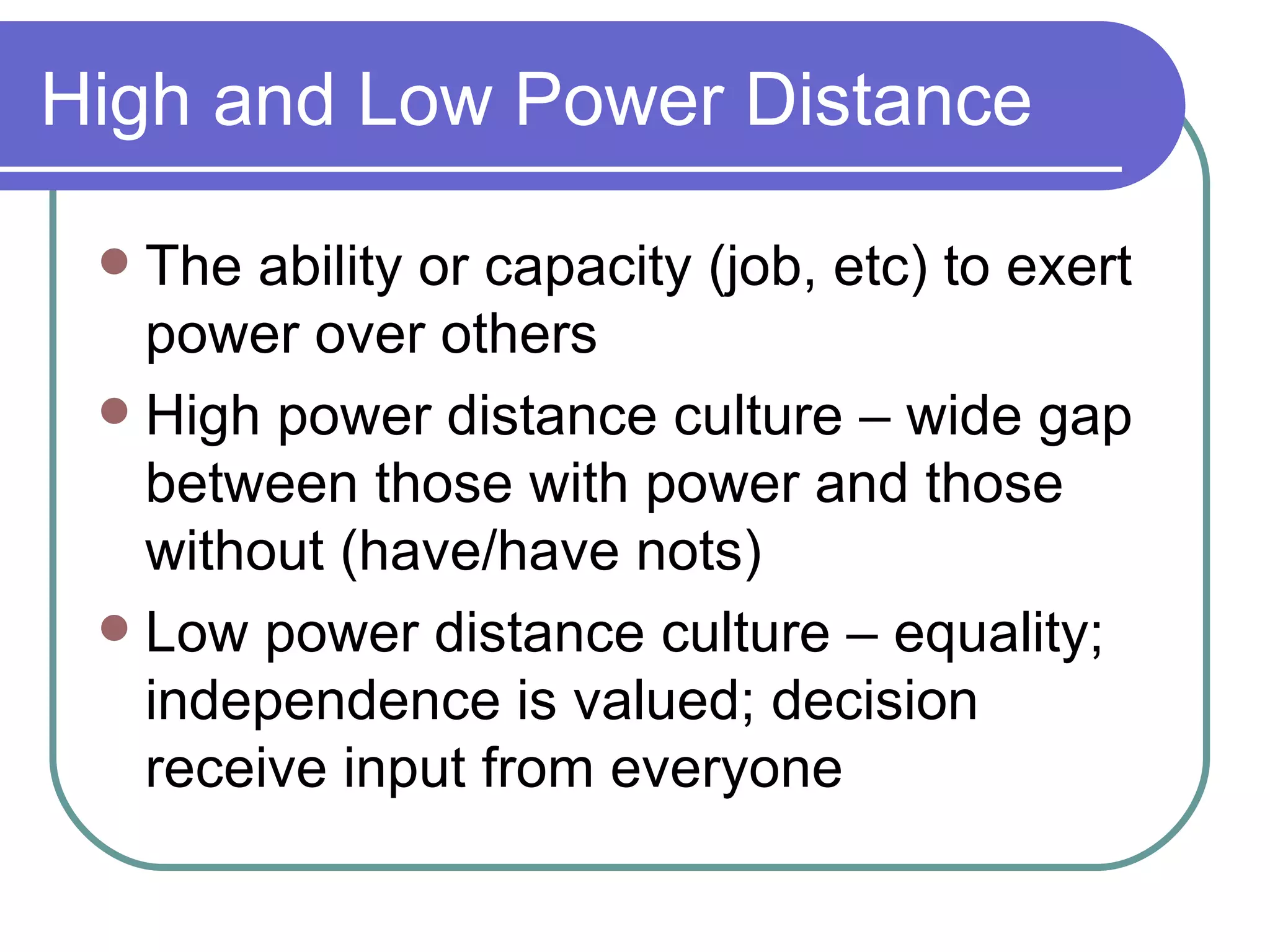
The document discusses cultural values and dimensions that impact behavior. It describes how values can differ in importance, direction, and intensity between individuals and cultures. Some dominant American values mentioned are individuality, freedom, equality, democracy, and achievement. It also outlines four dimensions identified by Hofstede as impacting culture: power distance, uncertainty avoidance, individualism vs collectivism, and masculinity vs femininity. High power distance cultures have a large gap between those with and without power while low power distance cultures value equality and independence.