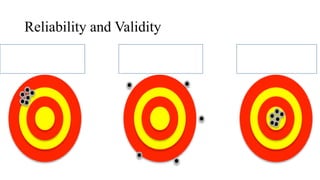
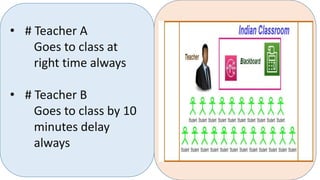
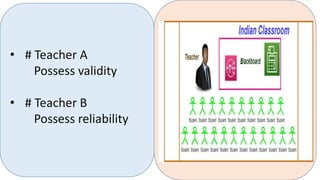
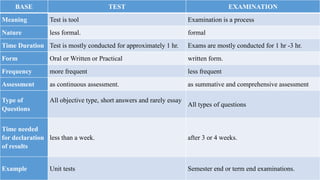
This document discusses the key characteristics of a good test: objectivity, reliability, validity, and usability. It defines each characteristic and provides examples from authors such as Gronlund and Linn (1995) and C.V. Good (1973). Objectivity refers to tests being free from personal bias. Reliability means tests produce consistent results. Validity is the degree to which a test measures what it is intended to measure. Usability considers ease of administration, duration, and interpretation. The document also compares tests and examinations, noting examinations are more formal, comprehensive assessments conducted less frequently than tests.







![References
• Henry E Garrett. (1961). Statistics in education and psychology.
Paragaon International Publisher.
• Marami Goswami. (2014). Measurement and evaluation in psychology and
education. Neelkamal Publication.
• Mathew, T.K., and Mollykutty, T.M. (2011). Science education -Theoretical bases of
teaching and pedagogic analysis - Physical Science and Natural Science.
Rainbow Book Publishers
• NCERT. (2013). Teaching of science. Delhi: Author
• Radha Mohan. (2007). Teaching of physical science. (3rd ed.). PHI Learning
• Rathinasabapathy, P. (2001). கல்வியில் தேர்வு [Examination in Education].
(2nd ed.). Shantha Publishers.
• Srinivasan, P. (2011). அறிவியல் கற்பிே்ேல் [Teaching of science]. DDE, Tamil
Univeristy
• Images from google](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/characteristicofgoodtest-210509071304/85/Characteristic-of-good-test-12-320.jpg)