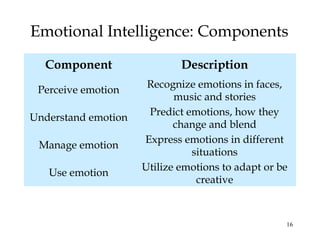
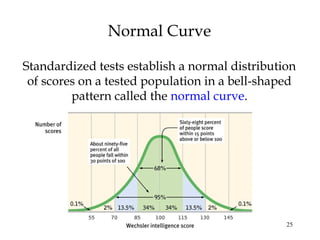
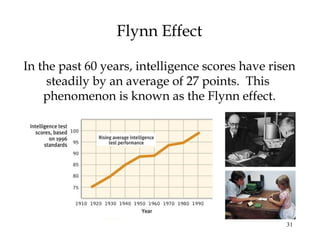
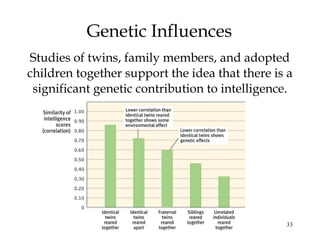
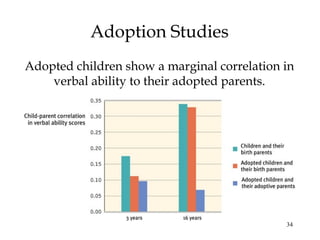
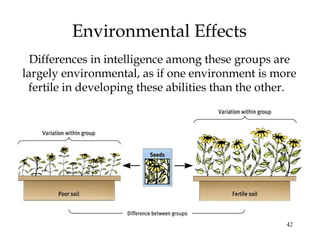
This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 11 on intelligence from the 9th edition of the psychology textbook by David Myers. It discusses theories of intelligence, including the idea of general intelligence versus multiple intelligences. It covers topics like emotional intelligence, how intelligence is assessed through testing, the genetics and environment influences on intelligence, and differences in intelligence scores between demographic groups. The document uses bullet points and headings to structure the information presented across 46 slides.