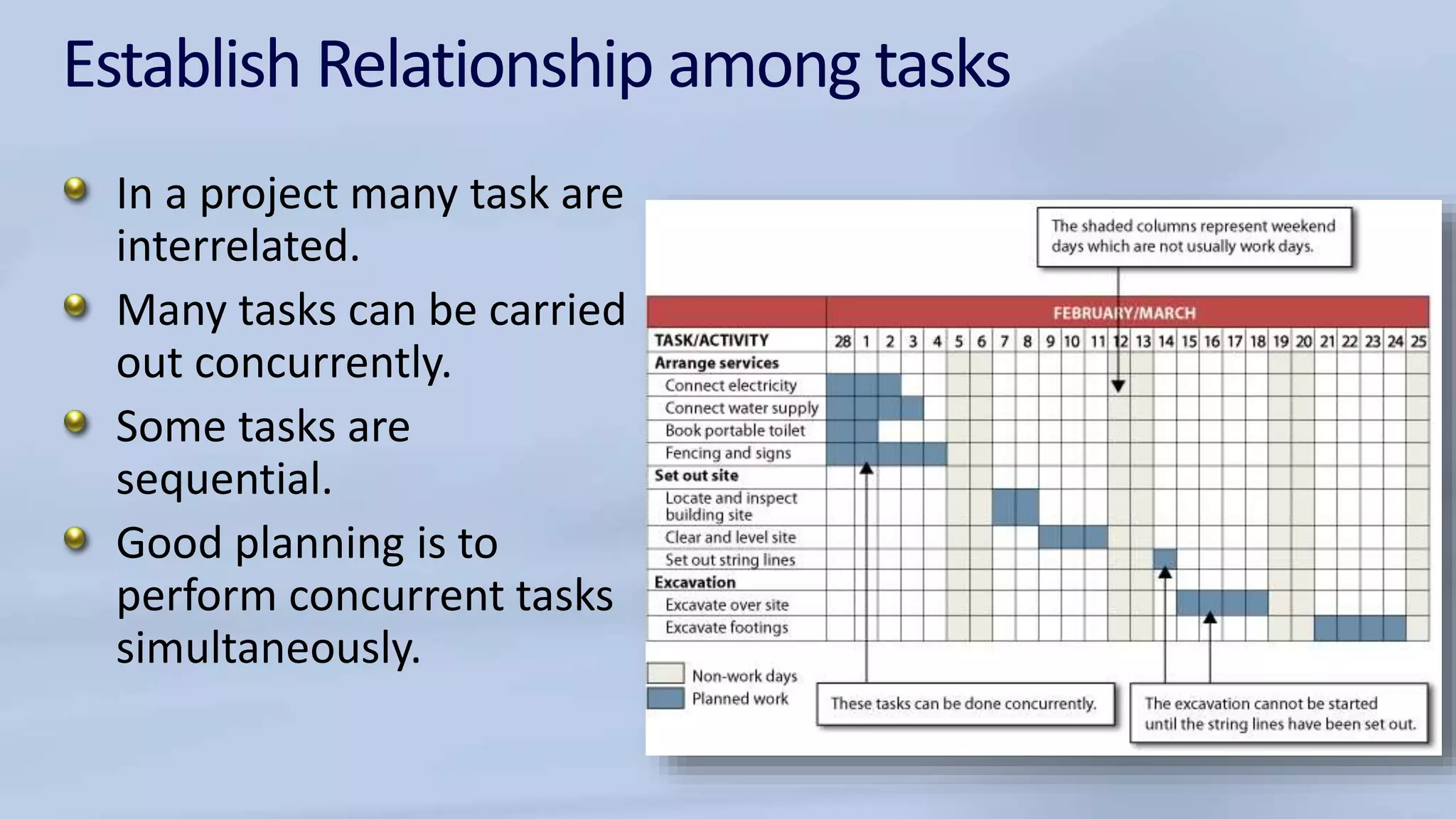
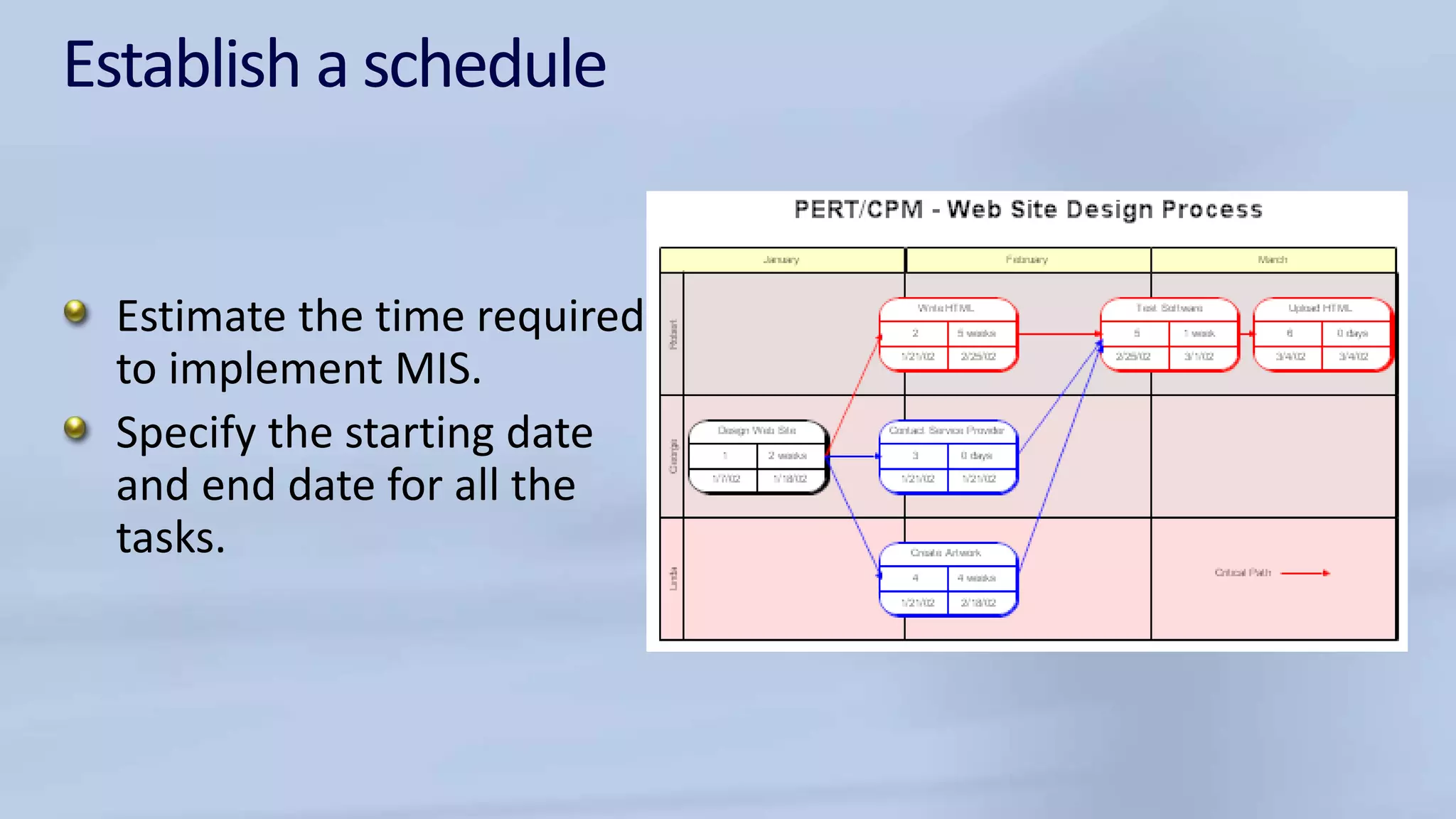
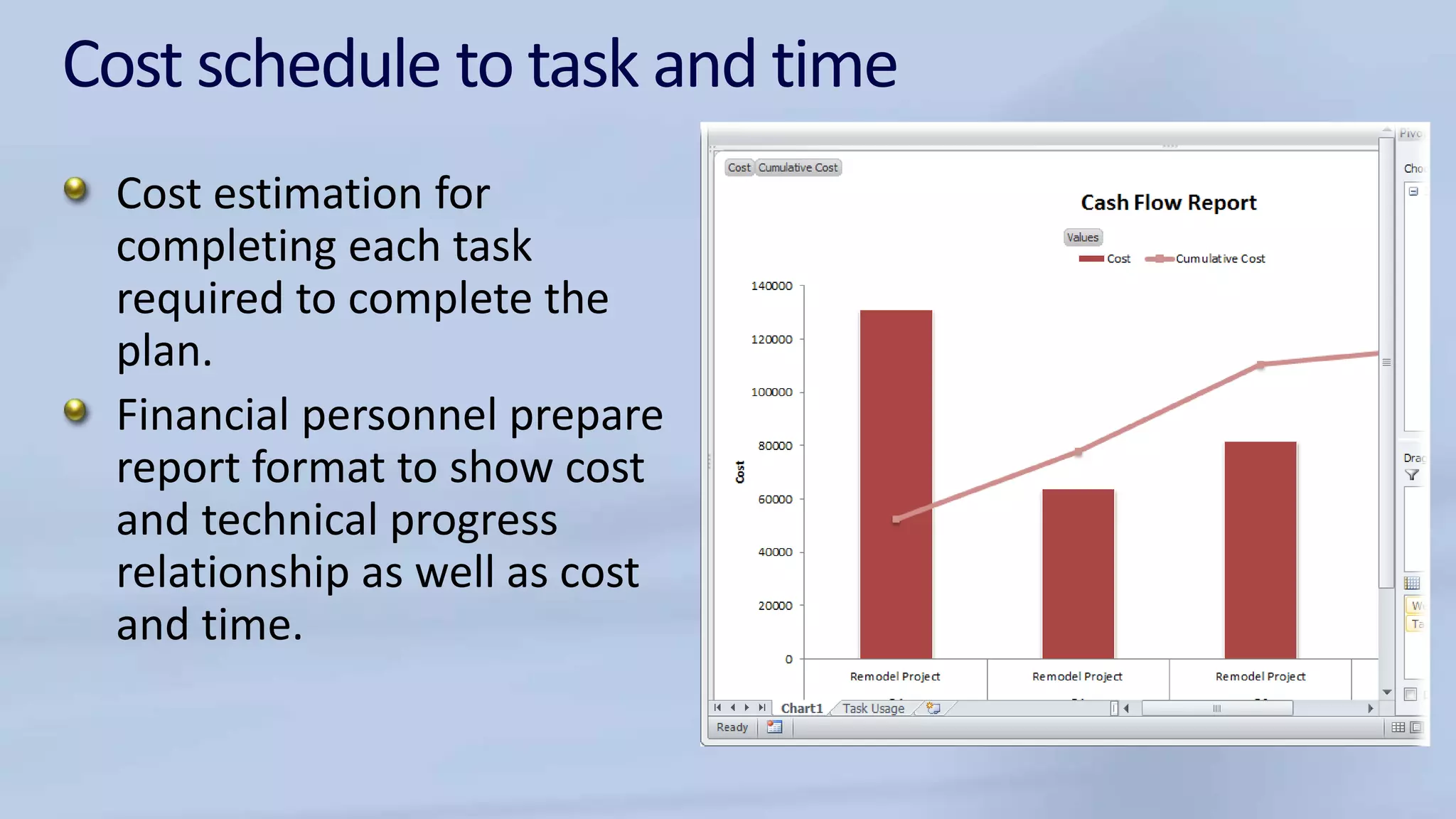
The document discusses the structure and components of a management information system (MIS). It can be described in various ways, such as by its physical components, processing functions, outputs for users, and organizational functions. An MIS typically includes hardware, software, databases, procedures, and operating personnel. It processes transactions, maintains master files, produces reports and inquiries, and provides decision support. The outputs of an MIS include documents, reports, and results from user-machine dialogs. Effective implementation of an MIS requires planning, organizing tasks and timelines, training users, and evaluating the system once completed.