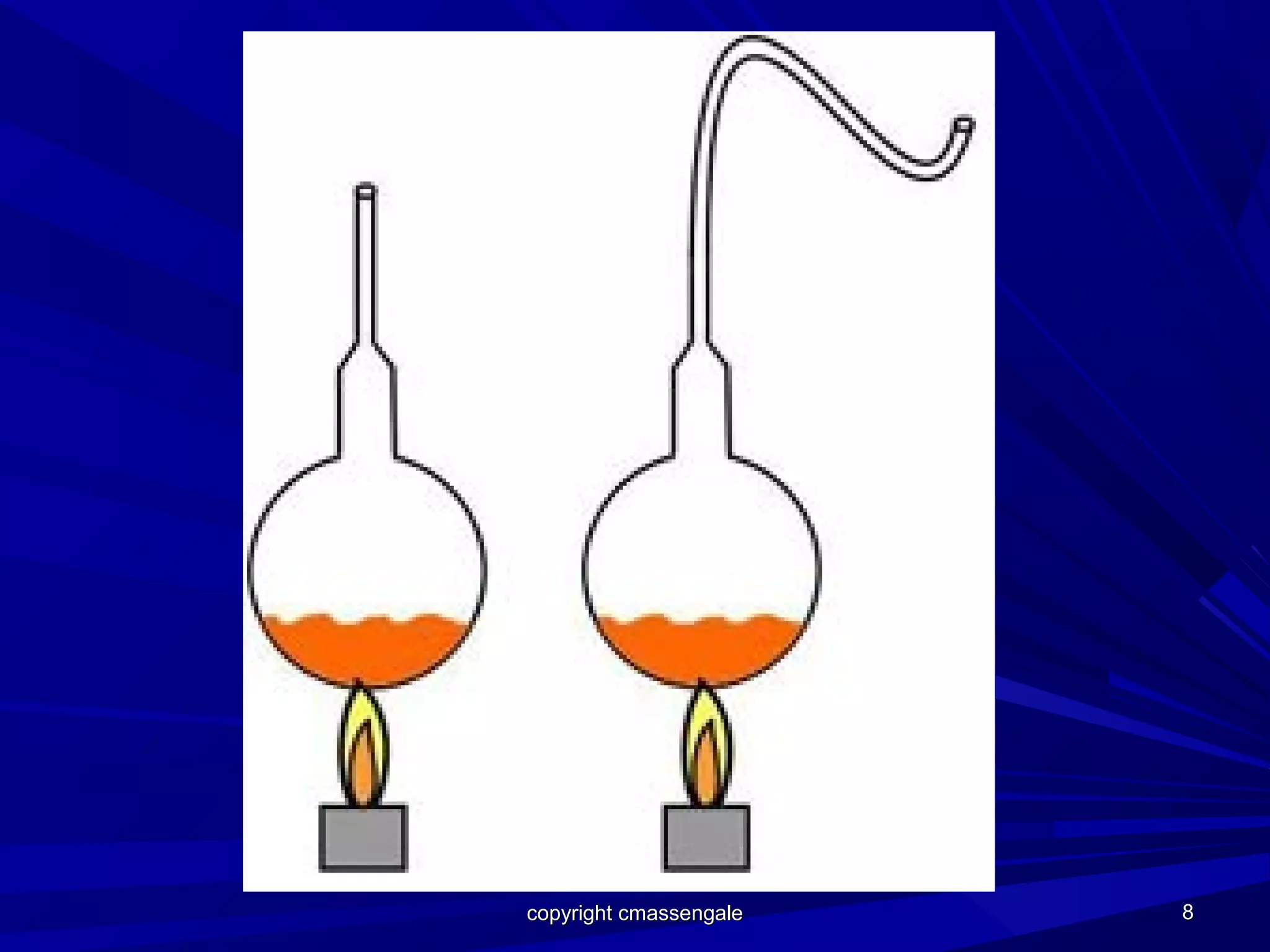
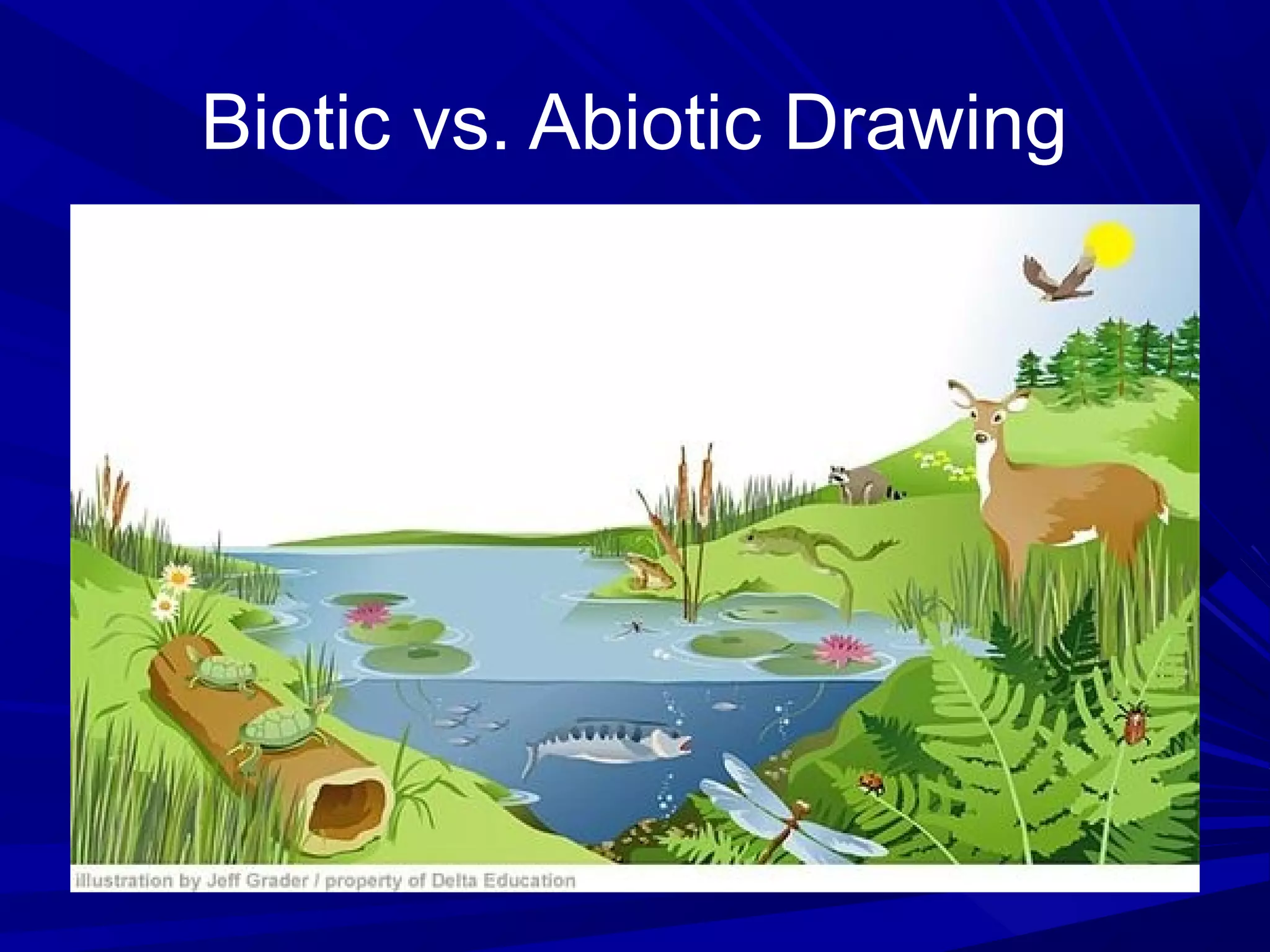
The document outlines the fundamentals of biology, defining it as the study of living organisms and introducing key concepts like biotic and abiotic factors. It delves into the scientific method, including steps like hypothesis formation and experiment conduction, while discussing historical experiments that debunked the theory of spontaneous generation. It emphasizes common characteristics of all living things, such as cellular organization, reproduction, and evolution.