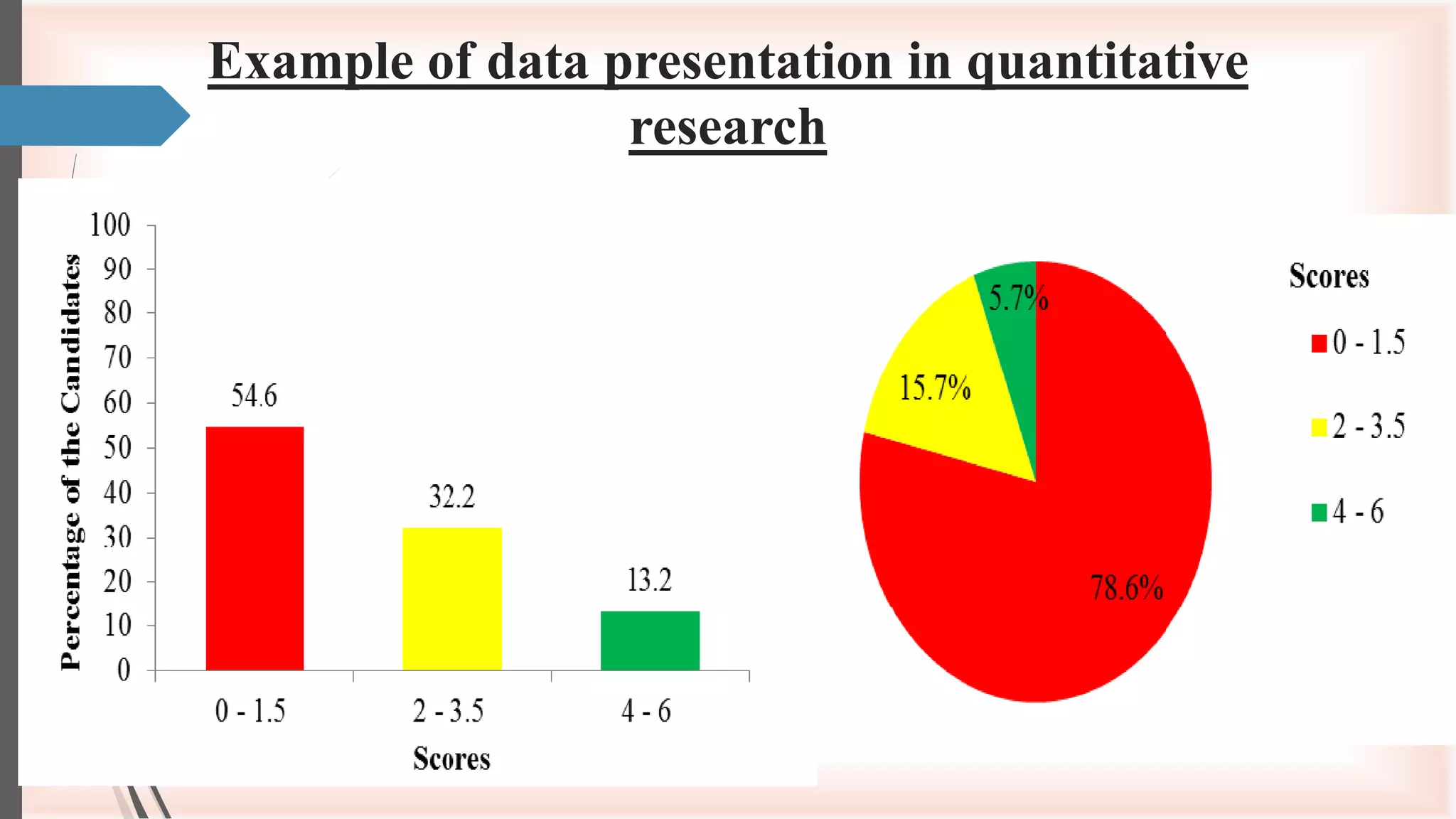
The document describes quantitative research and its key characteristics. It defines quantitative research as objective and systematic examination of numerical data to describe and explain phenomena. It then lists 5 key characteristics: 1) large sample sizes, 2) collection of numerical data, 3) structured data collection methods like questionnaires, 4) data analysis using statistical software to produce descriptive and inferential statistics, and 5) highly reliable and reusable outcomes typically presented using tables and graphs. Examples are provided for some of the characteristics.