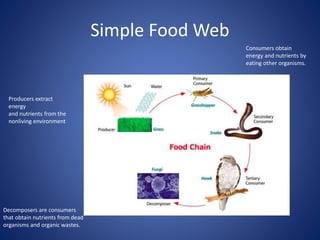
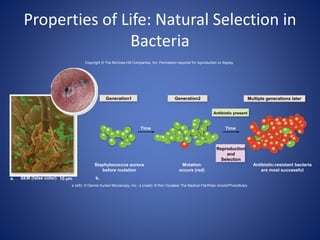
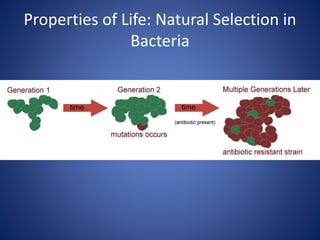
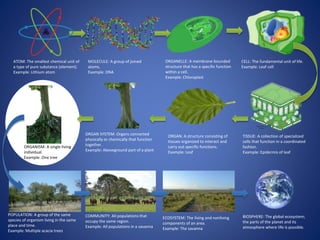
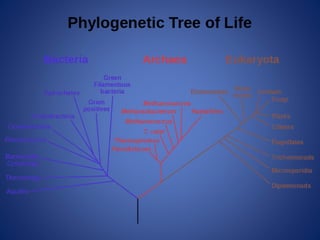
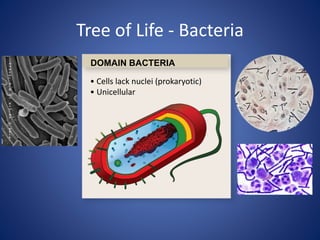
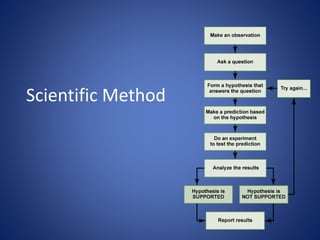
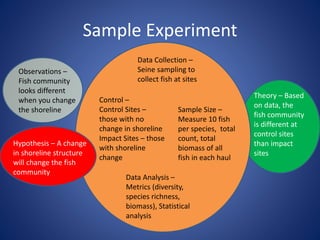
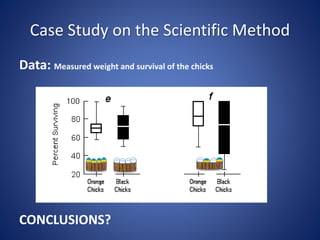
This document discusses the key concepts of life and biology. It defines life as being organized at the cellular level with DNA, and outlines the basic properties of life including order, reproduction, growth and development, energy use, response to the environment, regulation, and evolution. Each property is then discussed in more detail with examples provided. The document also covers the scientific method and how it is used to study life scientifically through hypotheses, experiments, analysis and conclusions.