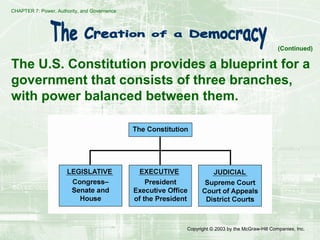
This document discusses different forms of government and how power and authority are organized through government. It describes monarchy, dictatorship, oligarchy, theocracy, and democracy as different systems of government. It also discusses the US system of checks and balances and individual responsibilities and ways for citizens to engage in democracy.