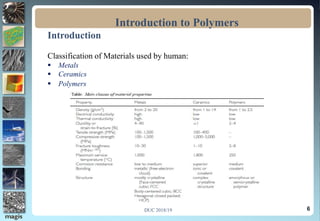
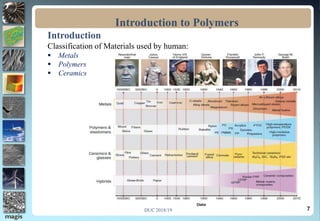
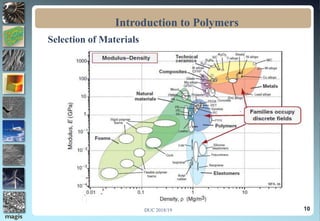
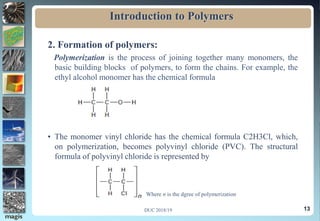
The document discusses the classification of materials used by humans including metals, ceramics, and polymers. It then provides details on the course content which covers topics like the introduction, definition, and formation of polymers as well as their characteristics and applications. The presentation concludes by emphasizing the importance of polymers in fields such as automobiles, medicine, sports, and consumer goods.