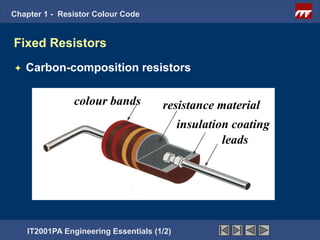
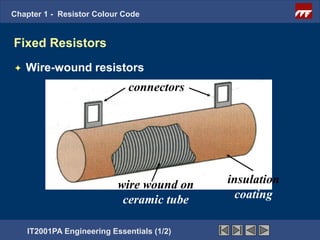
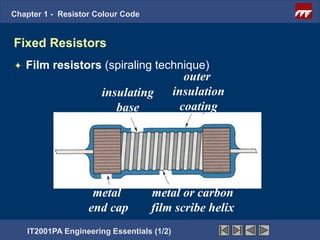
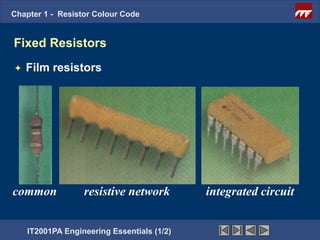
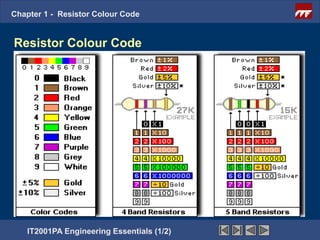
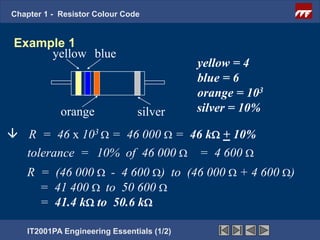
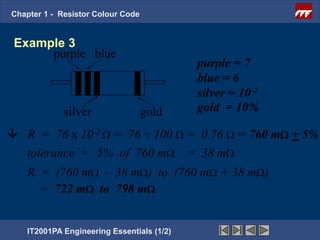
The document discusses the basics of resistor color codes and characteristics. It covers the objectives of interpreting resistor values and tolerances based on color bands, as well as computing resistances, identifying wattage ratings, and stating factors that affect resistance. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to determine resistance values and tolerances from given color codes. The different types of fixed and variable resistors are also described, along with their typical applications and power ratings.