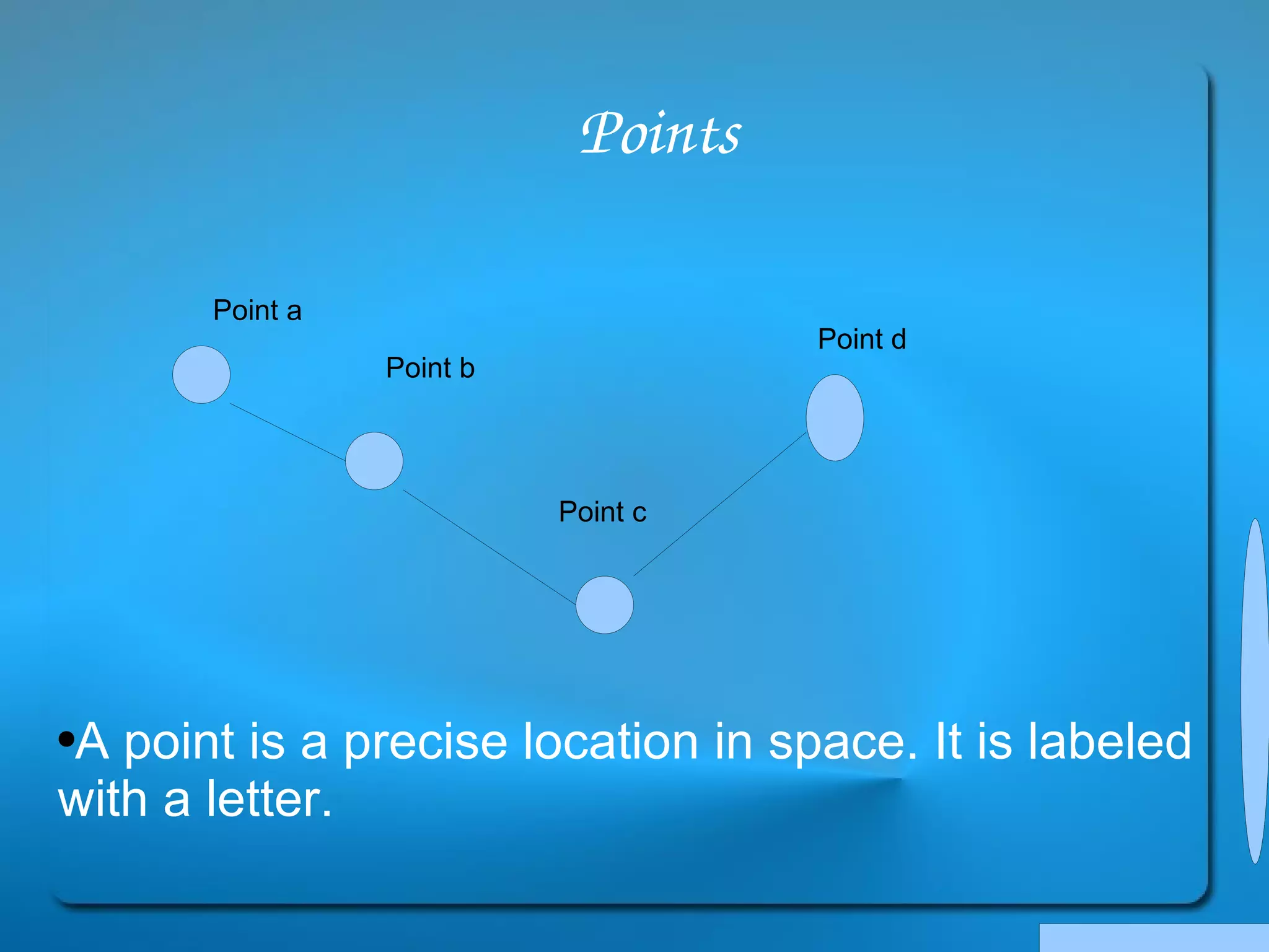
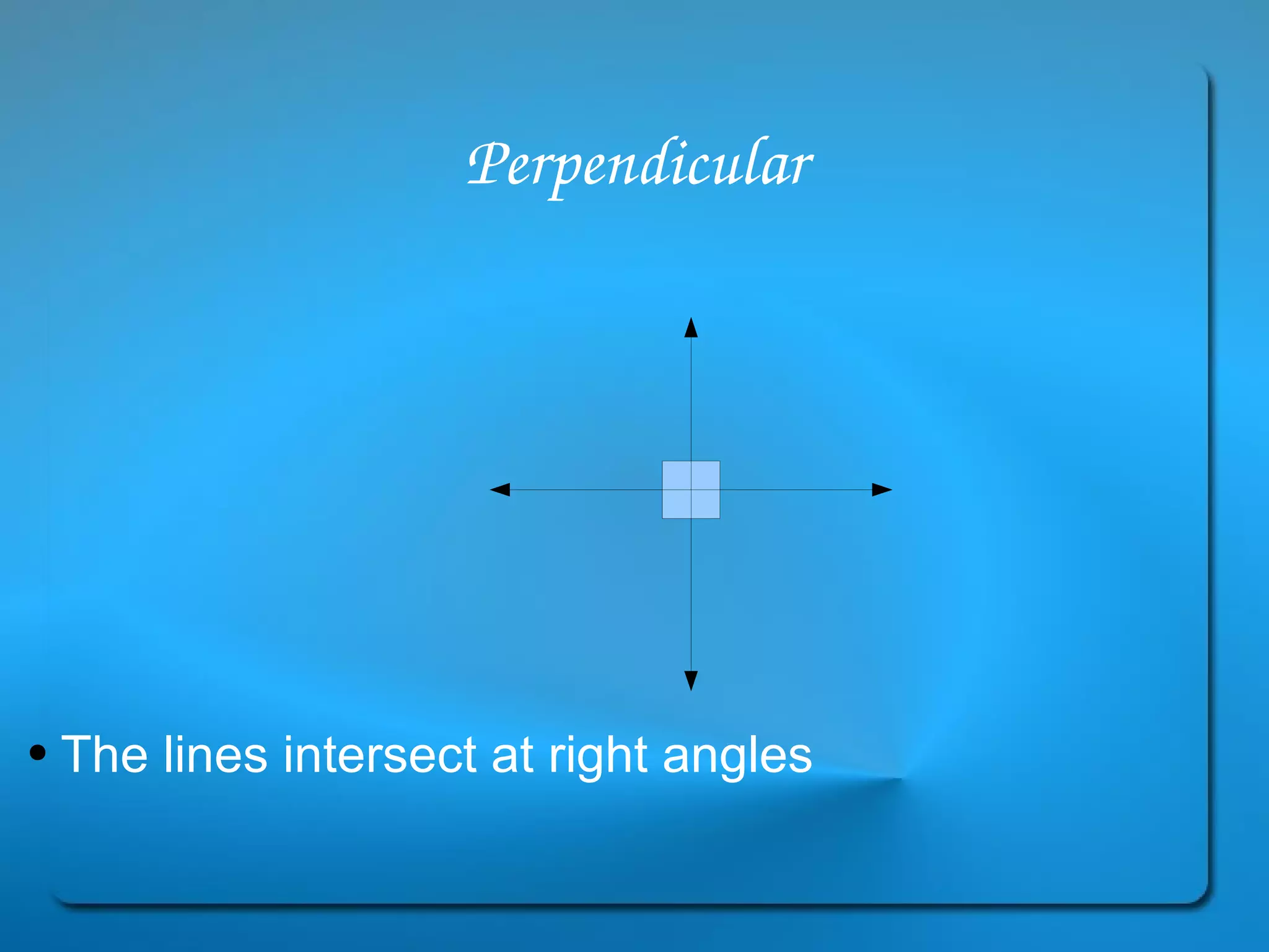
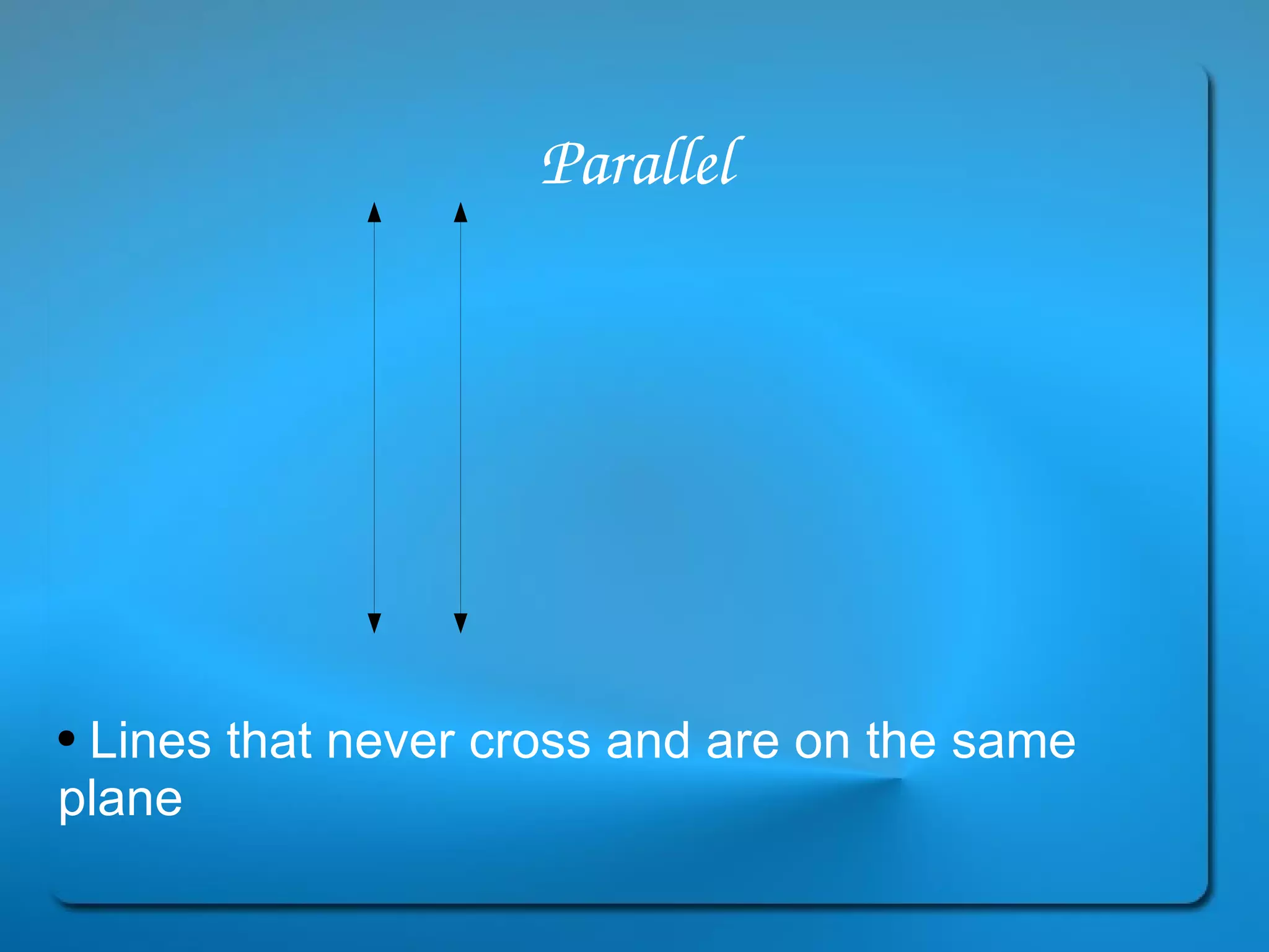
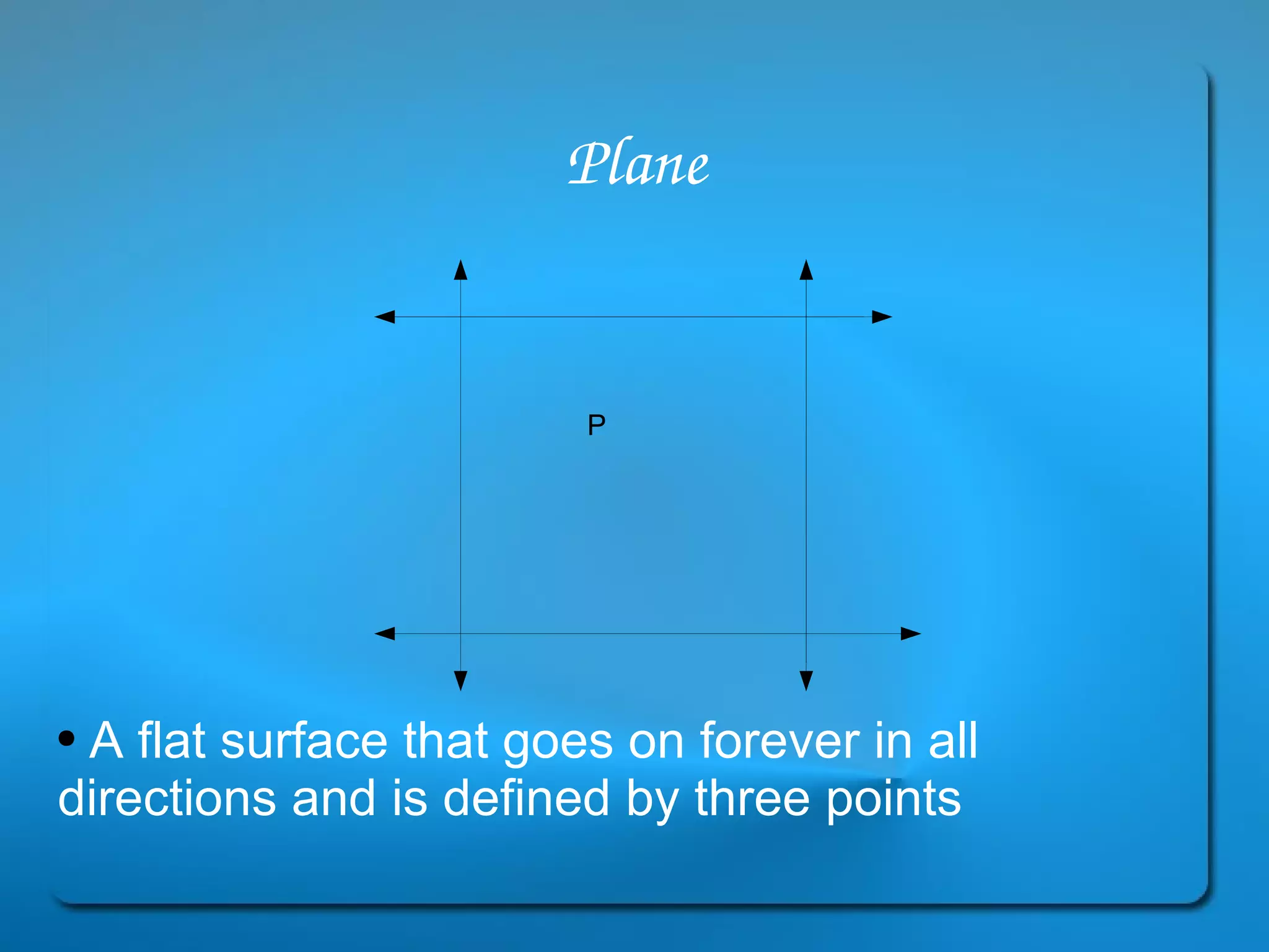
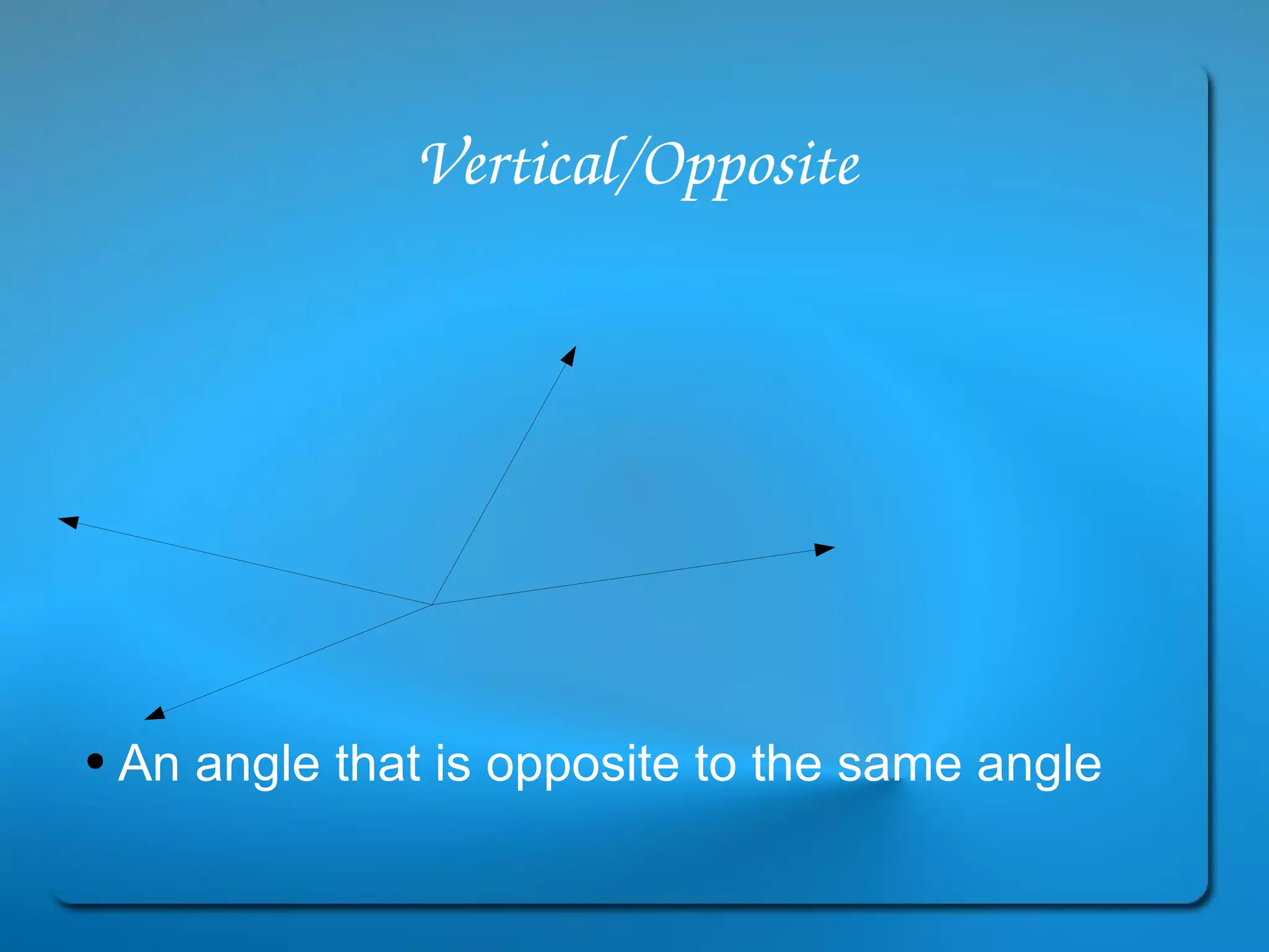
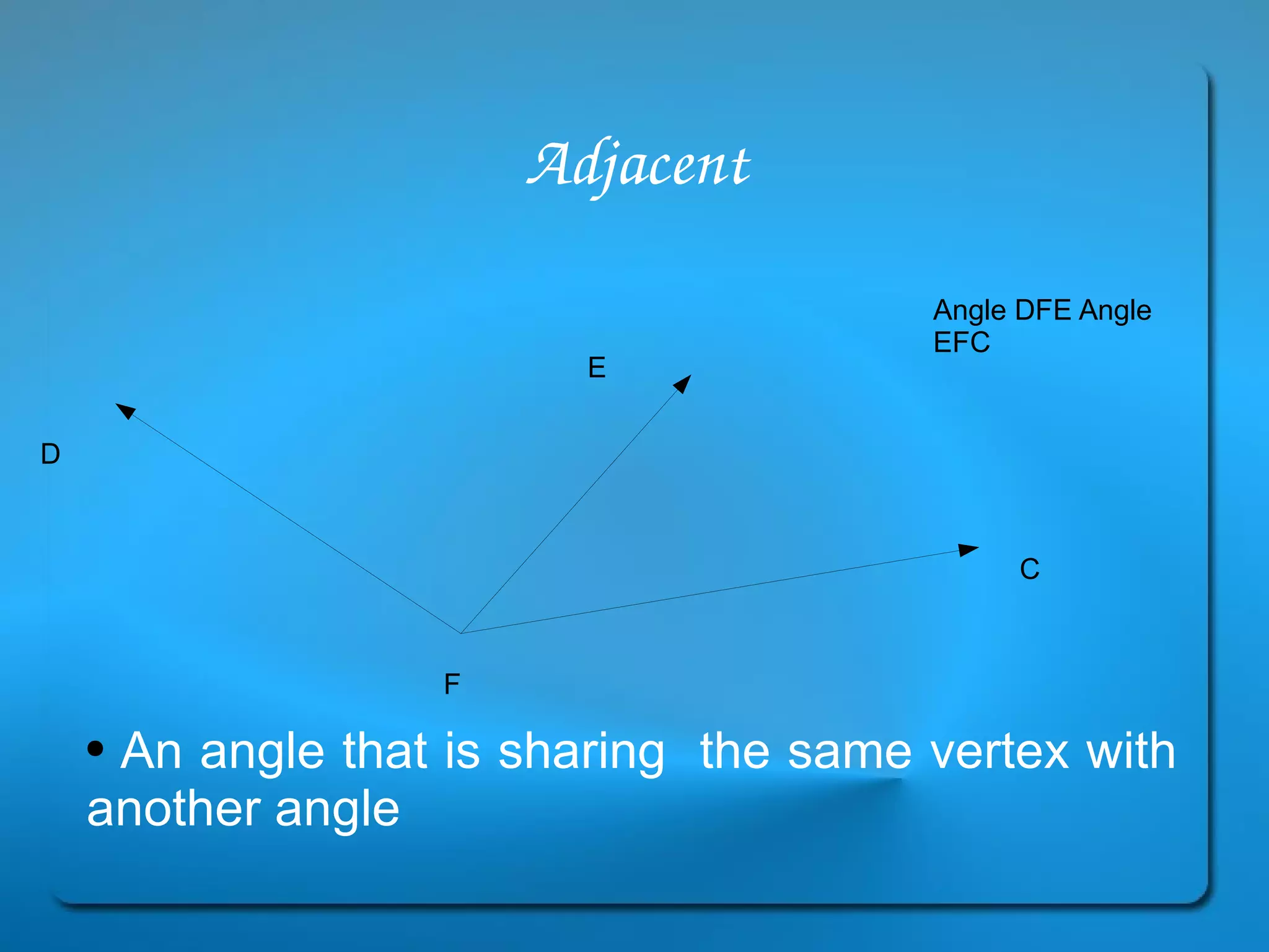
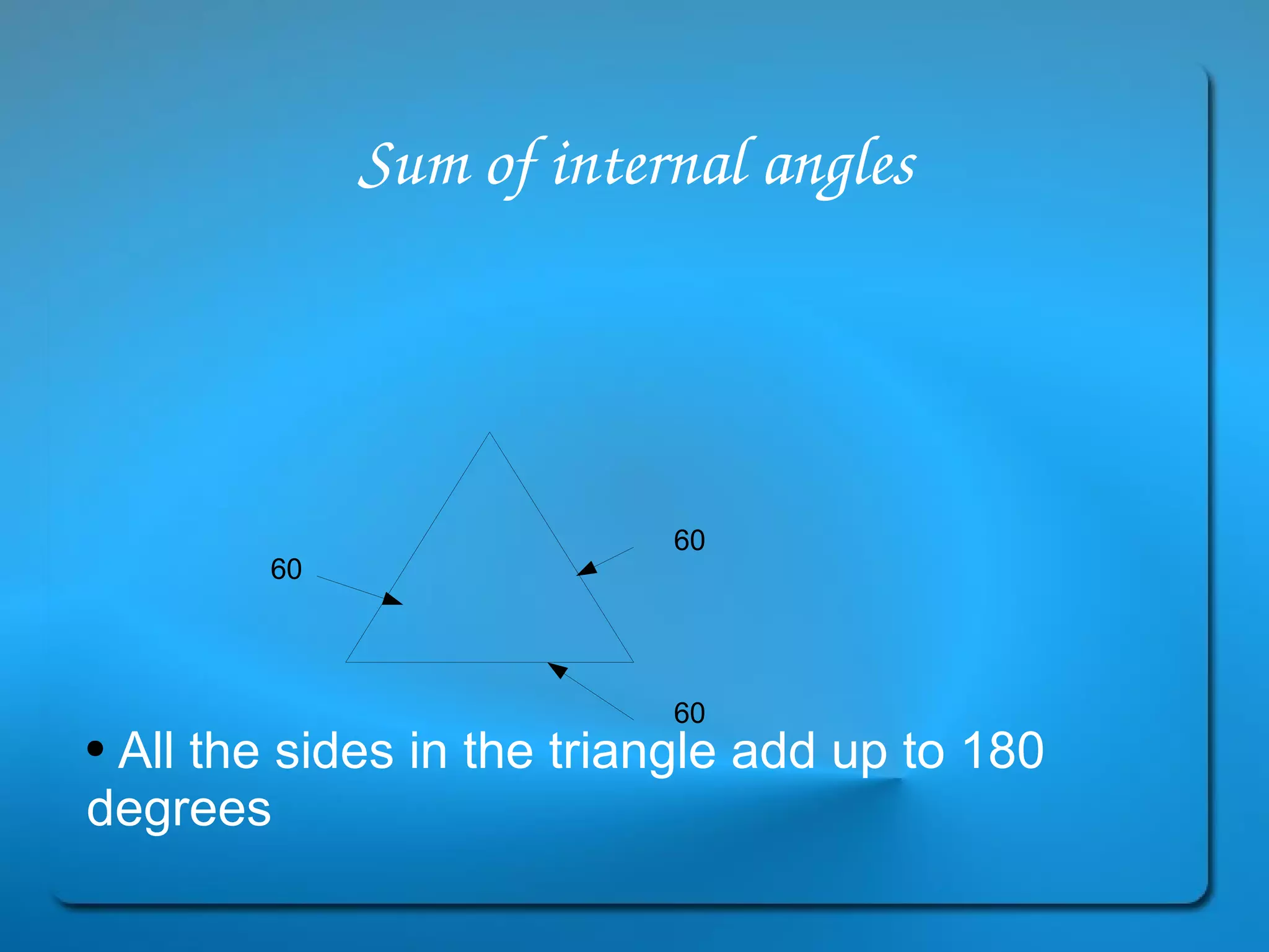
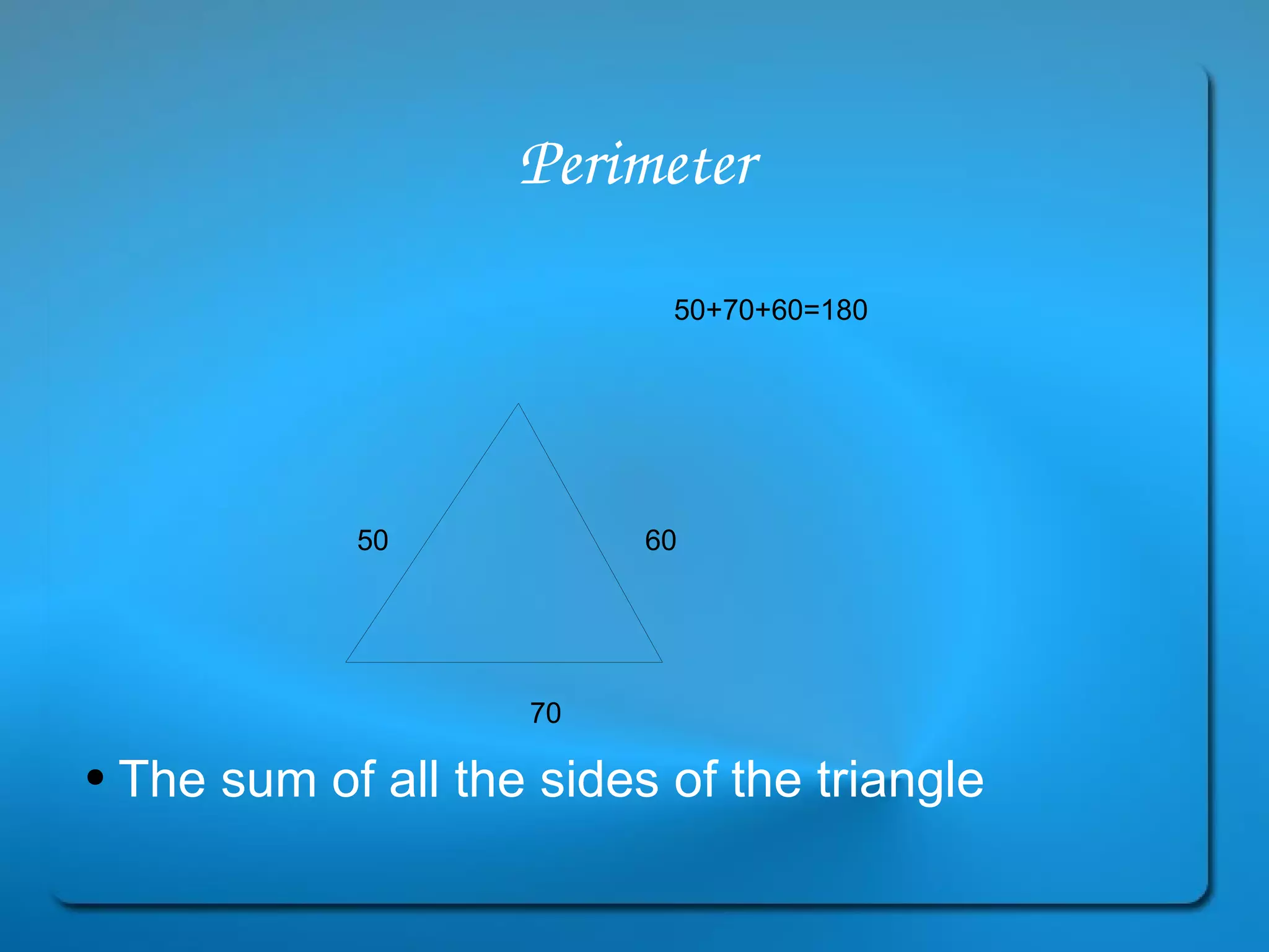
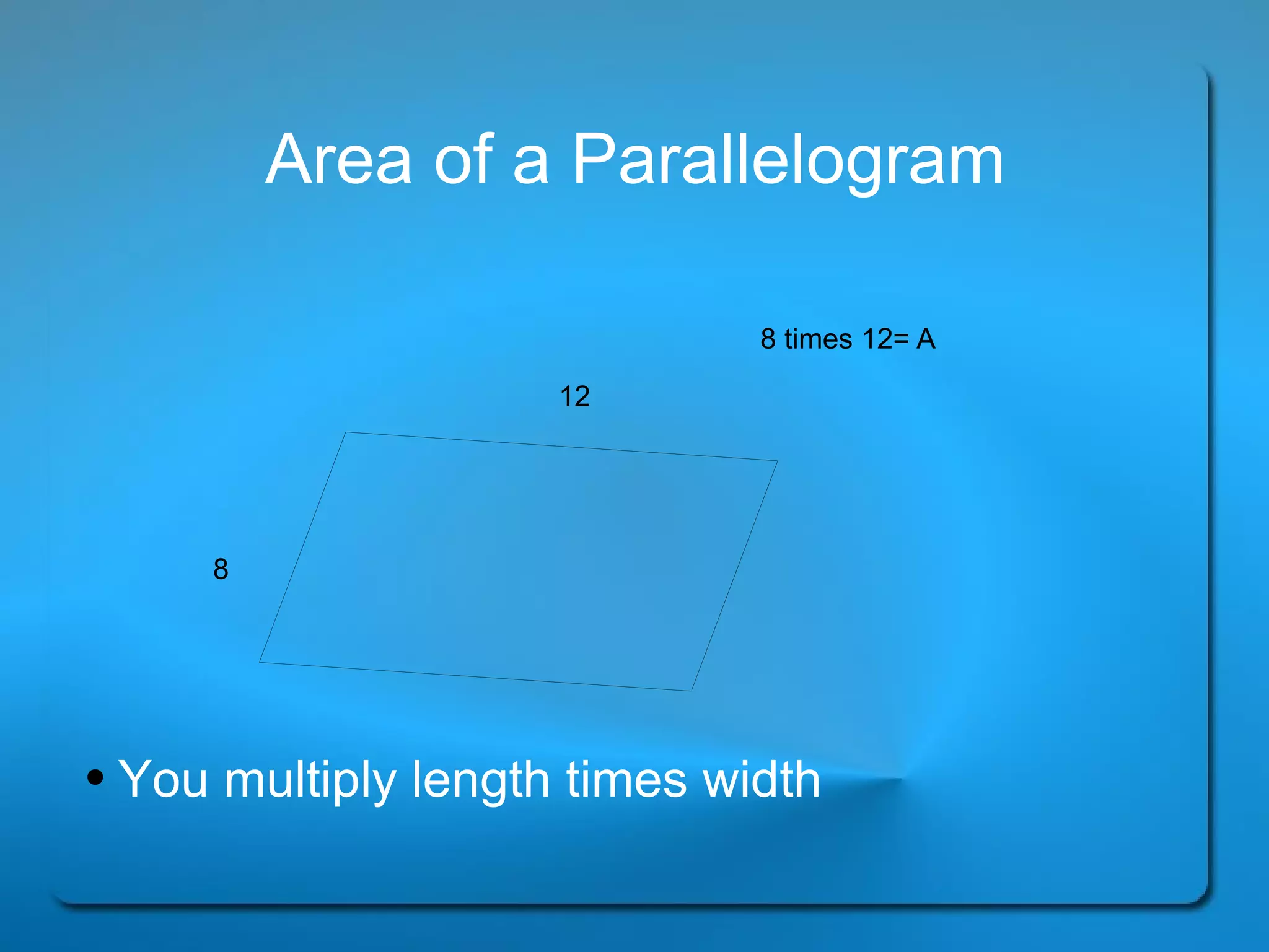
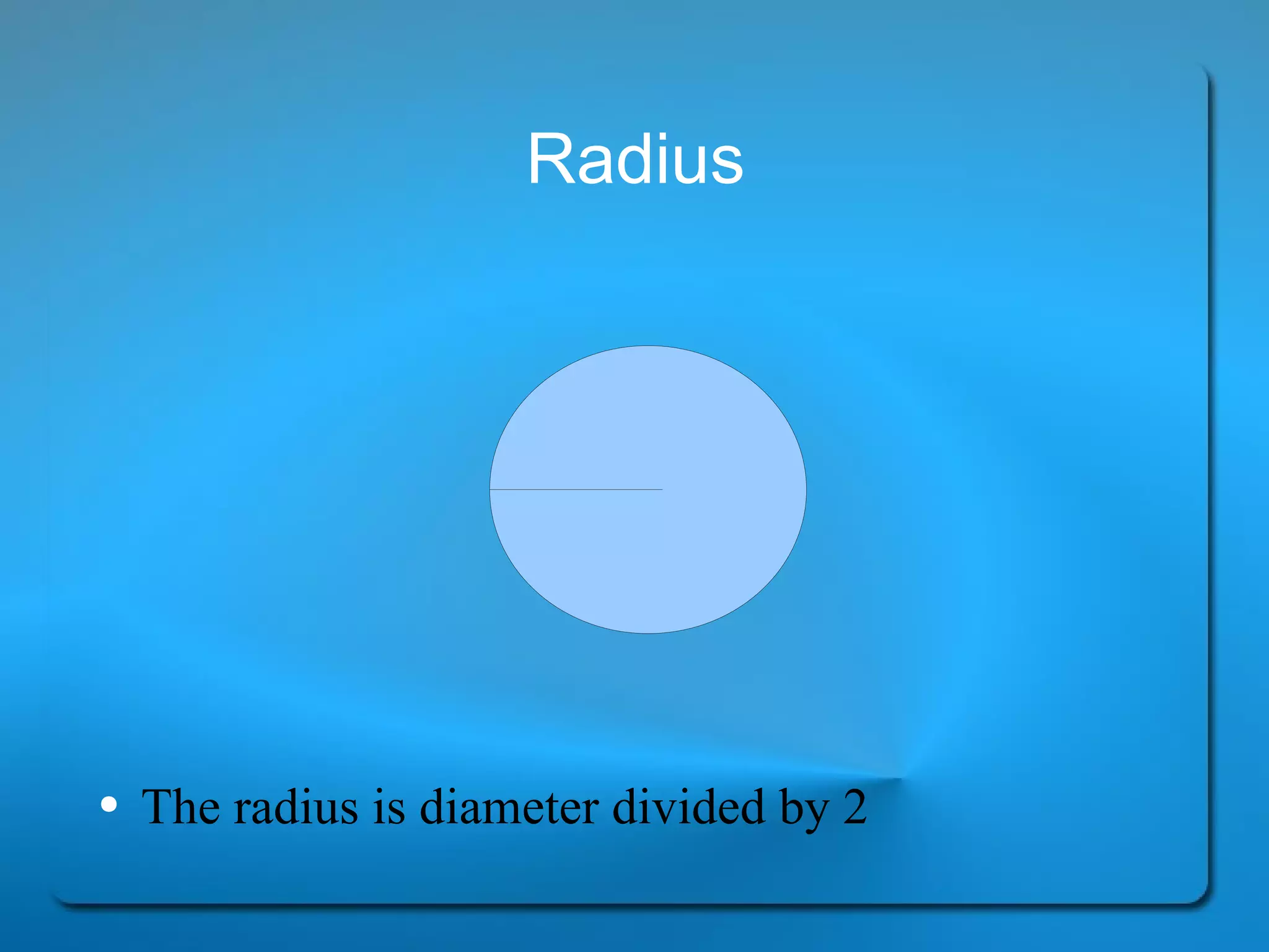
This document provides definitions and explanations of key geometry terms related to lines, angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, and other polygons. It defines points, line segments, rays, intersecting lines, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, acute angles, obtuse angles, right angles, complementary angles, supplementary angles, and more. It also explains the properties of different types of triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, and other polygons. Key terms include radius, diameter, chord, arc, sector, circumference, area, perimeter, scalene triangles, isosceles triangles, equilateral triangles, rectangles, squares, rhombuses, trapezoids, parallelograms, hexagons, octagons