This document summarizes different aspects of memory, including:
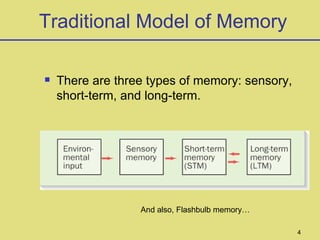
1. It discusses early studies on memory from Hermann Ebbinghaus in the late 1800s and describes the traditional model of memory as having sensory, short-term, and long-term components.
2. It describes flashbulb memory and procedural memory as memory for skills and tasks. Alterations in neural structures are thought to underlie changes in procedural skills.
3. Different approaches to studying memory are mentioned, including tip-of-the-tongue phenomena, flashbulb memories, and information processing models that draw parallels between computer and human memory. Factors like depth of processing can influence memory permanence.