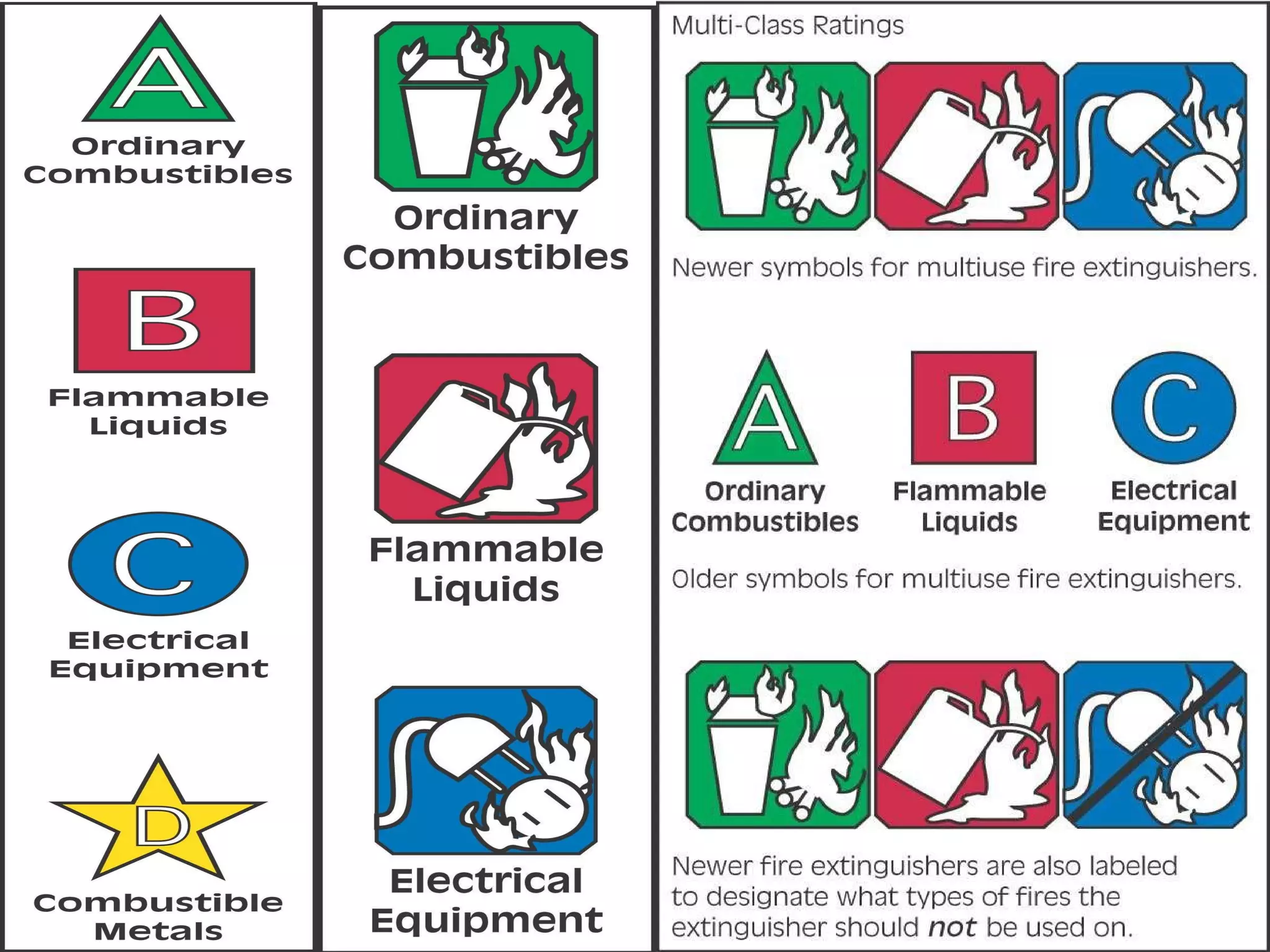
There are five classes of fires which require different types of fire extinguishers. Portable fire extinguishers come in various types that use different agents like water, dry chemical, wet chemical, foam, and carbon dioxide to fight specific classes of small fires. It is important to select the proper extinguisher for the class of fire, know how to operate it using the PASS method, and ensure extinguishers receive regular maintenance and inspections to keep them in good working order.