Embed presentation
Downloaded 20 times
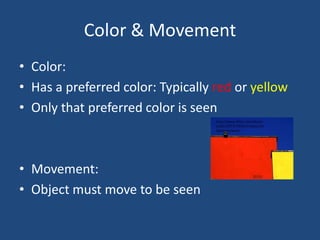




Cortical Visual Impairment (CVI) is caused by damage to the visual pathways between the eyes and brain, resulting in 10 common characteristics. These include preferring a single color like red or yellow, needing movement to see objects, delayed visual attention, gazing at lights, difficulty with complex visual scenes, focusing on limited areas, needing objects close by, lacking reflexes like blinking, only attending to familiar things, and separate looking and reaching without visual guidance.






