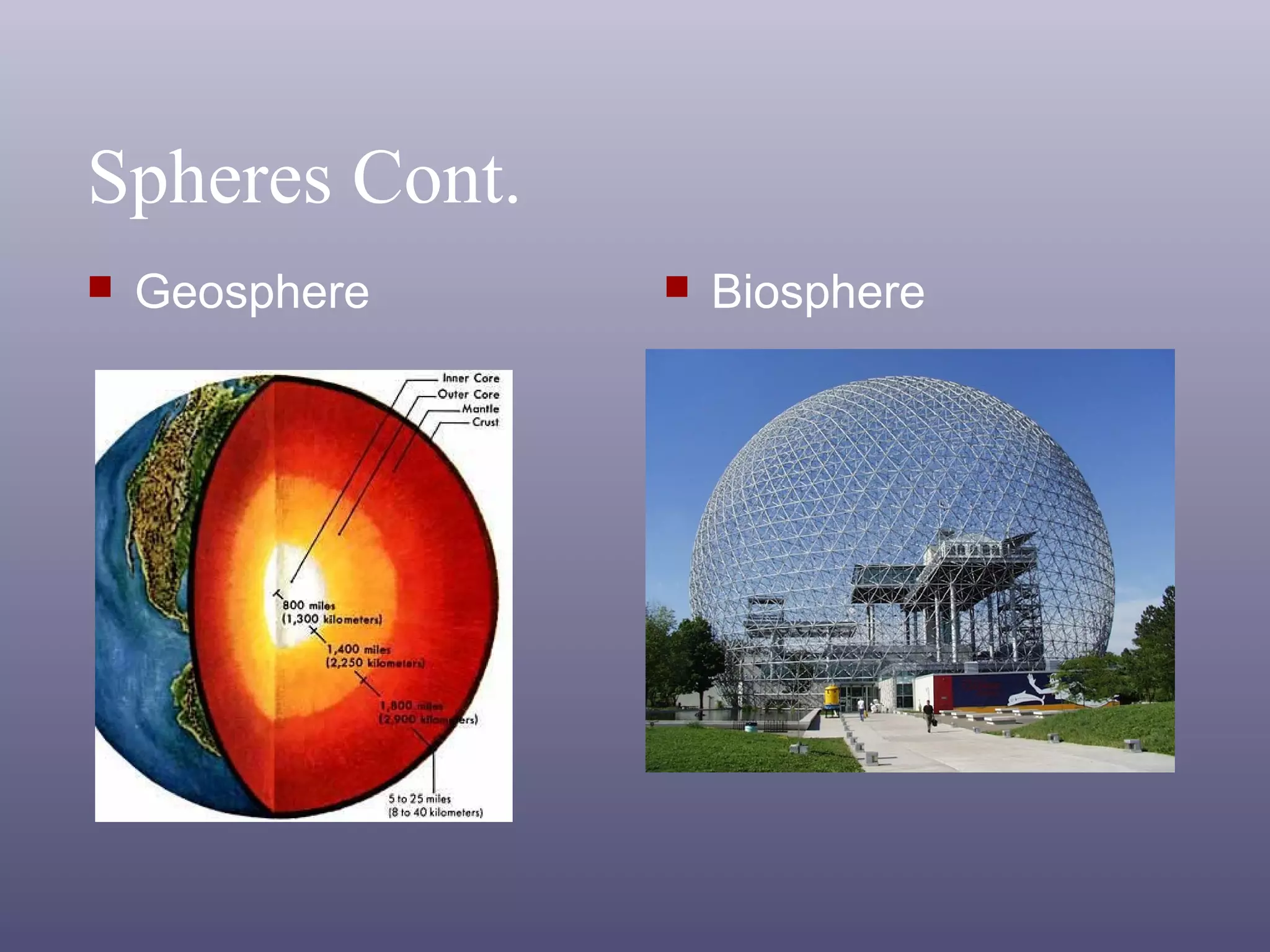
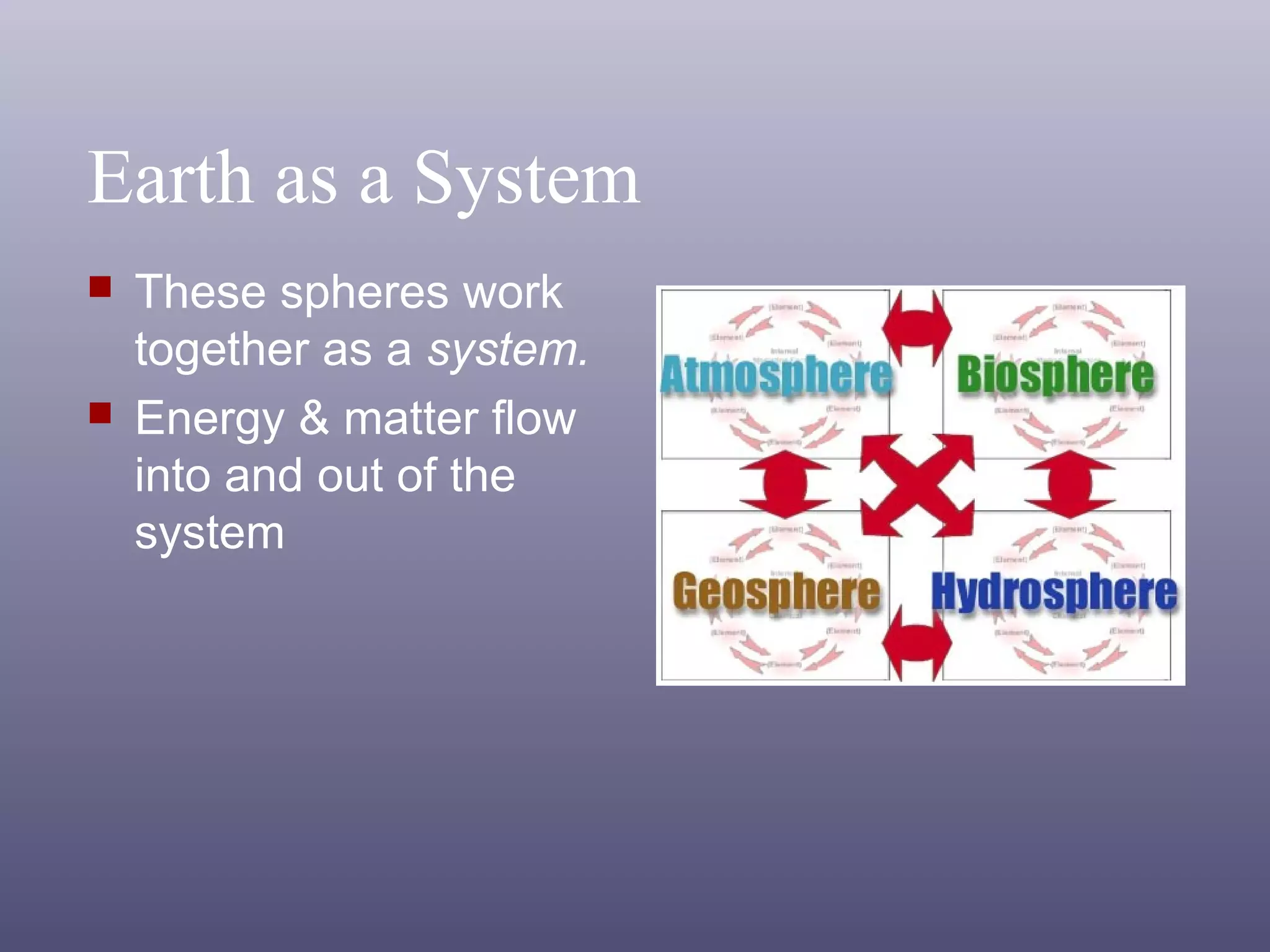
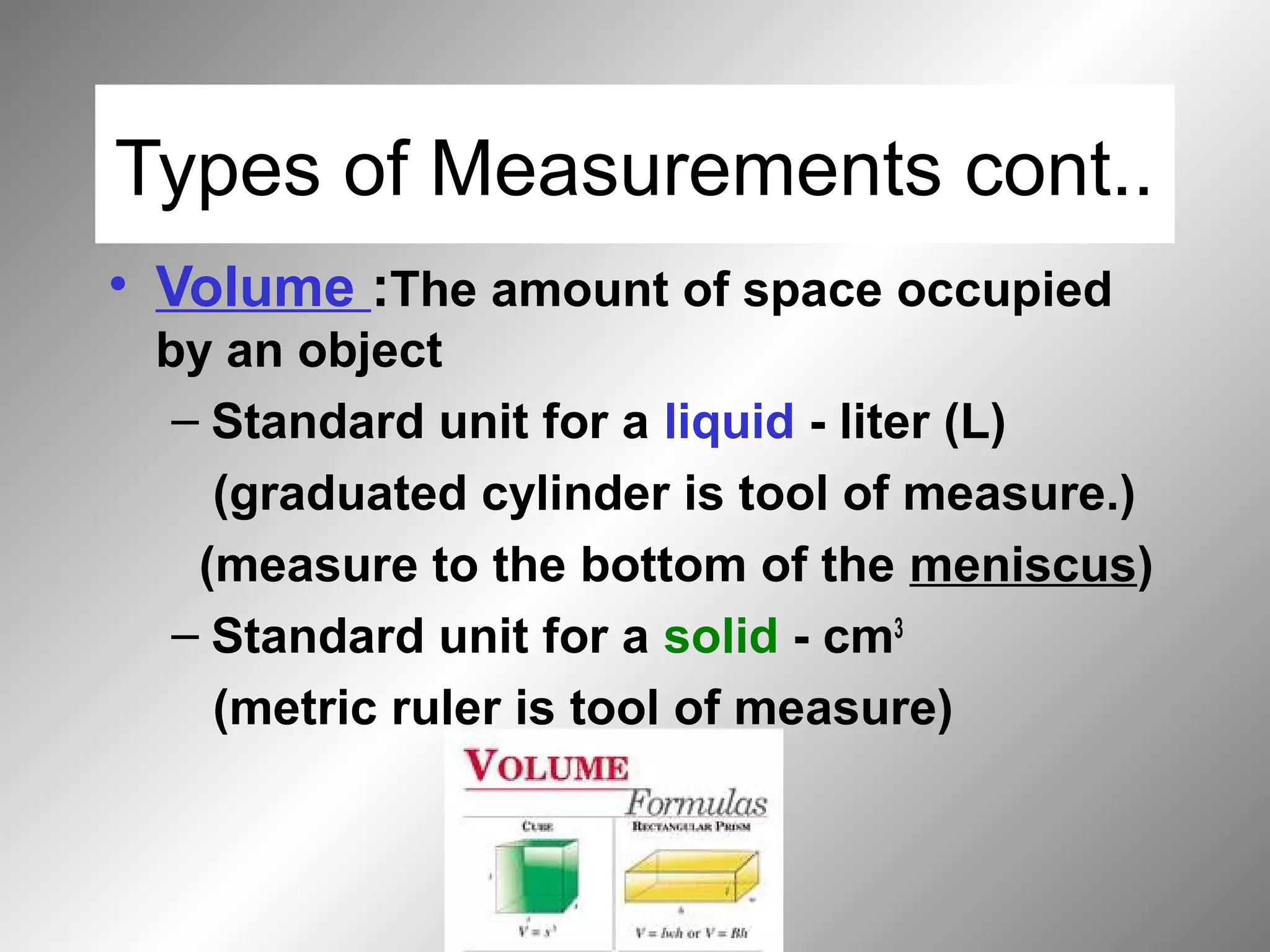
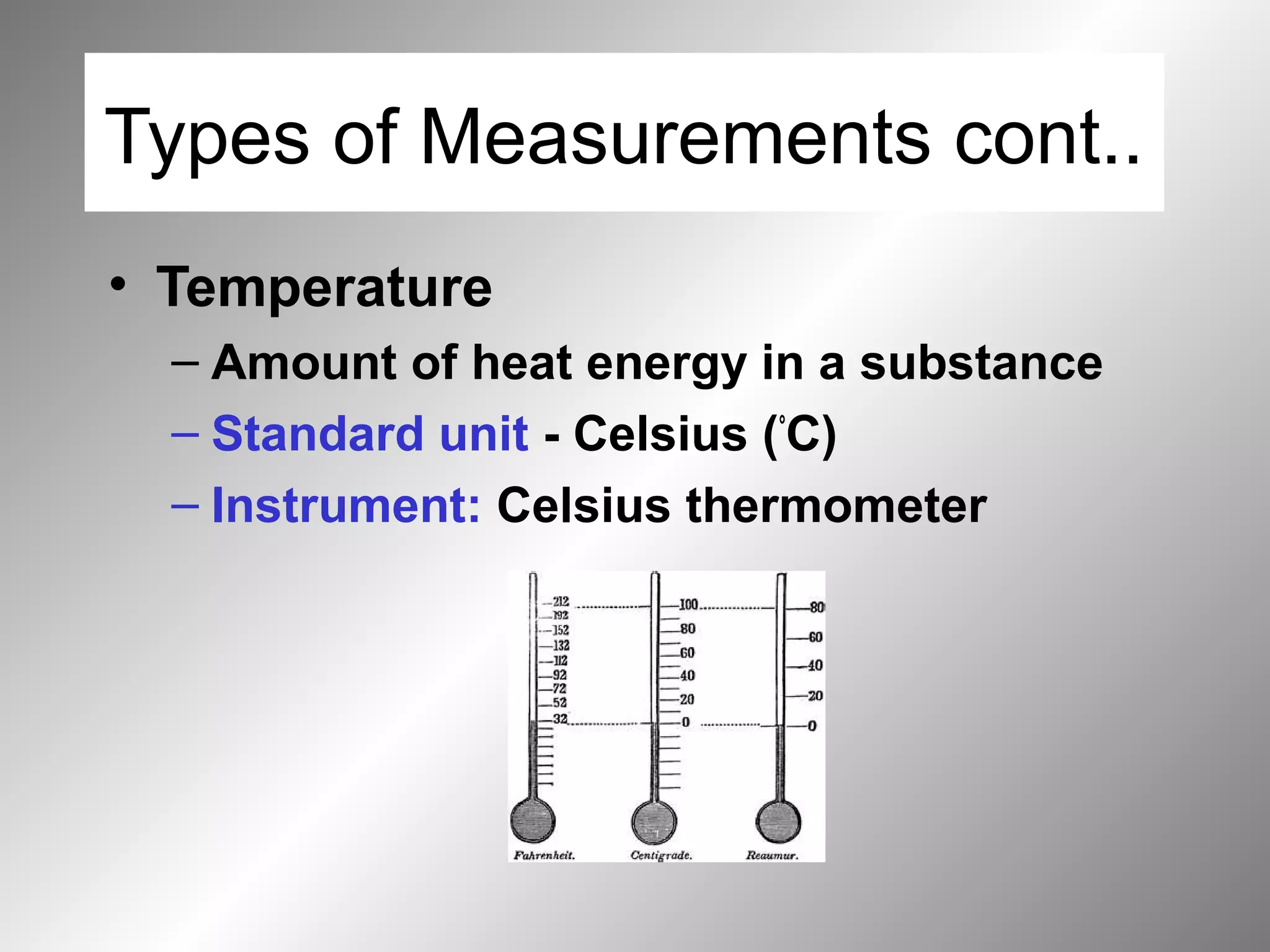
The document outlines important safety procedures and rules for science laboratories, including wearing proper eye protection, disposing of chemicals correctly, knowing the locations of safety equipment, and following instructions from teachers. Basic safe practices like tying back long hair and avoiding loose clothing or open-to